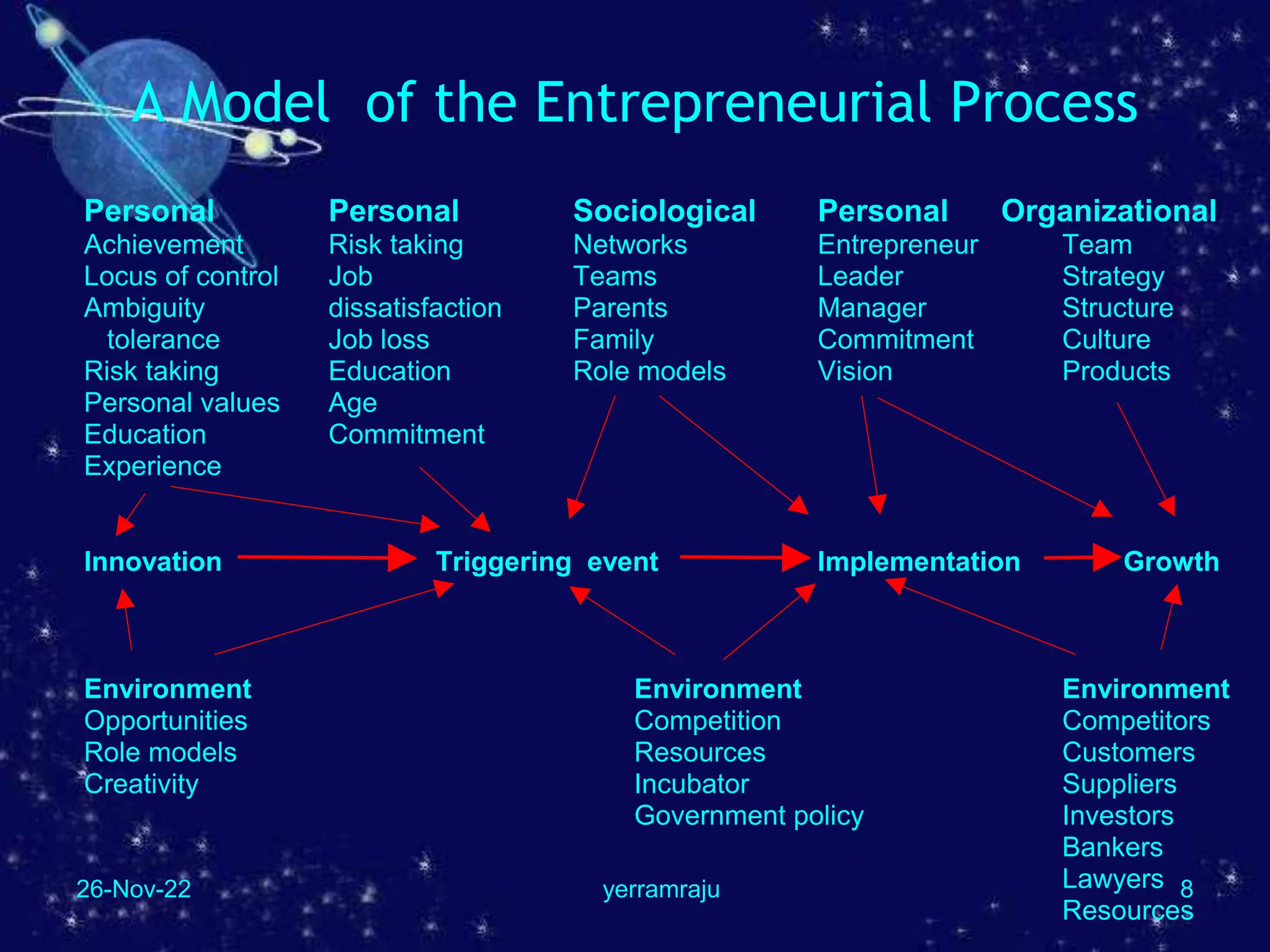
The document outlines an entrepreneurship lesson series focusing on the role, myths, processes, typologies, risks, and rewards of entrepreneurship. It emphasizes the importance of small enterprises in job creation and economic development, while addressing common misconceptions about entrepreneurs. Additionally, it provides a framework for assessing personal entrepreneurial traits and categorizes different types of entrepreneurship.