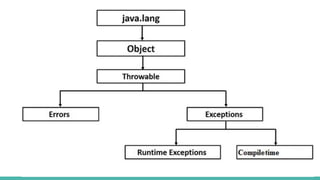
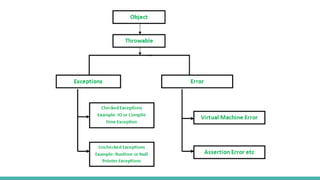
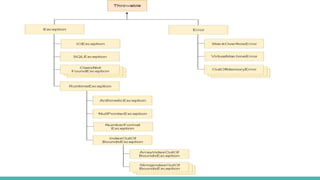
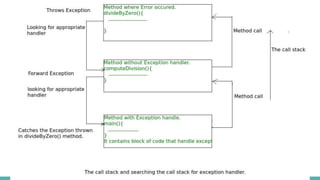
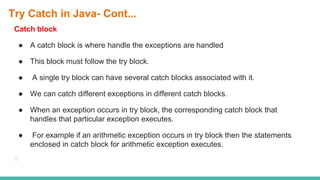
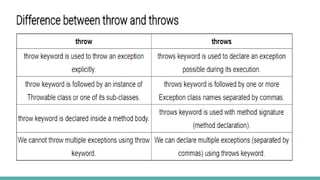
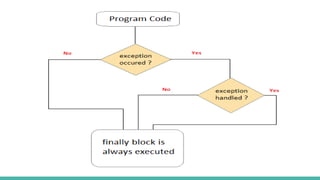
The document discusses exception handling in Java. It defines exceptions as problems that disrupt normal program flow. Exceptions can be caused by invalid user input, file errors, or other issues. Java exceptions are categorized as checked, unchecked, or errors. Checked exceptions must be caught or declared, while unchecked exceptions and errors typically are not. The try-catch block allows catching and handling exceptions. The catch block contains code to handle exceptions thrown in the try block. Exception handling allows programs to continue running after exceptions rather than crashing.