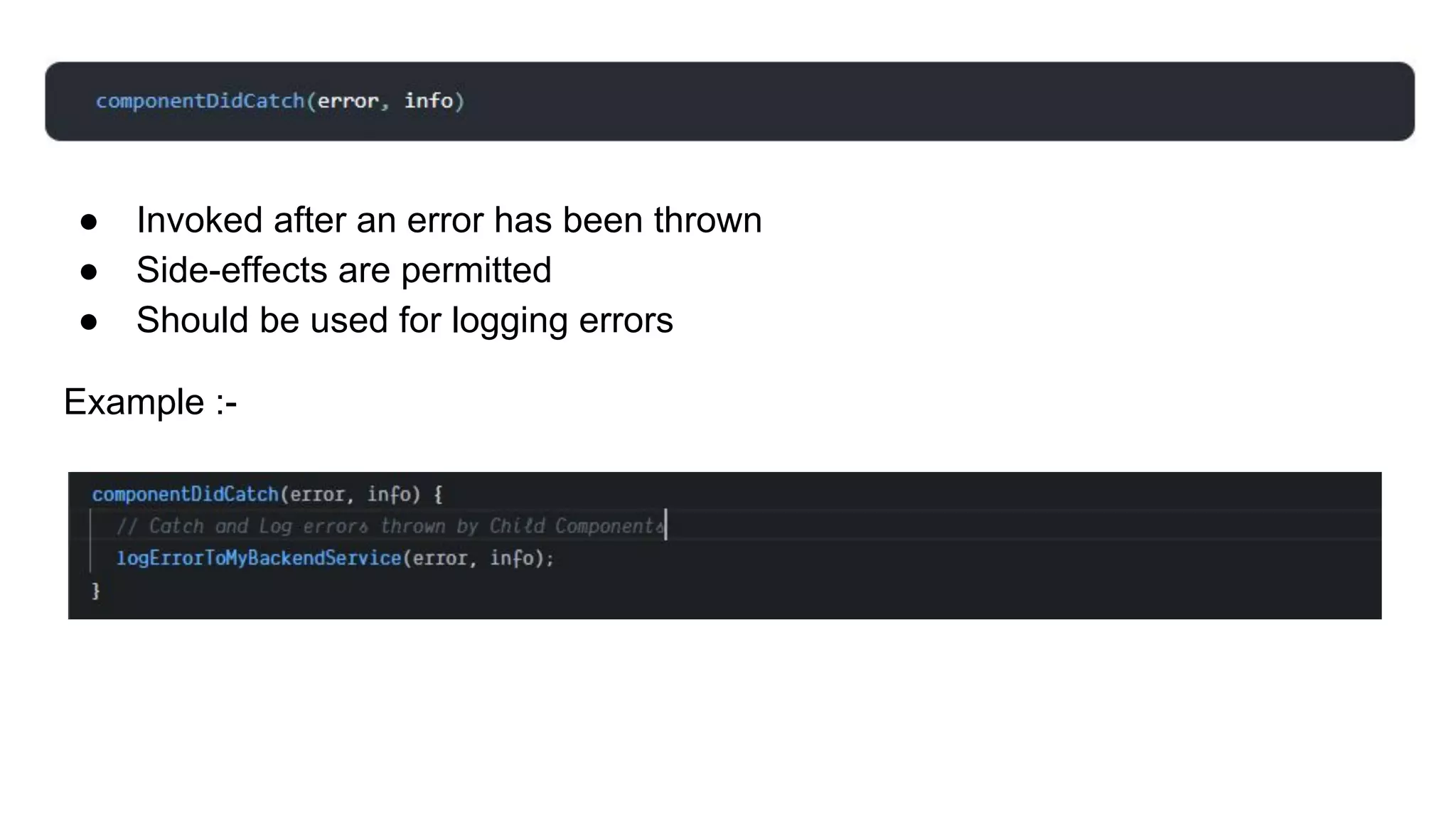
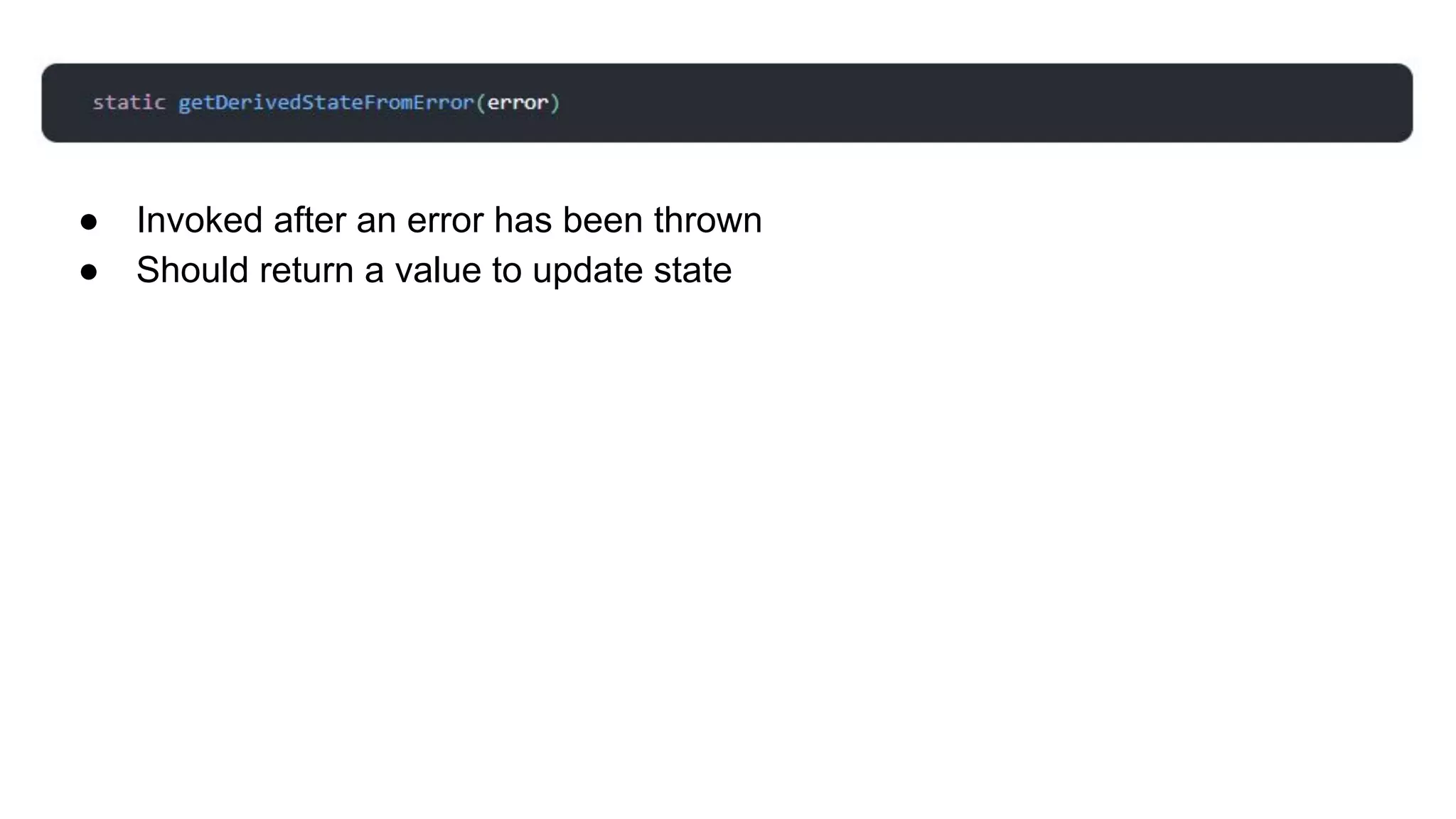
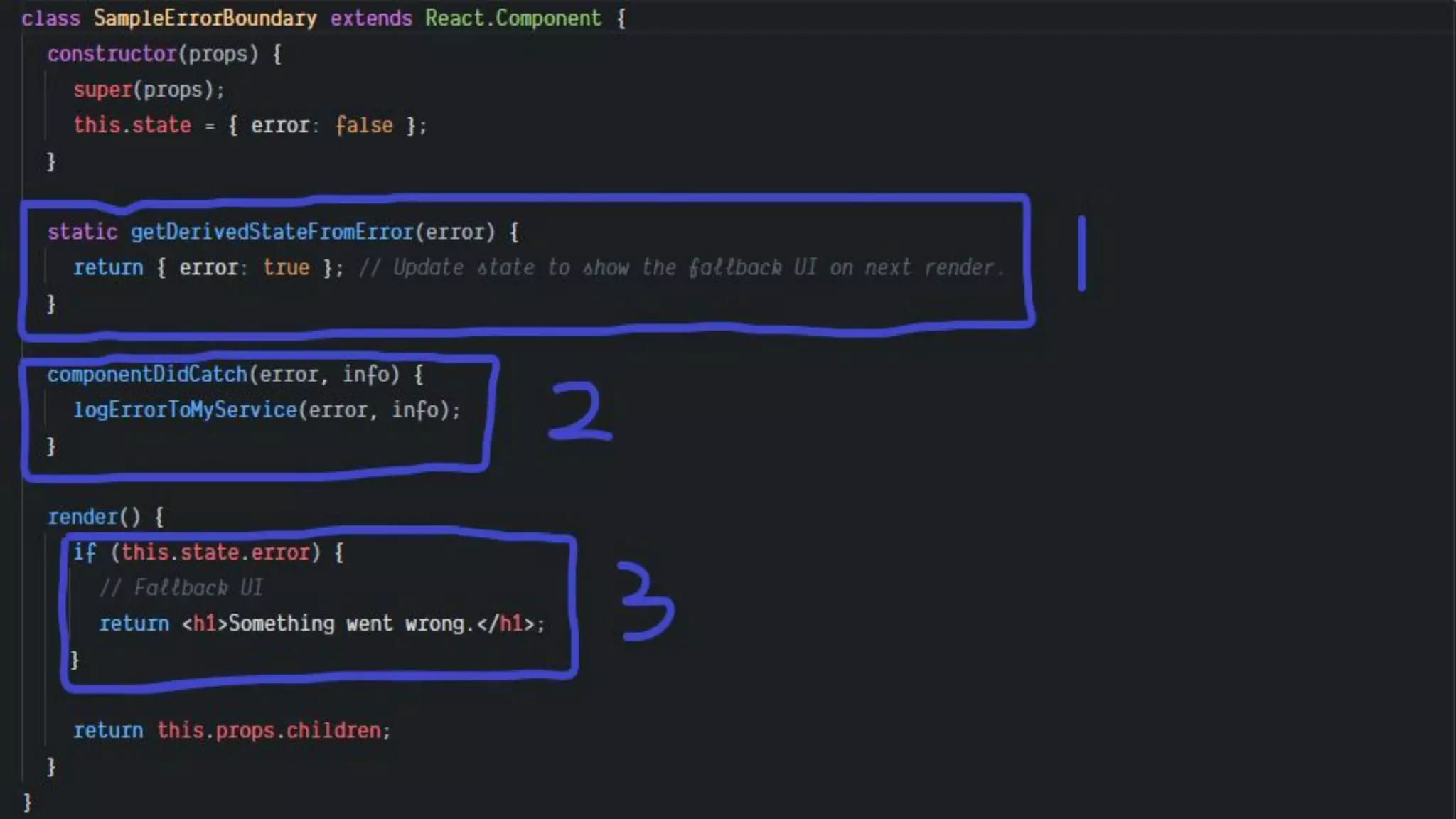
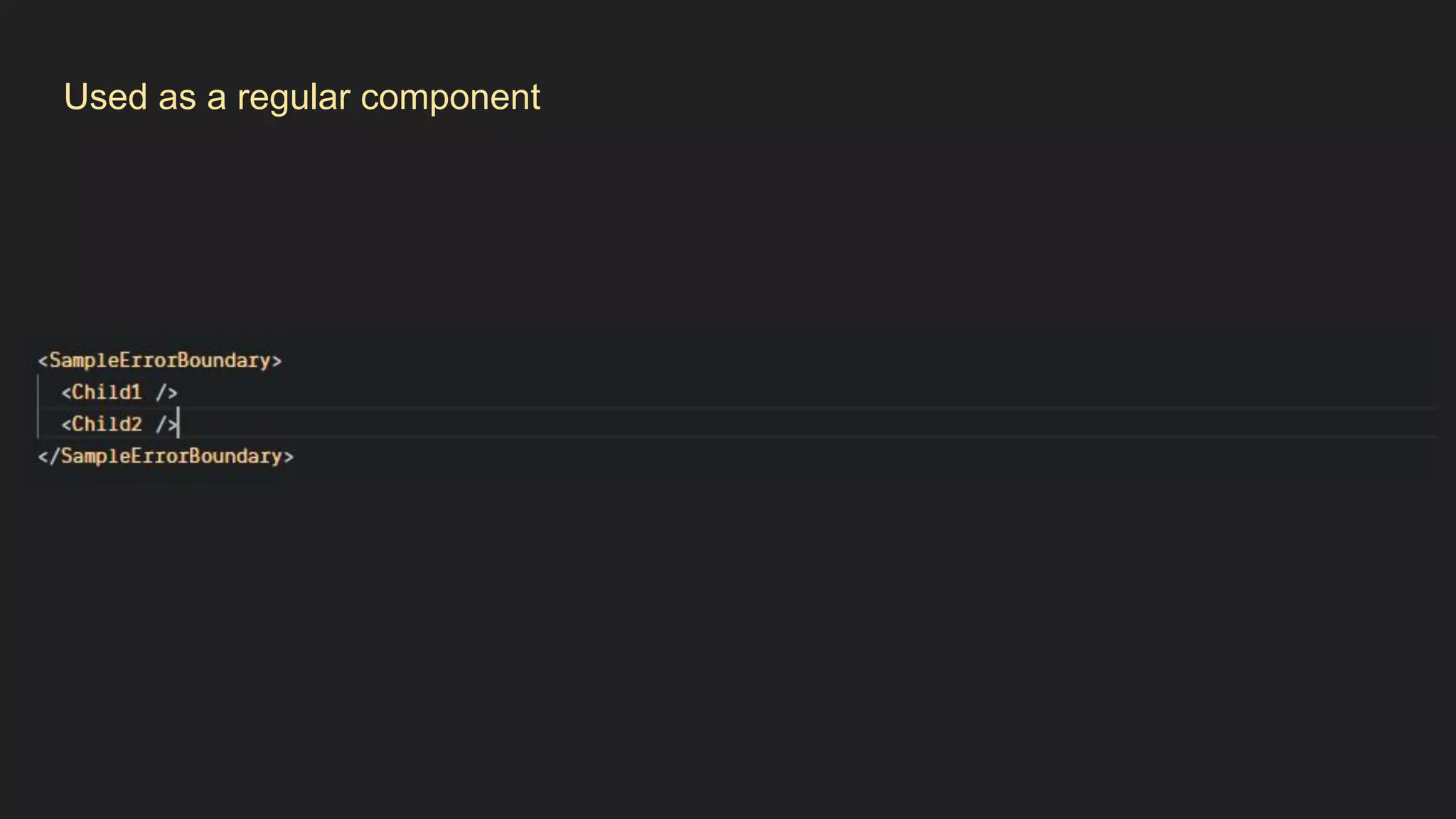
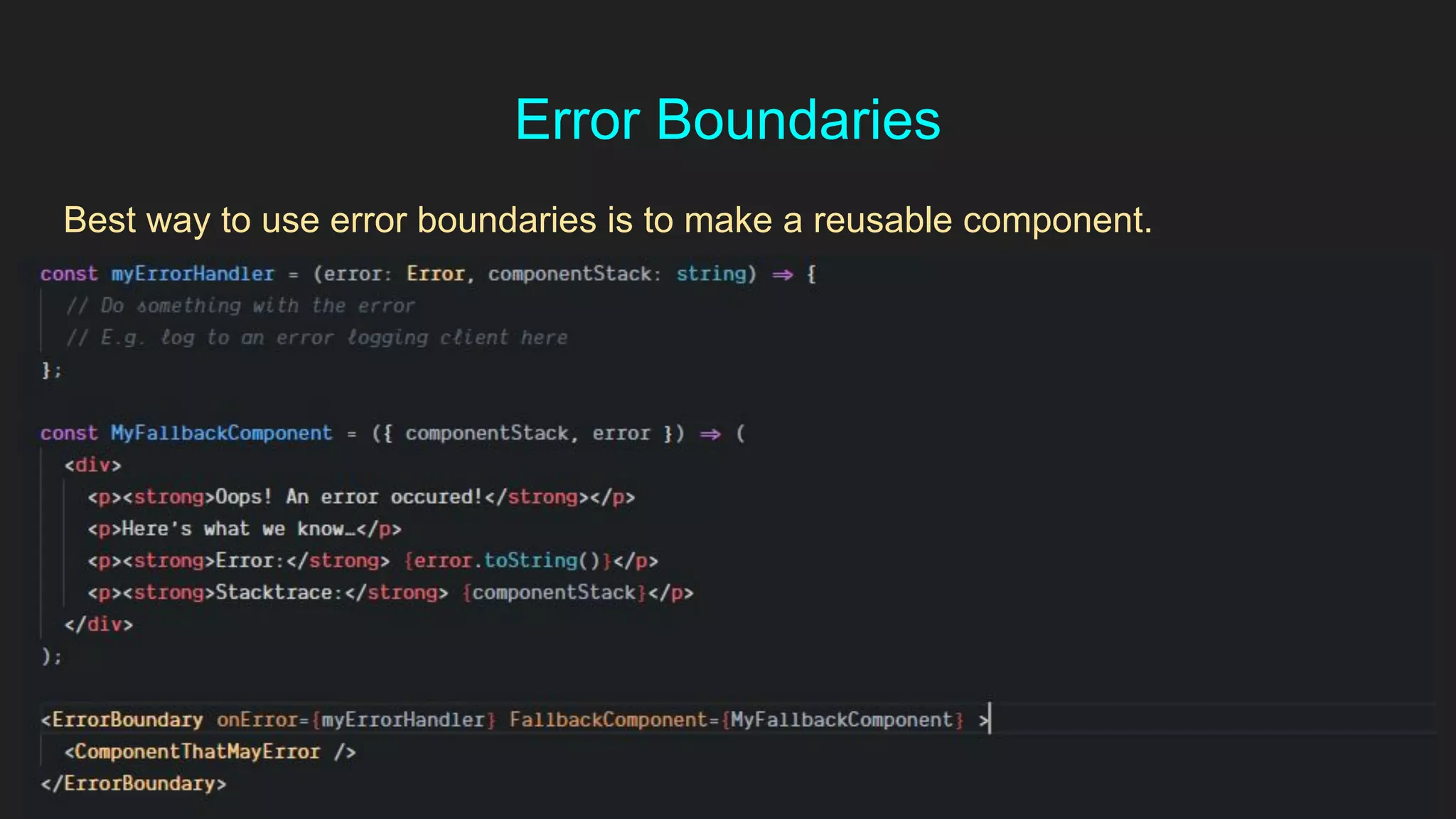
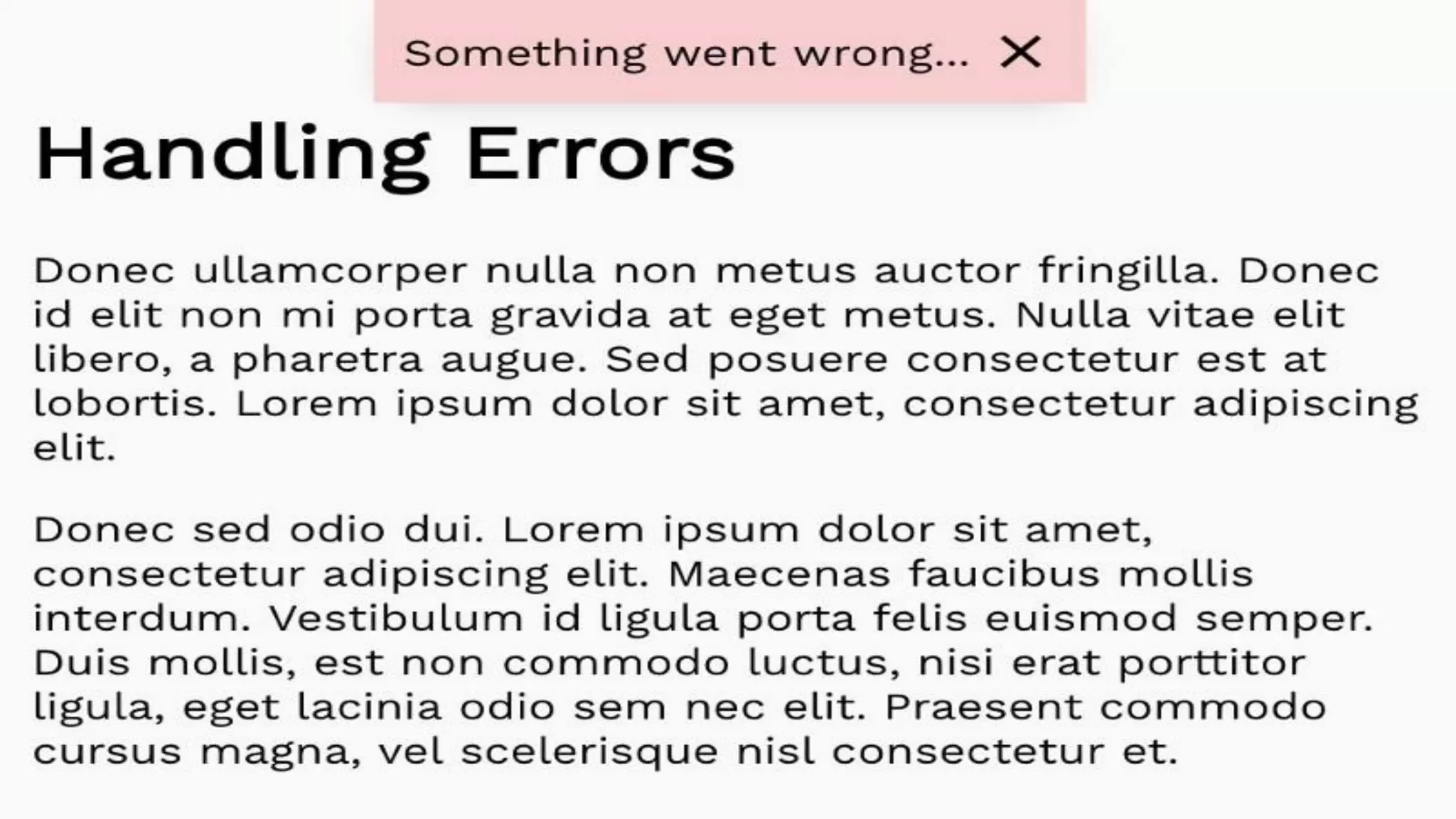
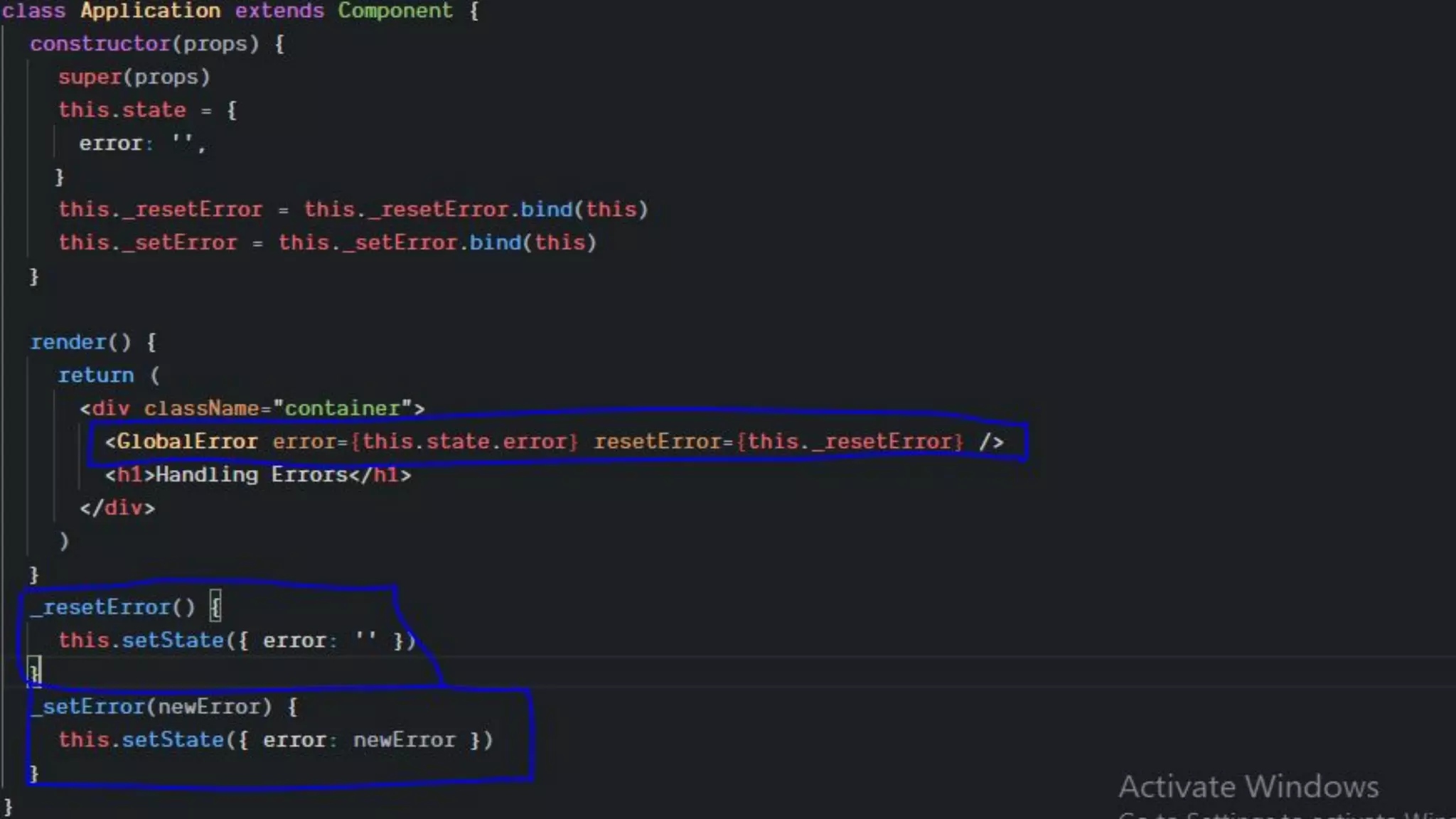
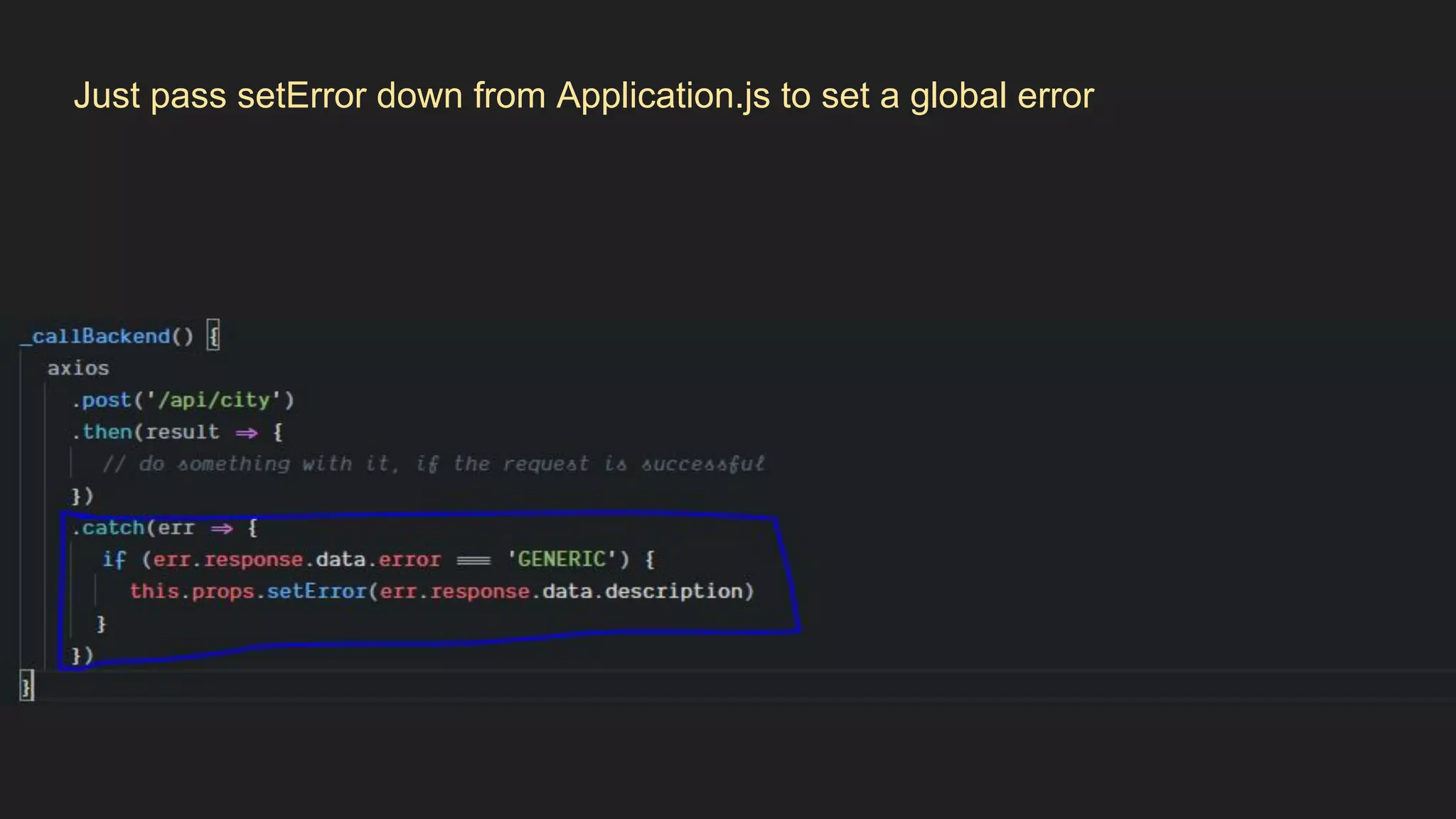
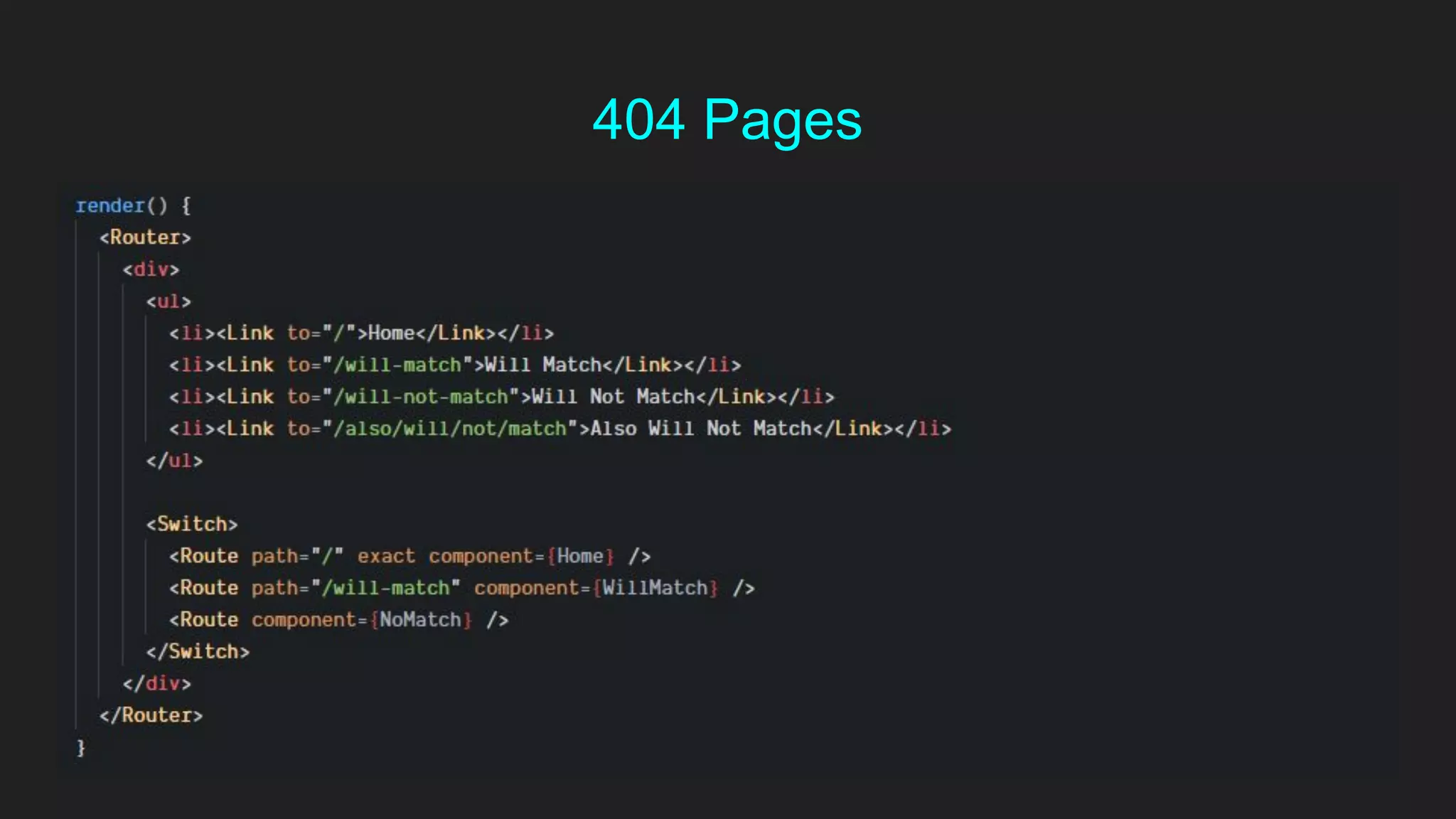
This document discusses how to gracefully handle errors with React. It defines what errors are and different types of errors. It introduces error boundaries in React, which are components that catch JavaScript errors anywhere in their child component tree. Error boundaries display a fallback UI and prevent errors from crashing the whole application. The document recommends making reusable error boundary components and discusses best practices around error handling in React.