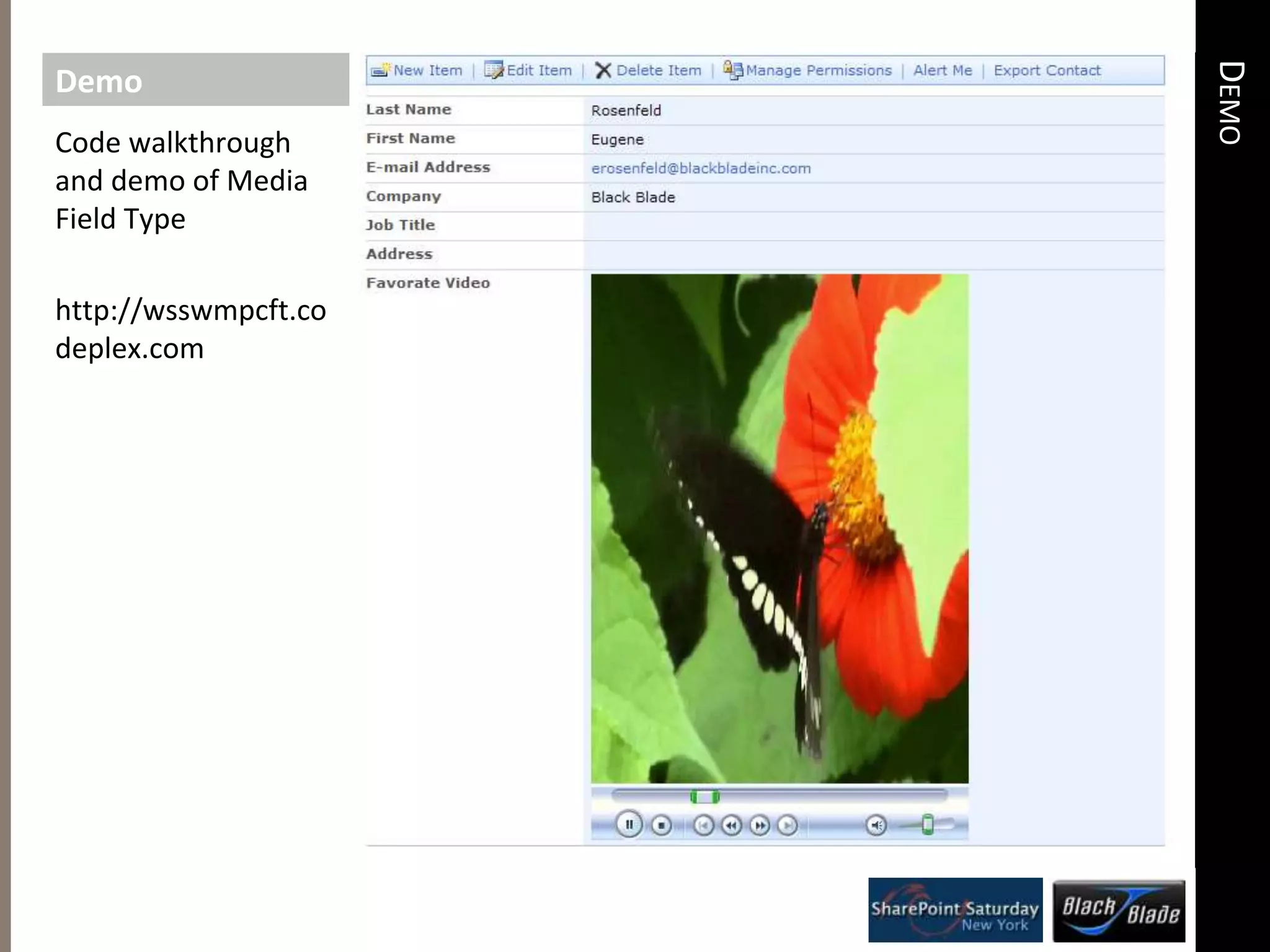
This document discusses custom field types in SharePoint. Custom field types allow developers to define custom data structures, validation, and rendering for fields. They combine aspects of fields, web parts, validators, and event receivers. Some examples of when to use custom field types include storing multicolumn data or data related to an external system. The document reviews implementing custom field types including defining the type, properties, validation, and deployment. It also compares custom field types to other extensibility options like content types, web parts, and event receivers.