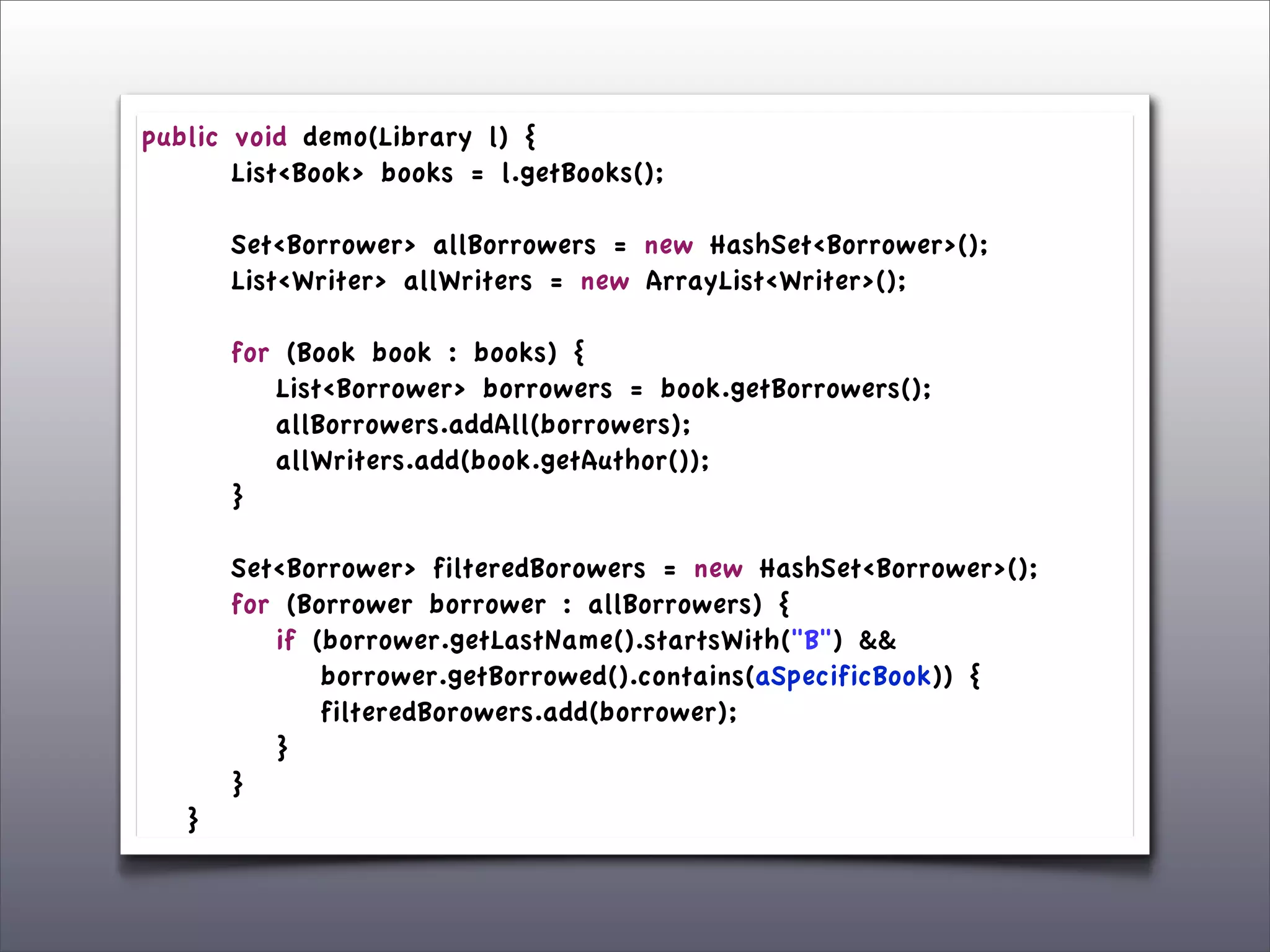
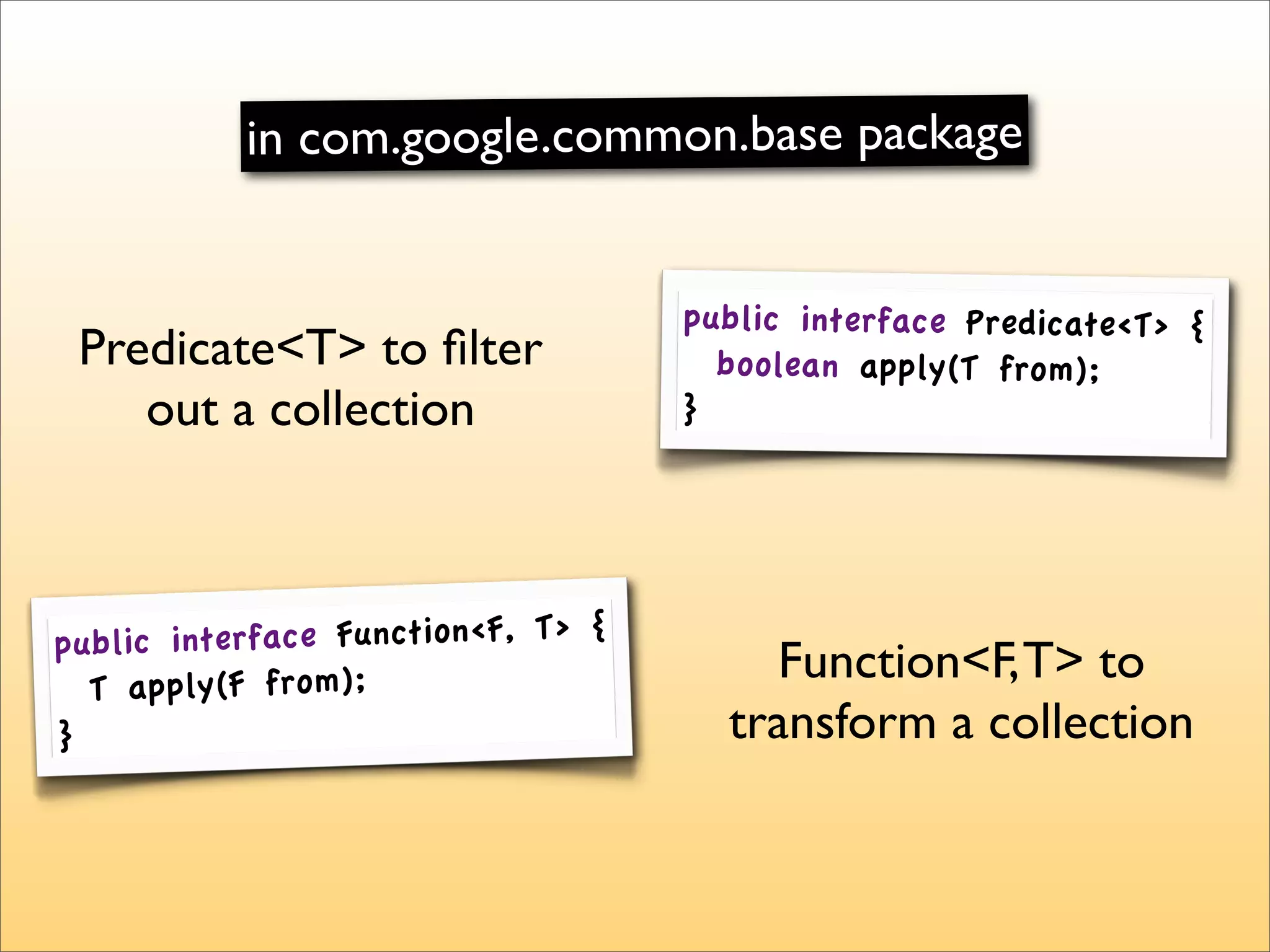
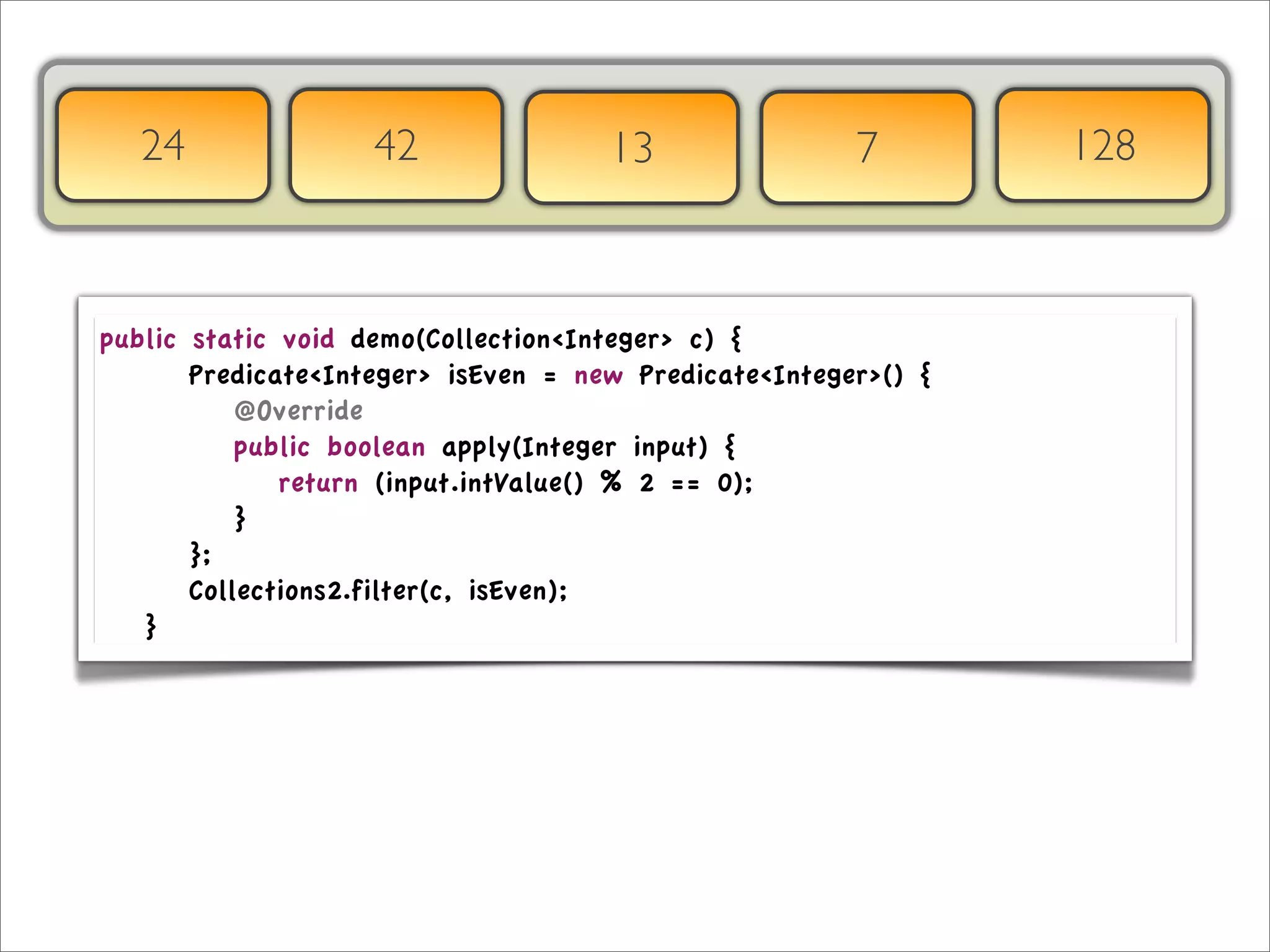
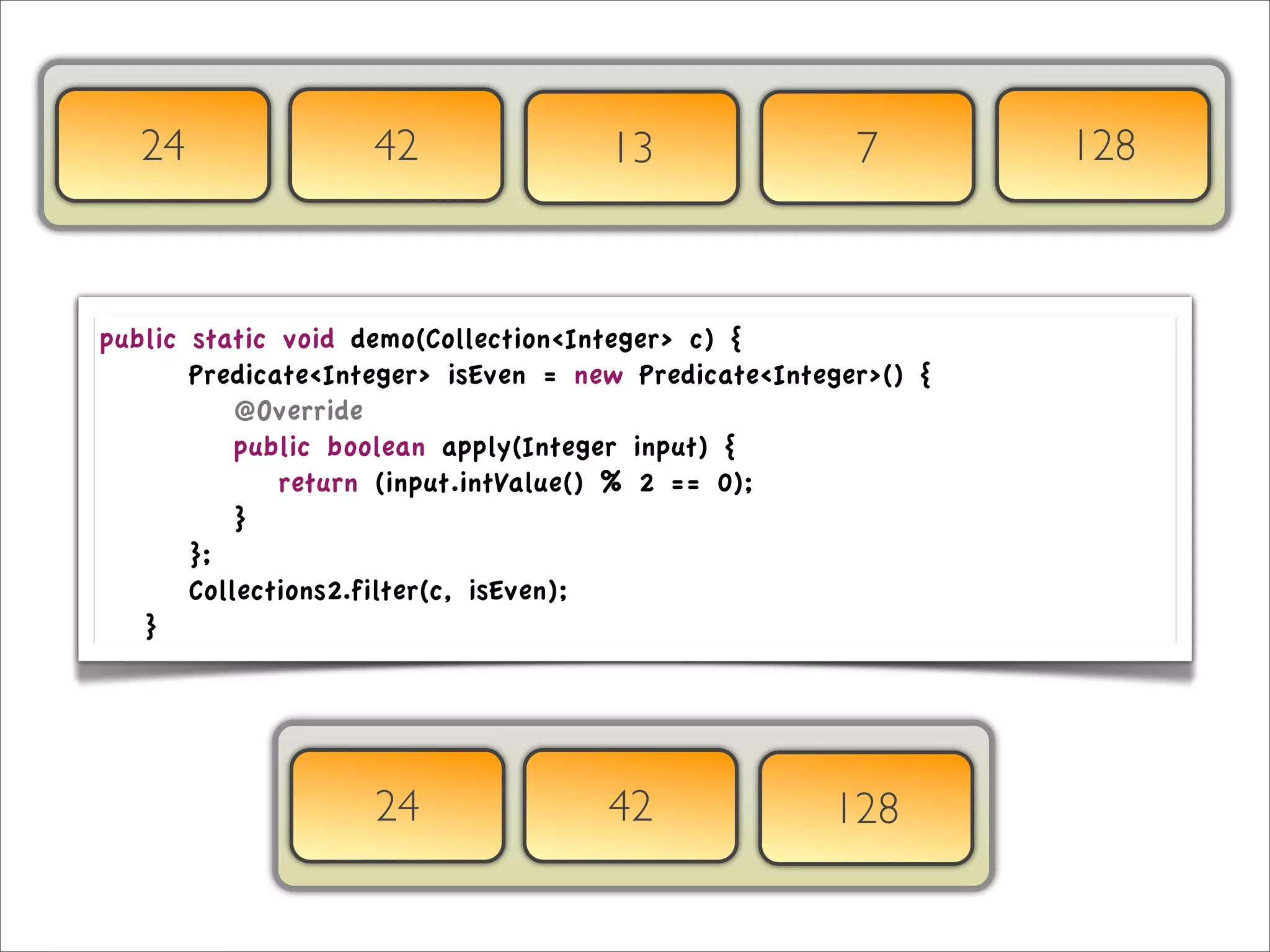
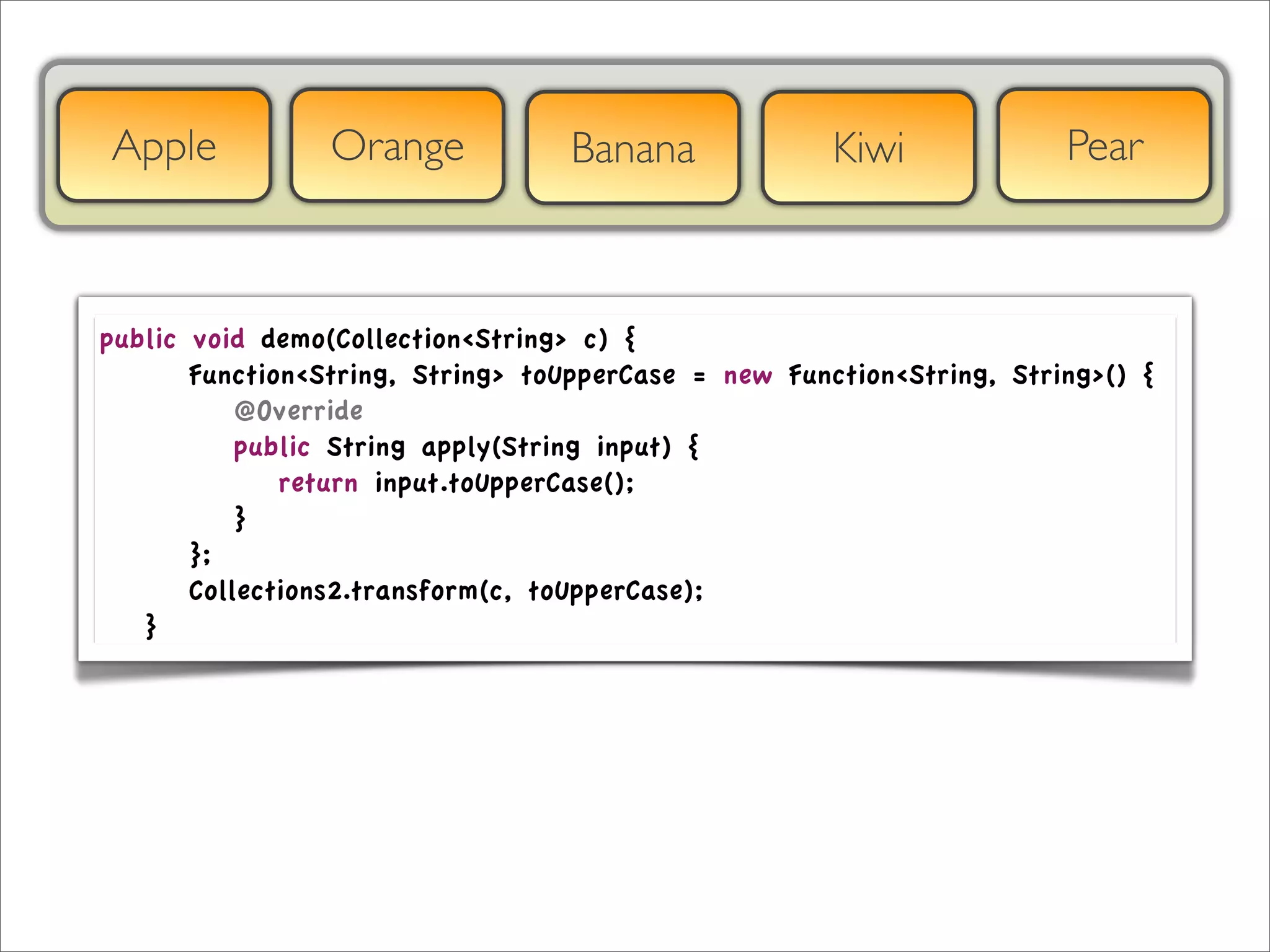
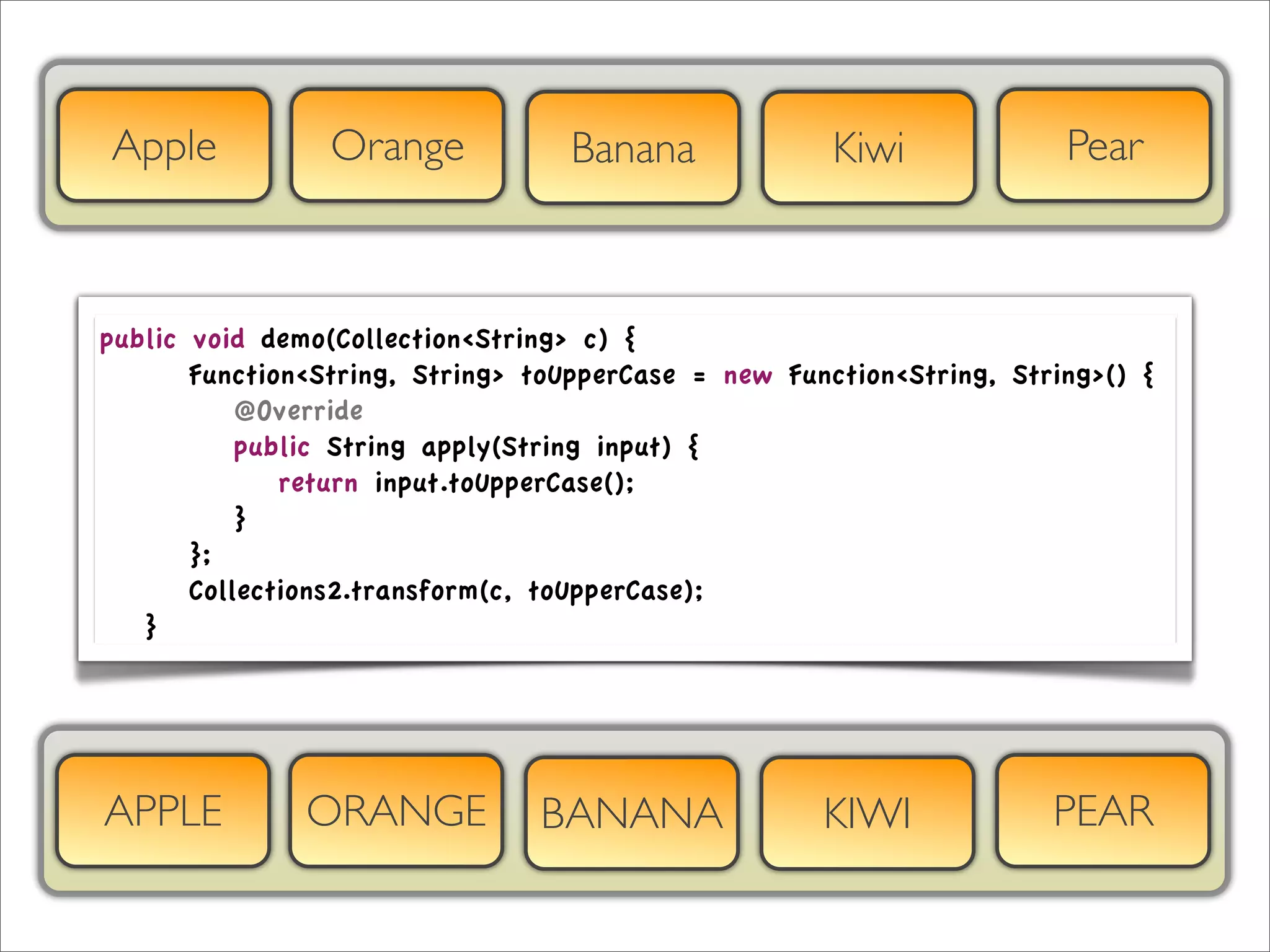
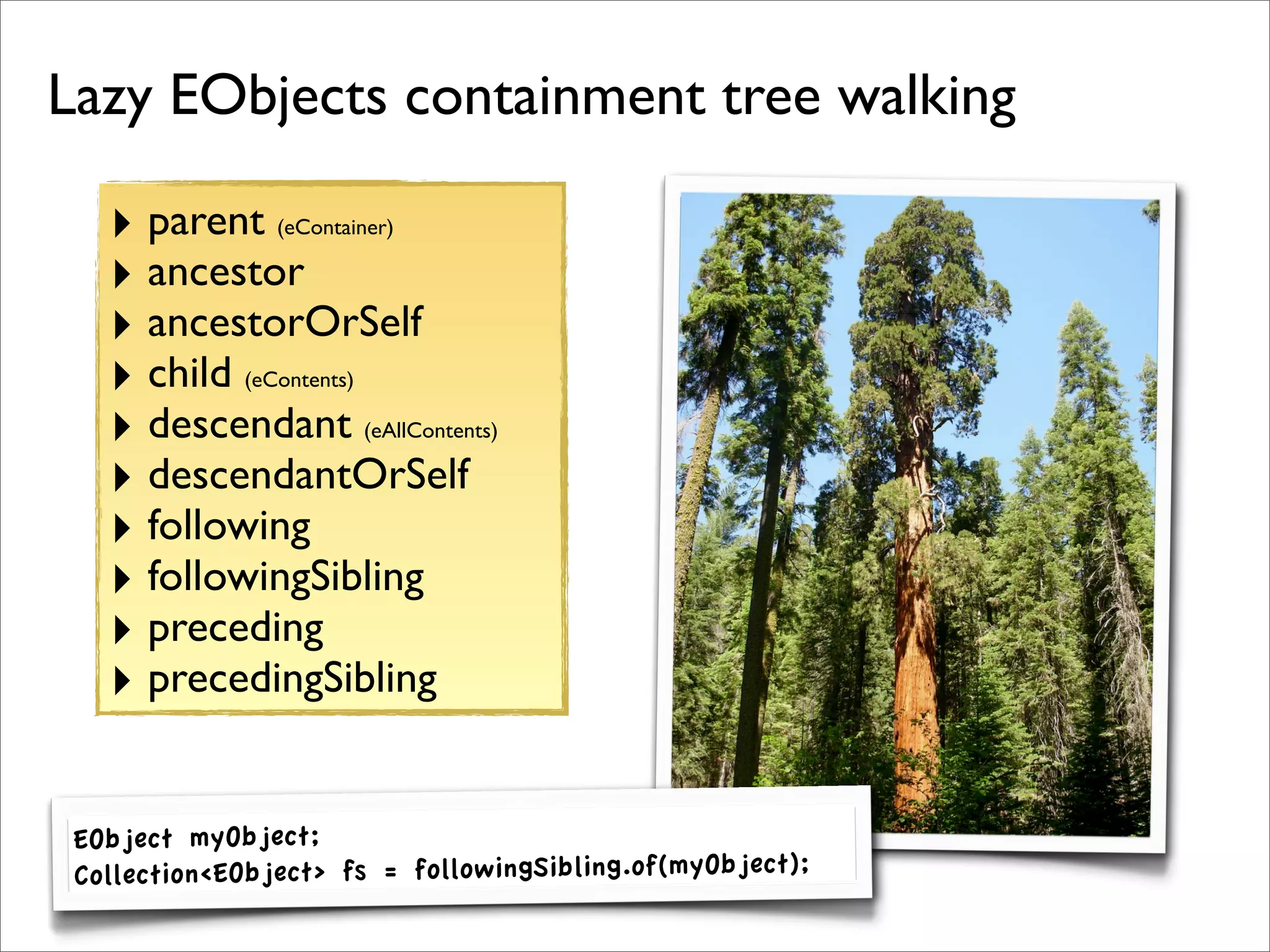
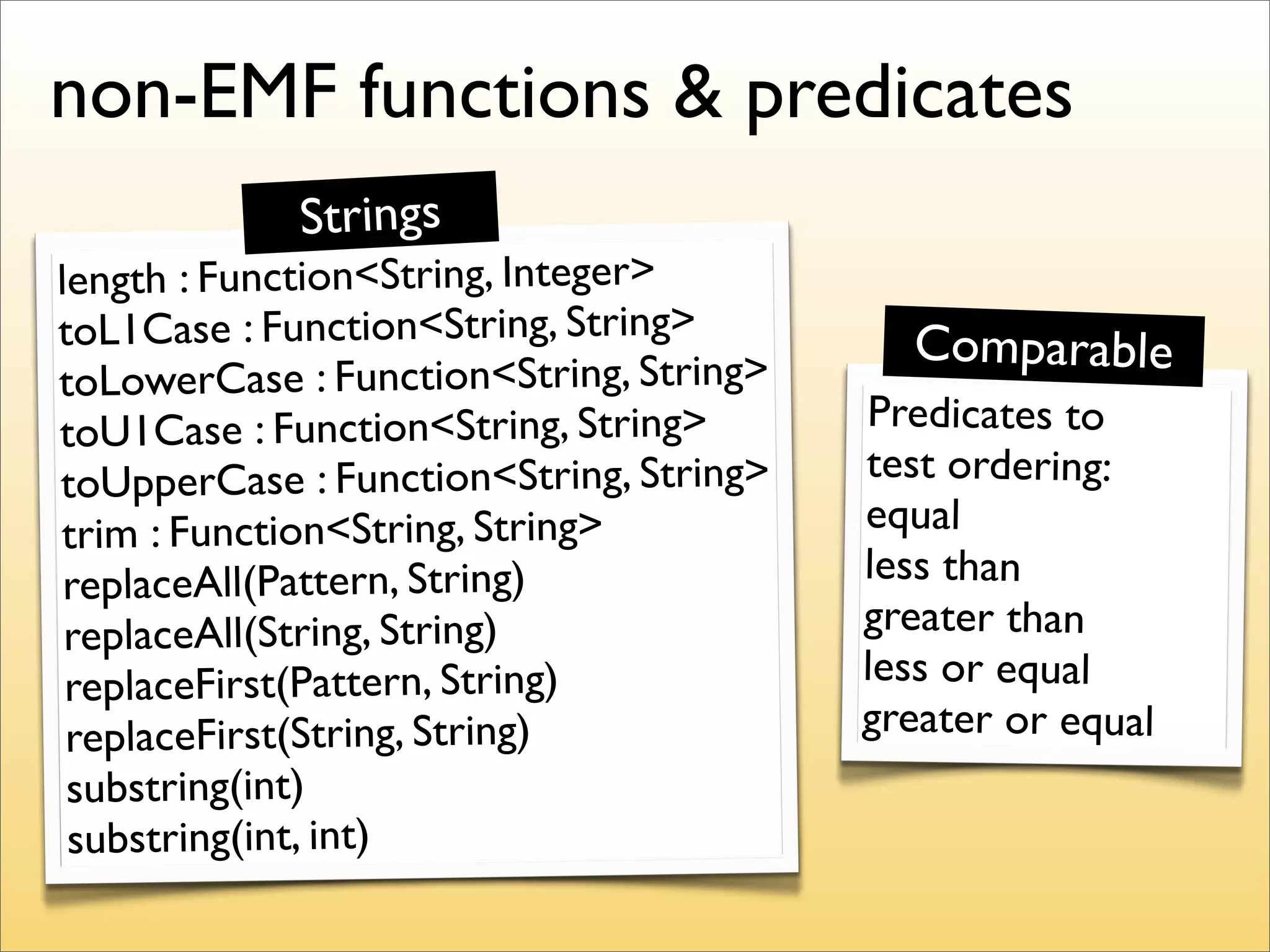
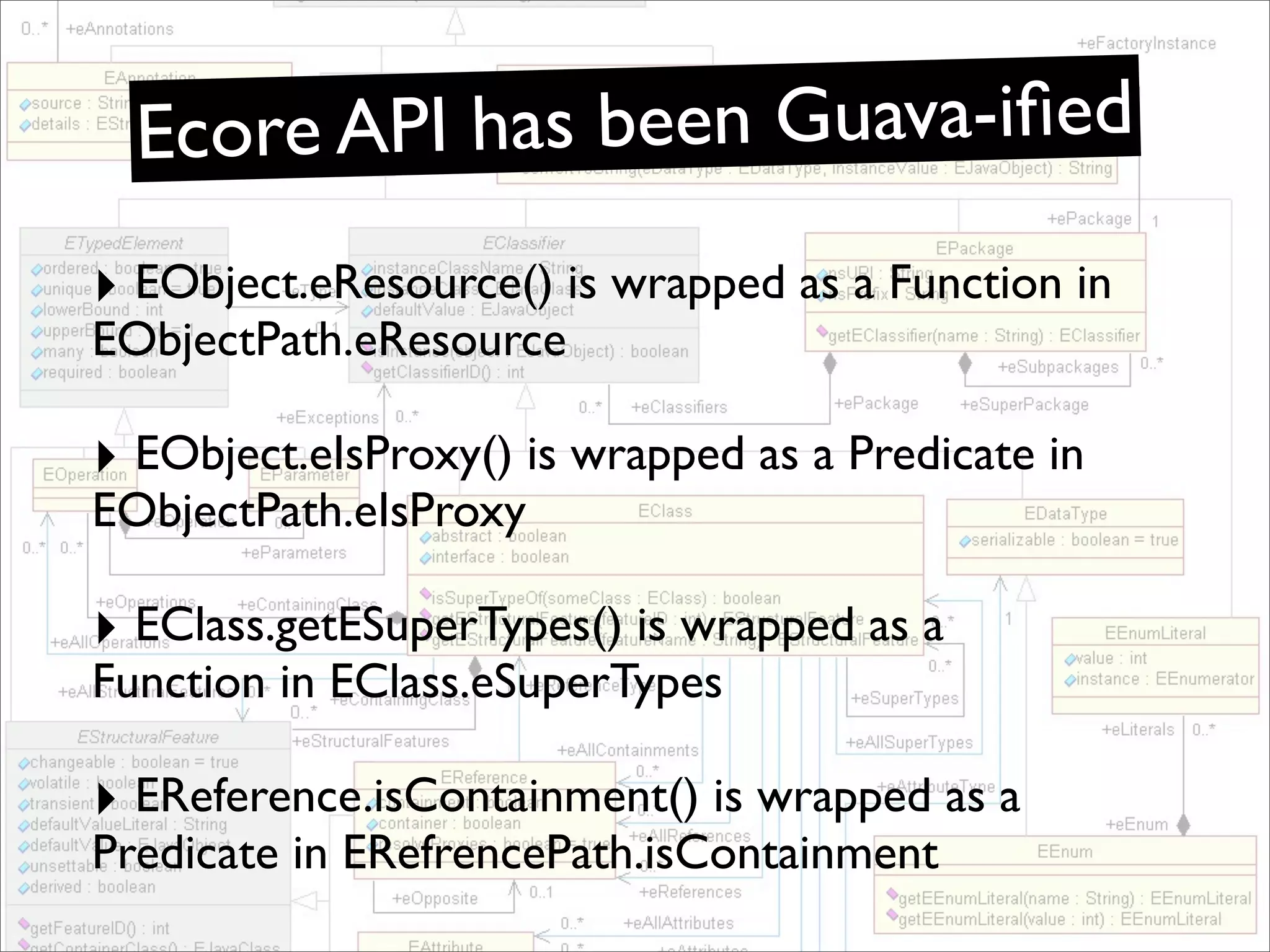
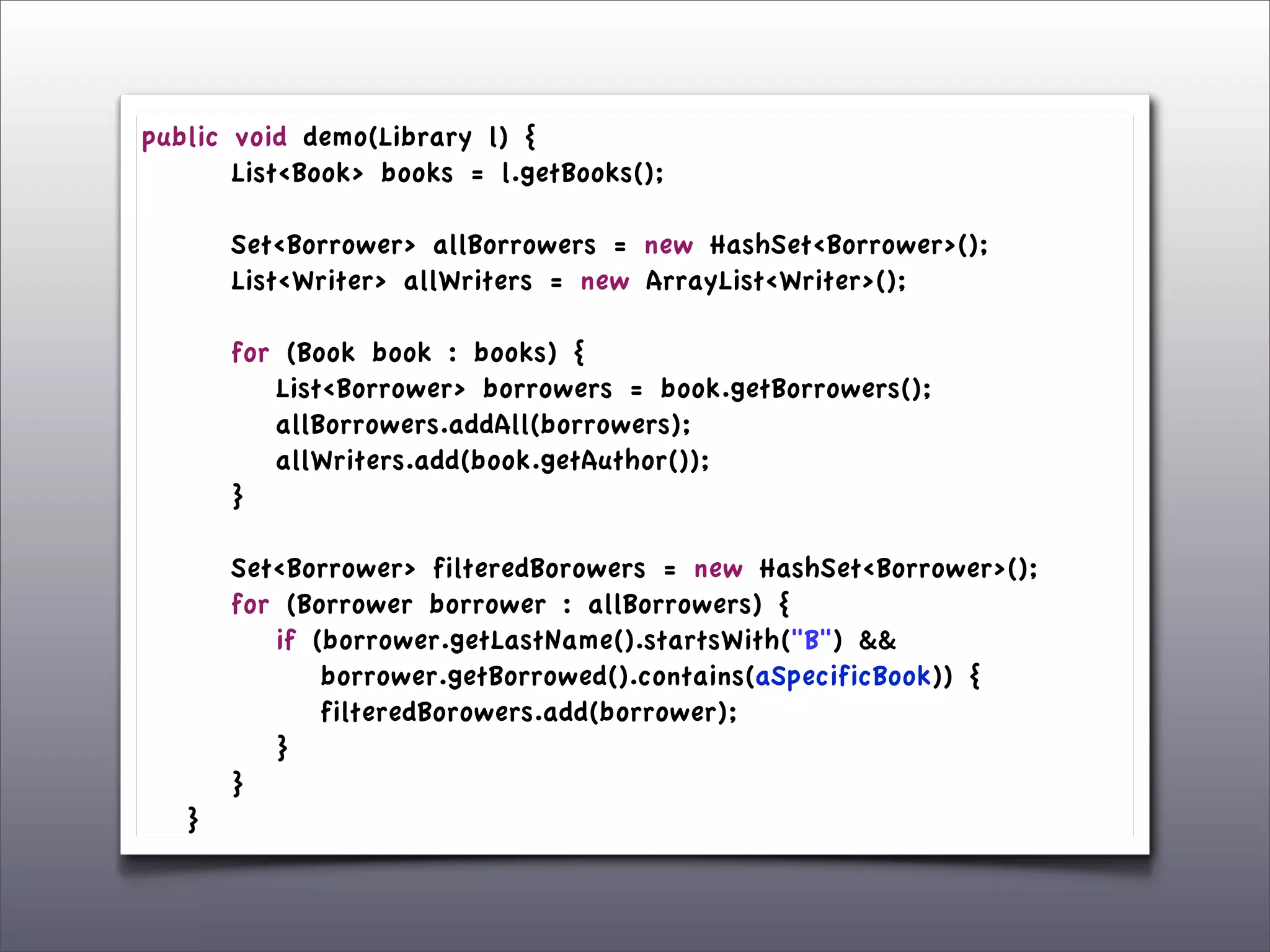
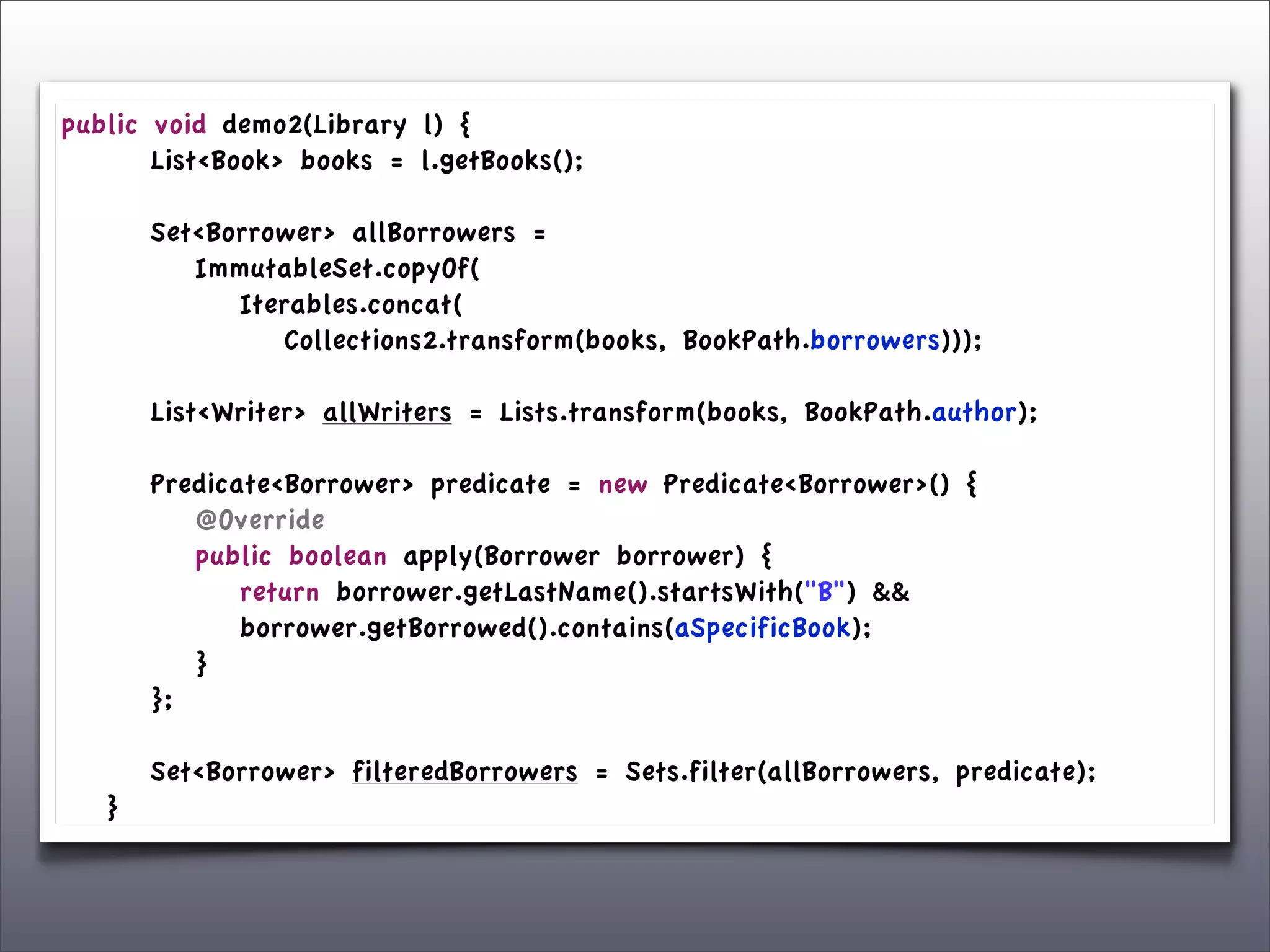
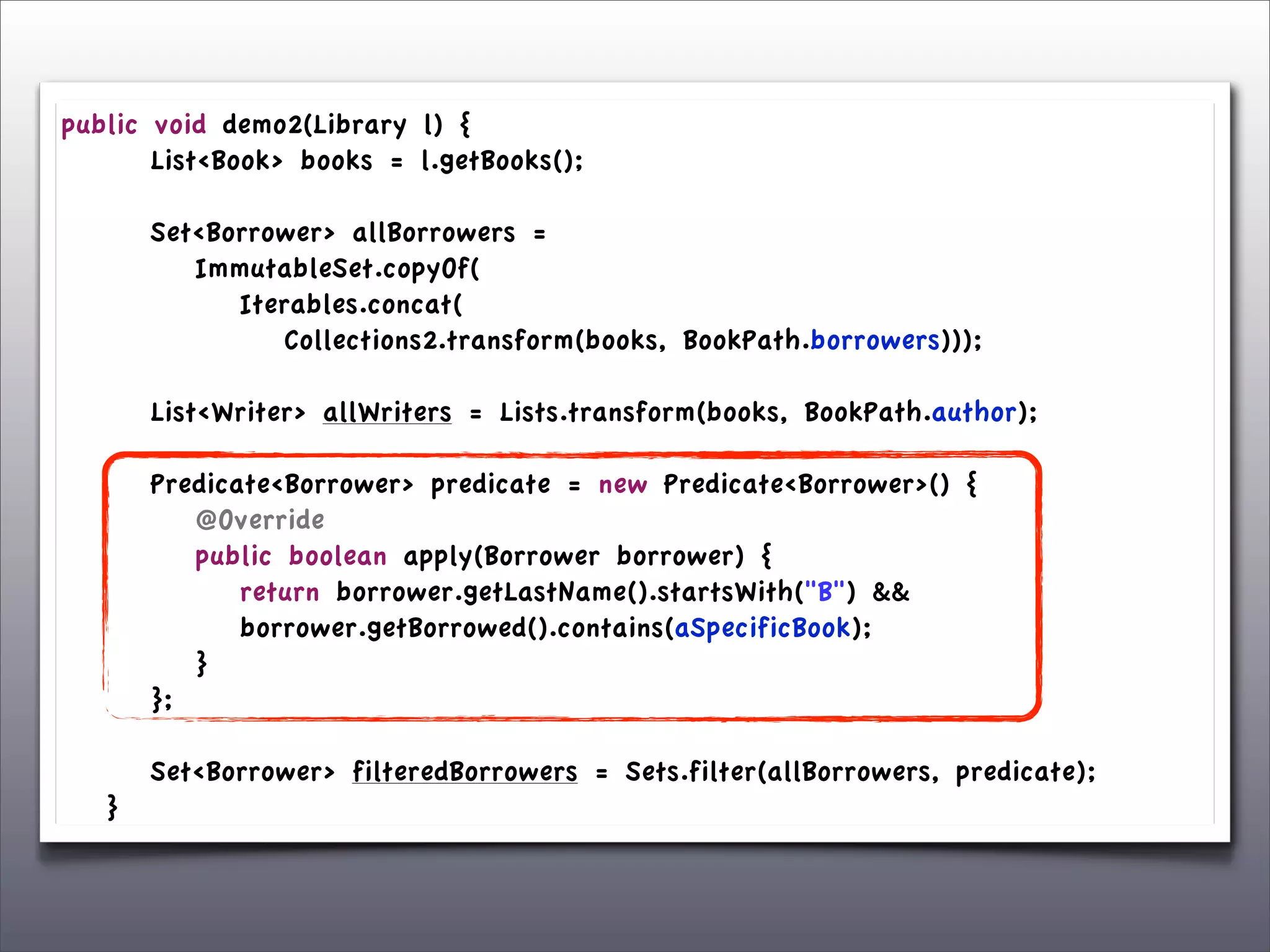
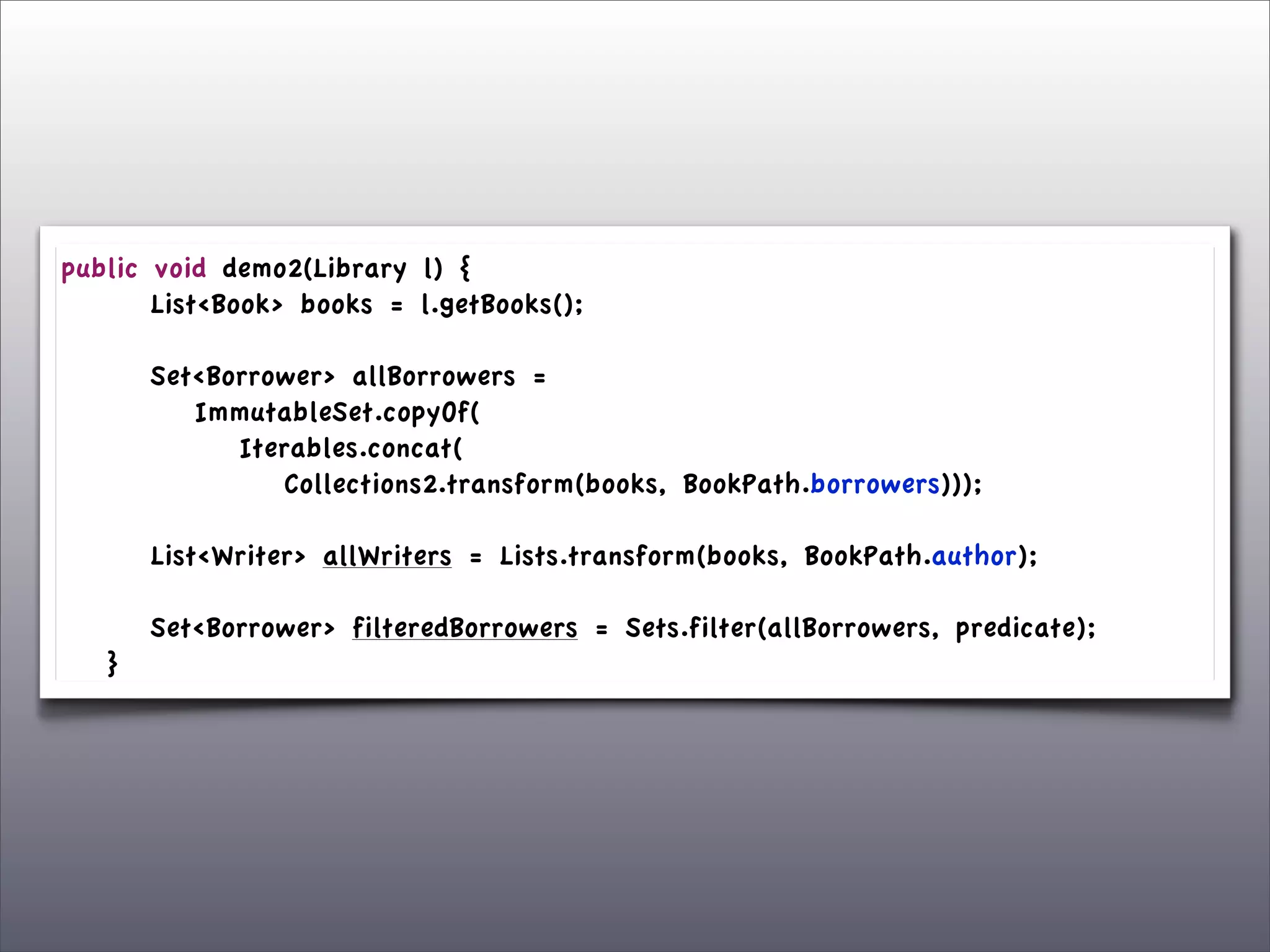
The document discusses the use of the Guava Java library for manipulating collections and implementing predicates and functions. It includes code examples demonstrating how to filter and transform collections and introducing concepts like laziness and containment tree walking. The presentation emphasizes the integration between Guava and EMF, highlighting the usefulness of the emfpath library.