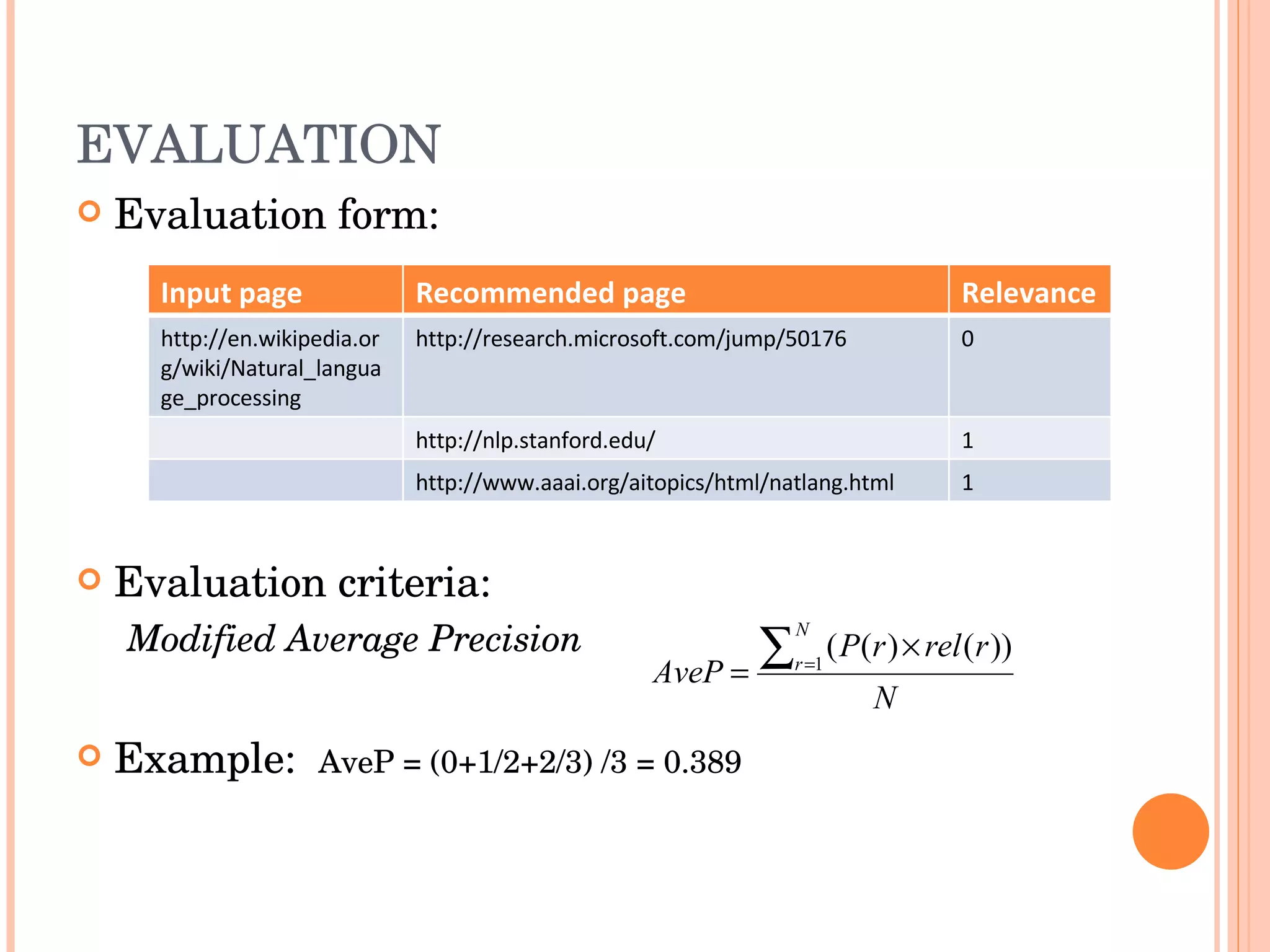
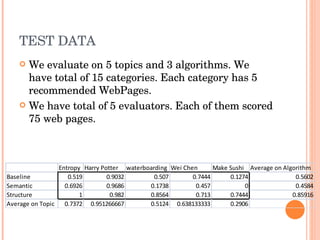
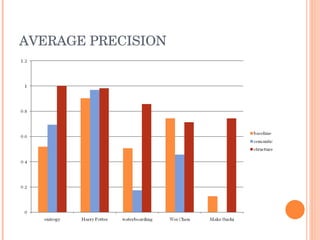
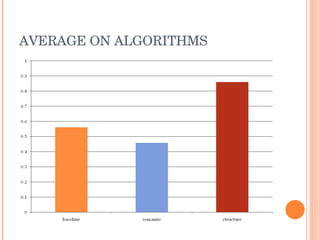
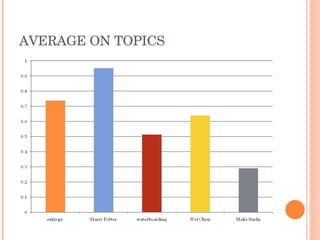
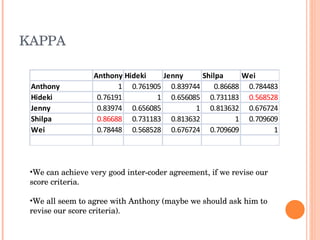
This document discusses evaluating different search algorithms on various topics. It describes evaluating algorithms on 5 topics with 3 algorithms each, for a total of 15 categories. 5 evaluators scored 75 web pages each. It calculates average precision for algorithms and topics and inter-coder agreement. While structure algorithm performed best, the document concludes more analysis is needed to understand algorithm differences and suggests designing a new experiment analyzing query terms generated by each algorithm.