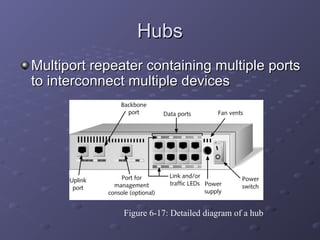
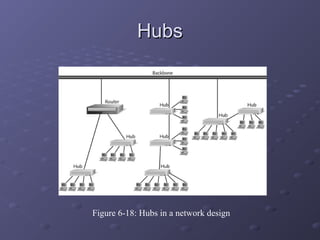
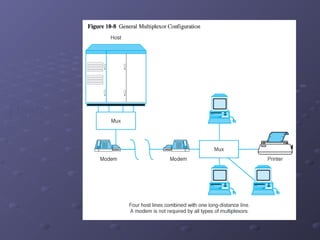
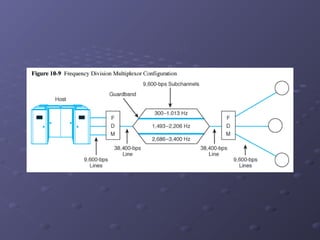
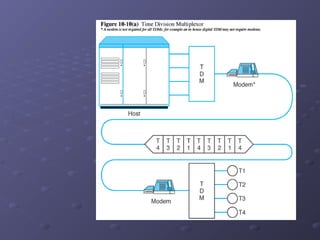
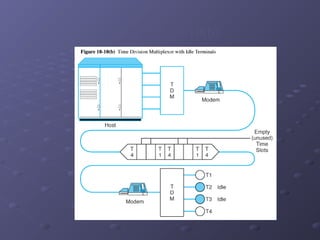
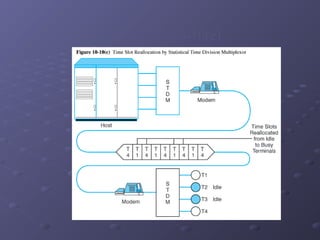
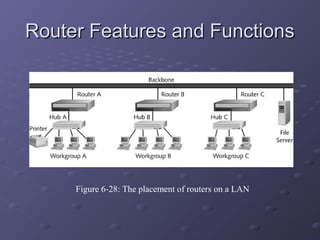
This document discusses various types of networking devices that can be used to expand and connect networks, including hubs, switches, bridges, routers, and multiplexers. Hubs are multiport repeaters that interconnect devices on a network. Switches subdivide networks into smaller logical segments. Bridges and routers can connect different networks, with routers operating at the network layer. Multiplexers allow multiple signals to share a single communication link.