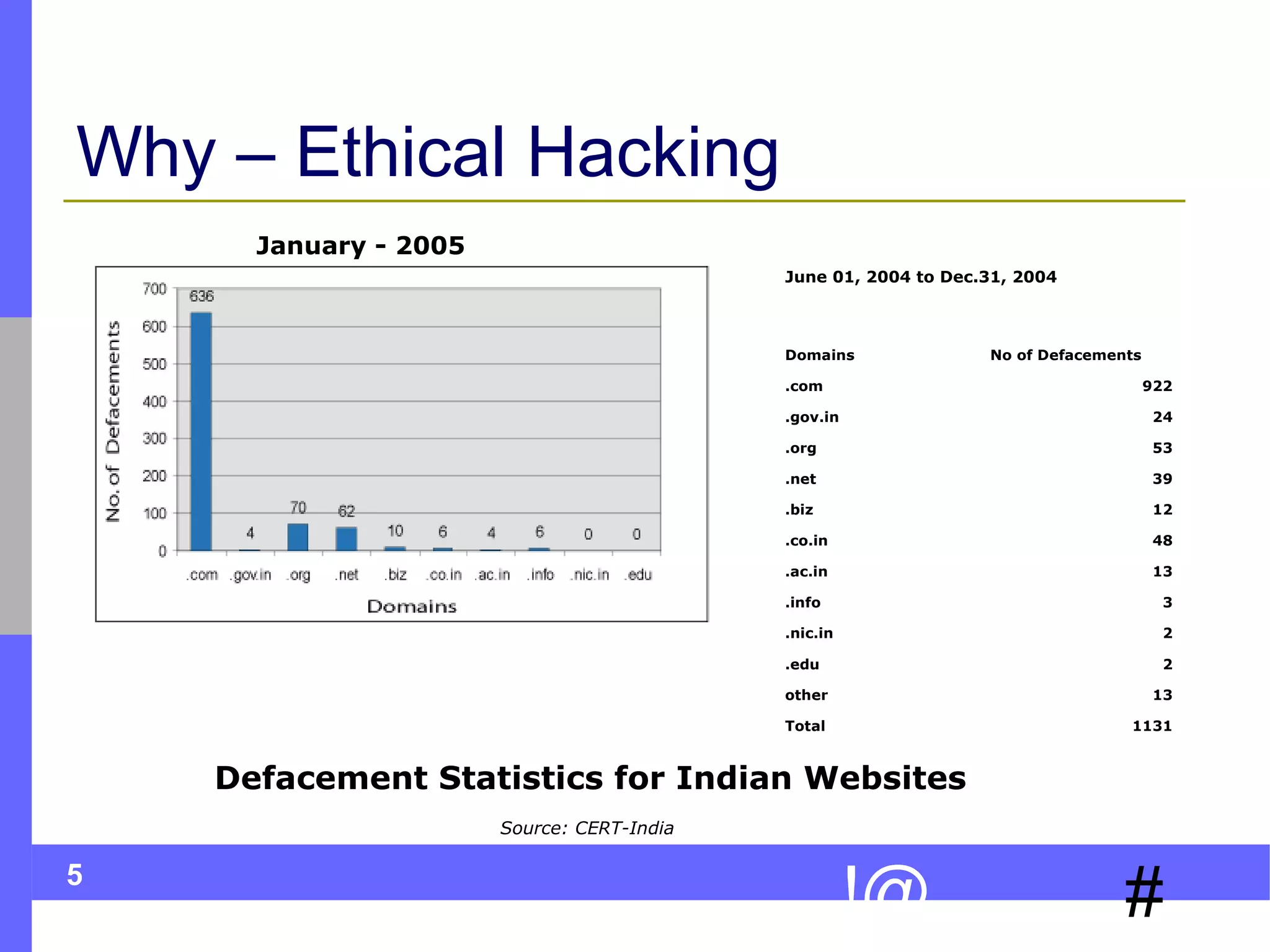
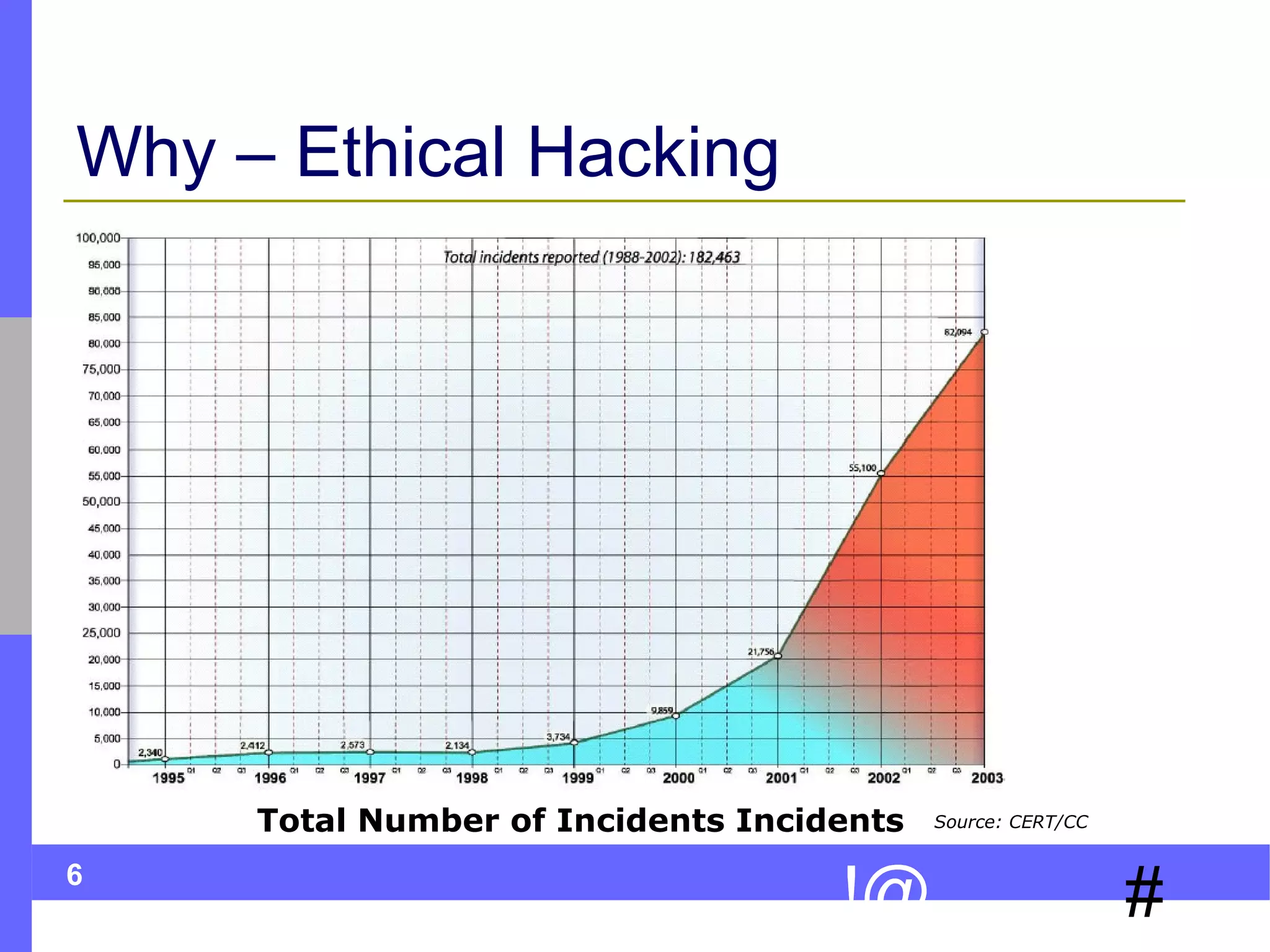
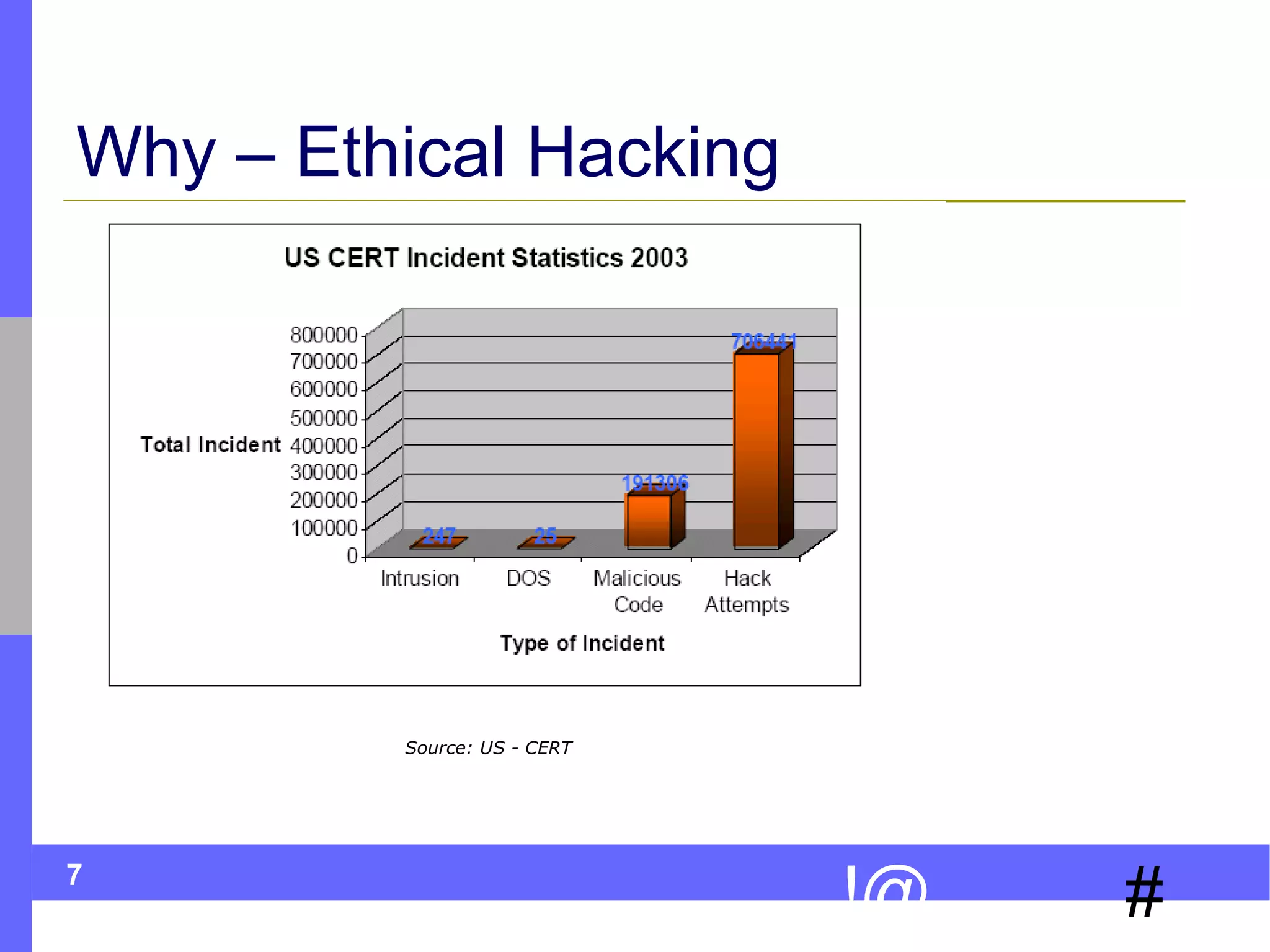
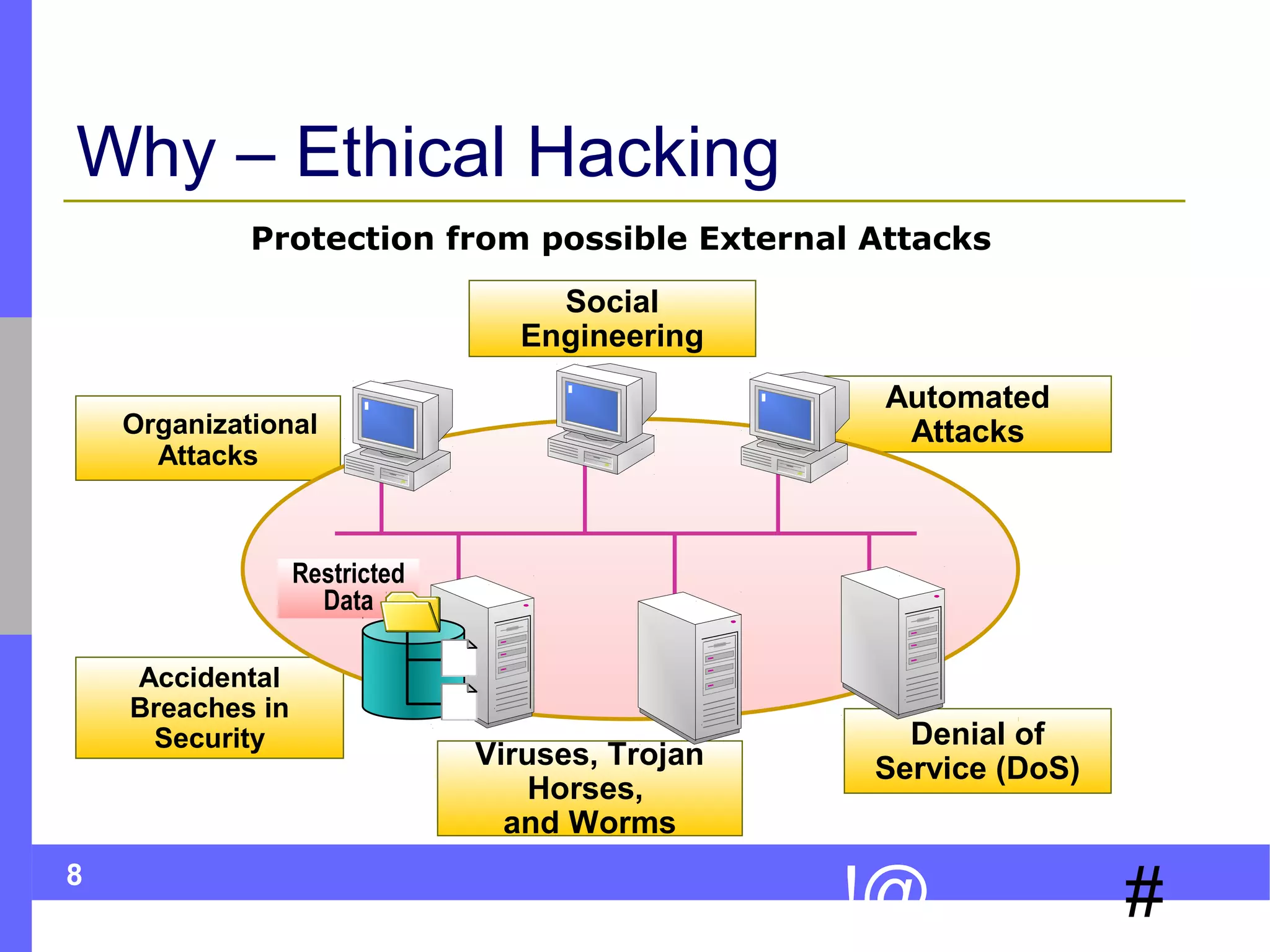
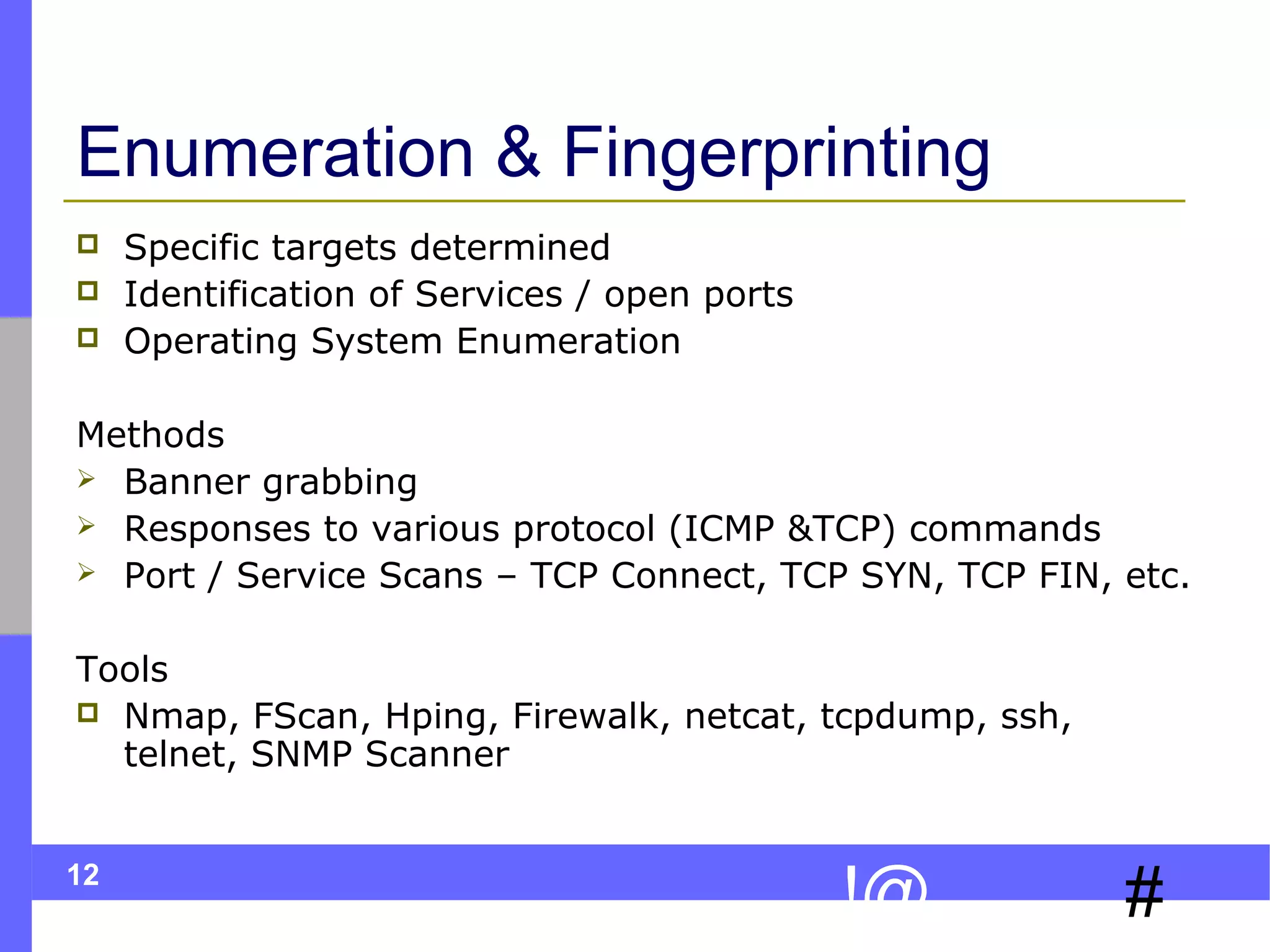
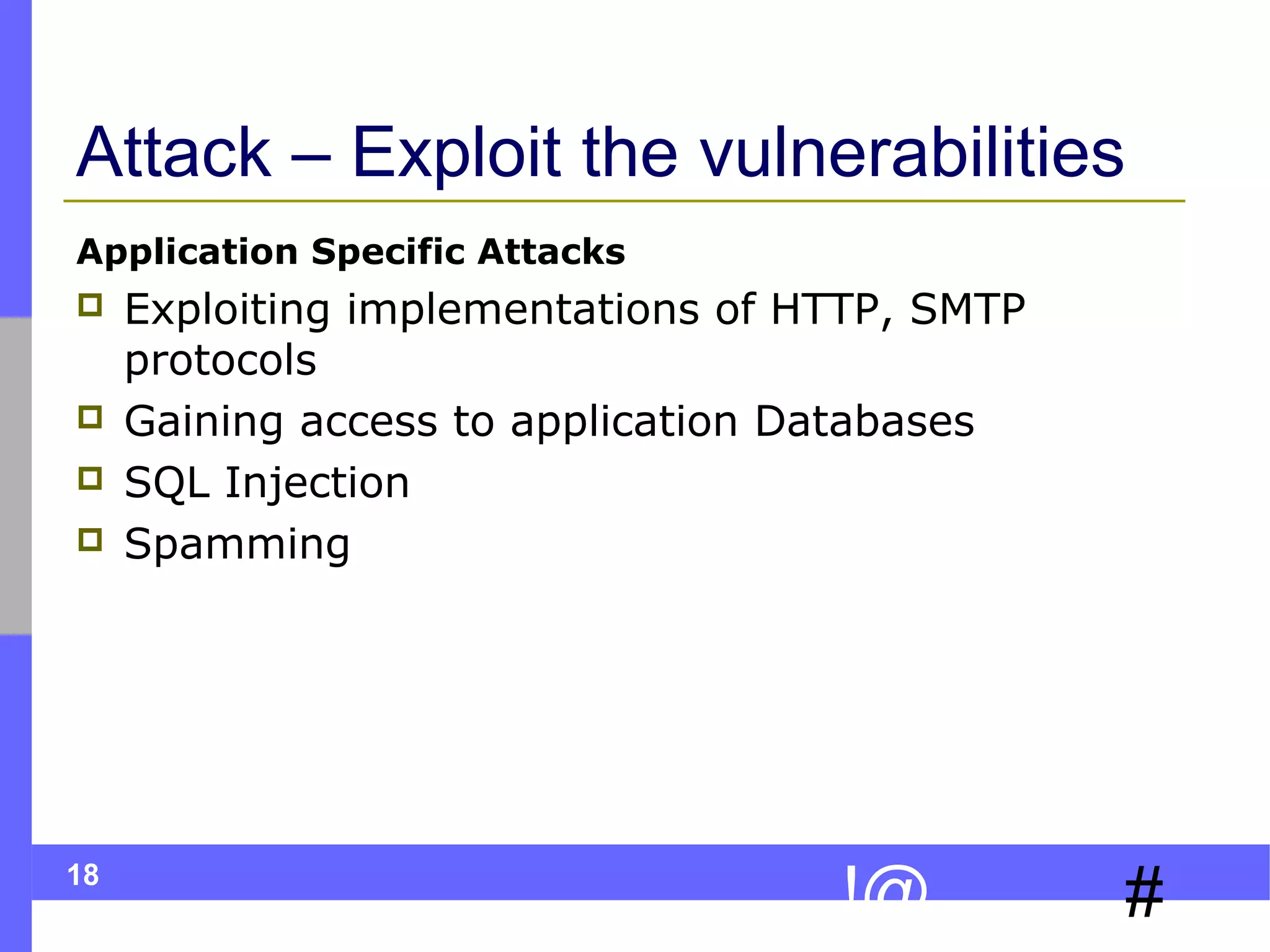
This document discusses ethical hacking, which involves legally testing a system's security vulnerabilities to help organizations identify and remedy weaknesses. The ethical hacking process involves preparation, footprinting, enumeration and fingerprinting to identify targets and services, vulnerability identification, and controlled attacks to exploit vulnerabilities. The goal is to help organizations protect themselves from real attacks by mimicking the methods used by hackers, but doing so legally and non-destructively. A final report details vulnerabilities found and recommendations for remediation. Ethical hackers adhere to principles of working legally and ethically, respecting privacy, and not causing harm.