Embed presentation
Downloaded 159 times

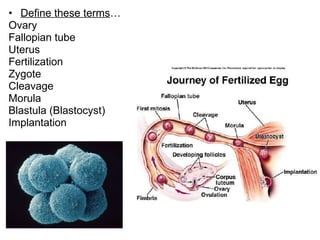
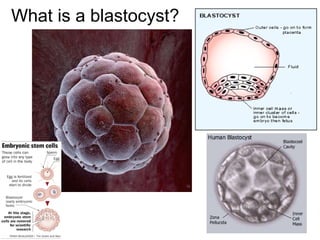
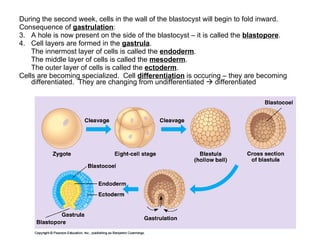
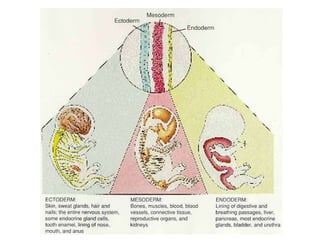
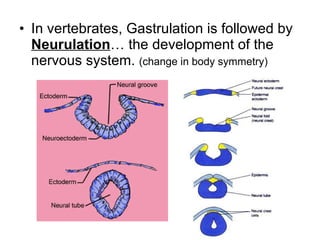

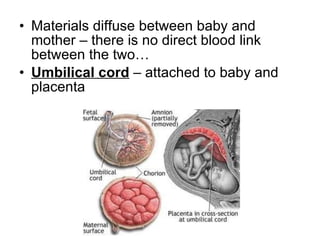
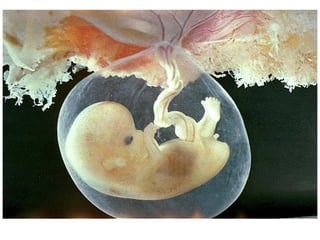
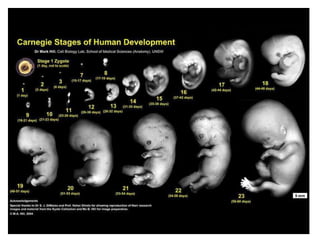
The document defines key terms related to early embryonic development including the ovary, fallopian tube, uterus, fertilization, zygote, cleavage, morula, and blastula. It explains that a blastocyst is a hollow ball of cells formed after cleavage and morula stages. During the second week, cells in the blastocyst wall begin to fold inward through the process of gastrulation, forming three distinct cell layers - endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm - and starting the specialization of cells through differentiation. By day 21, the amnion and chorion have formed embryonic membranes, with the chorion and uterine lining forming the placenta to allow nutrient exchange between the









