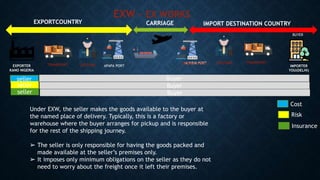
The document outlines the legal aspects of export contracts, defining them as consensus agreements between parties engaged in export trade. It addresses the requirements for forming such contracts, applicable international laws, and key clauses to include, as well as explaining Incoterms which dictate the responsibilities and risks of parties during the shipping process. Additionally, it highlights that Nigeria has not adopted the UN Convention on Contracts for International Sales of Goods (CISG) but acknowledges its applicability in lieu of domestic law.