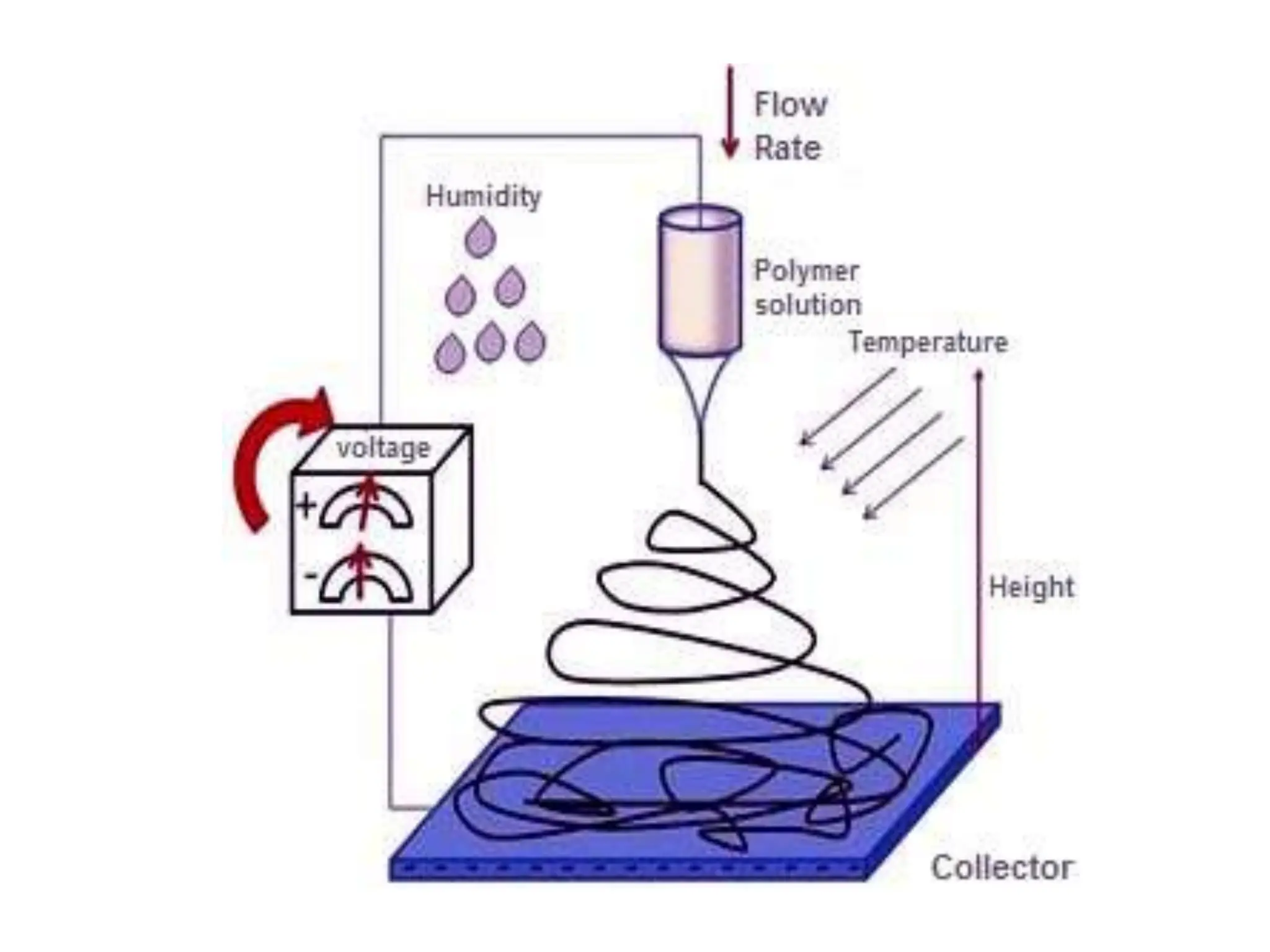
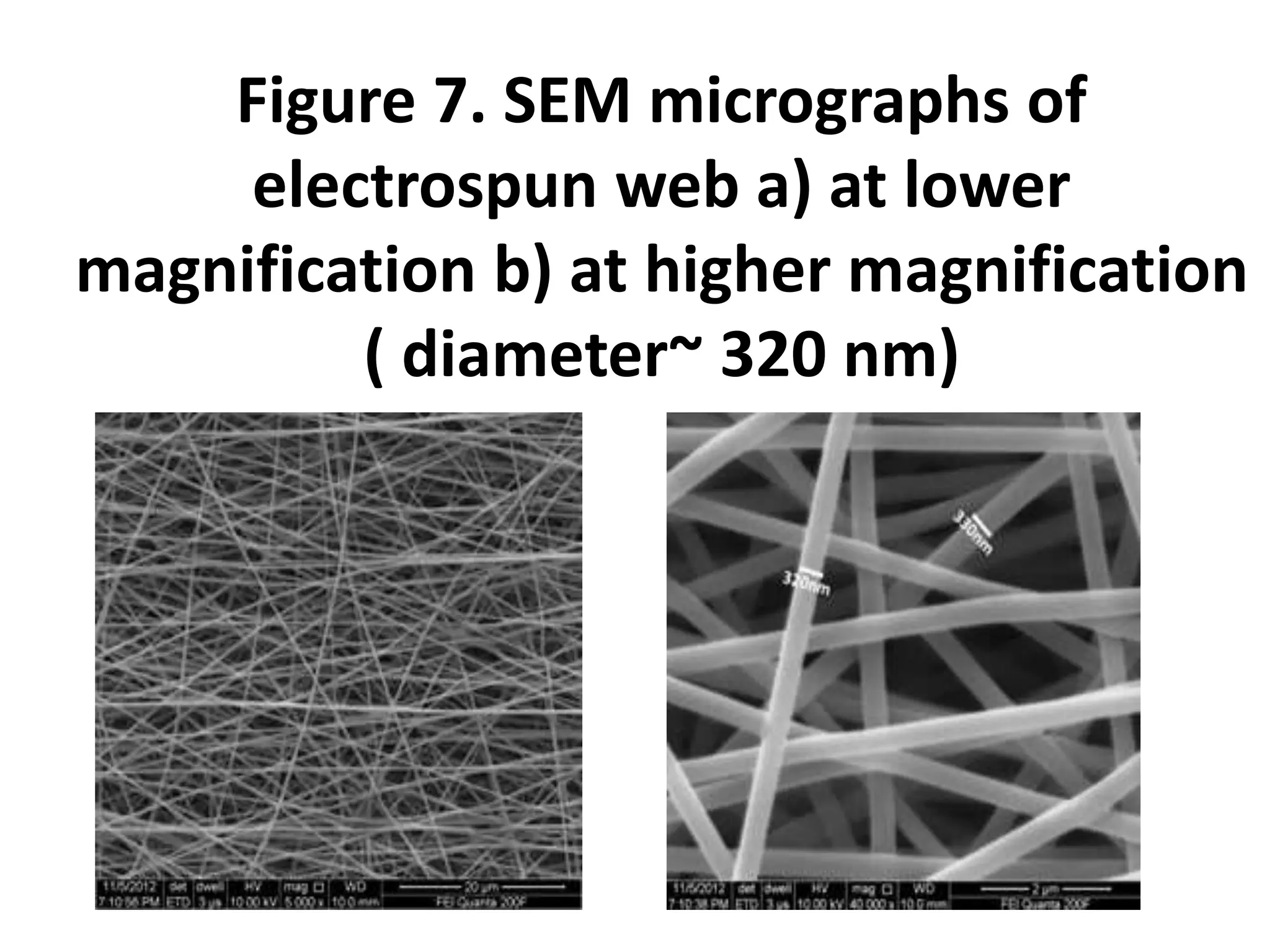
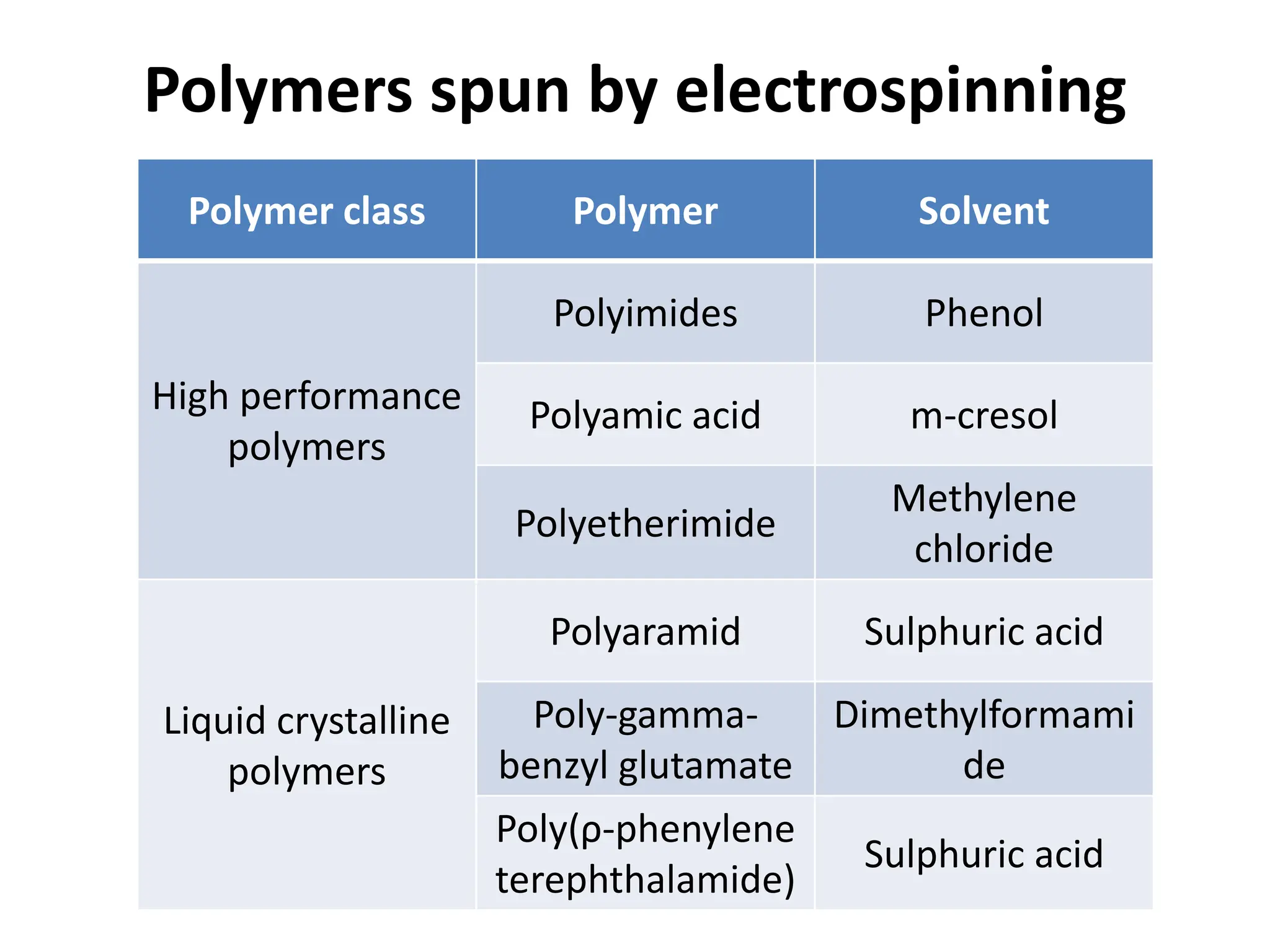
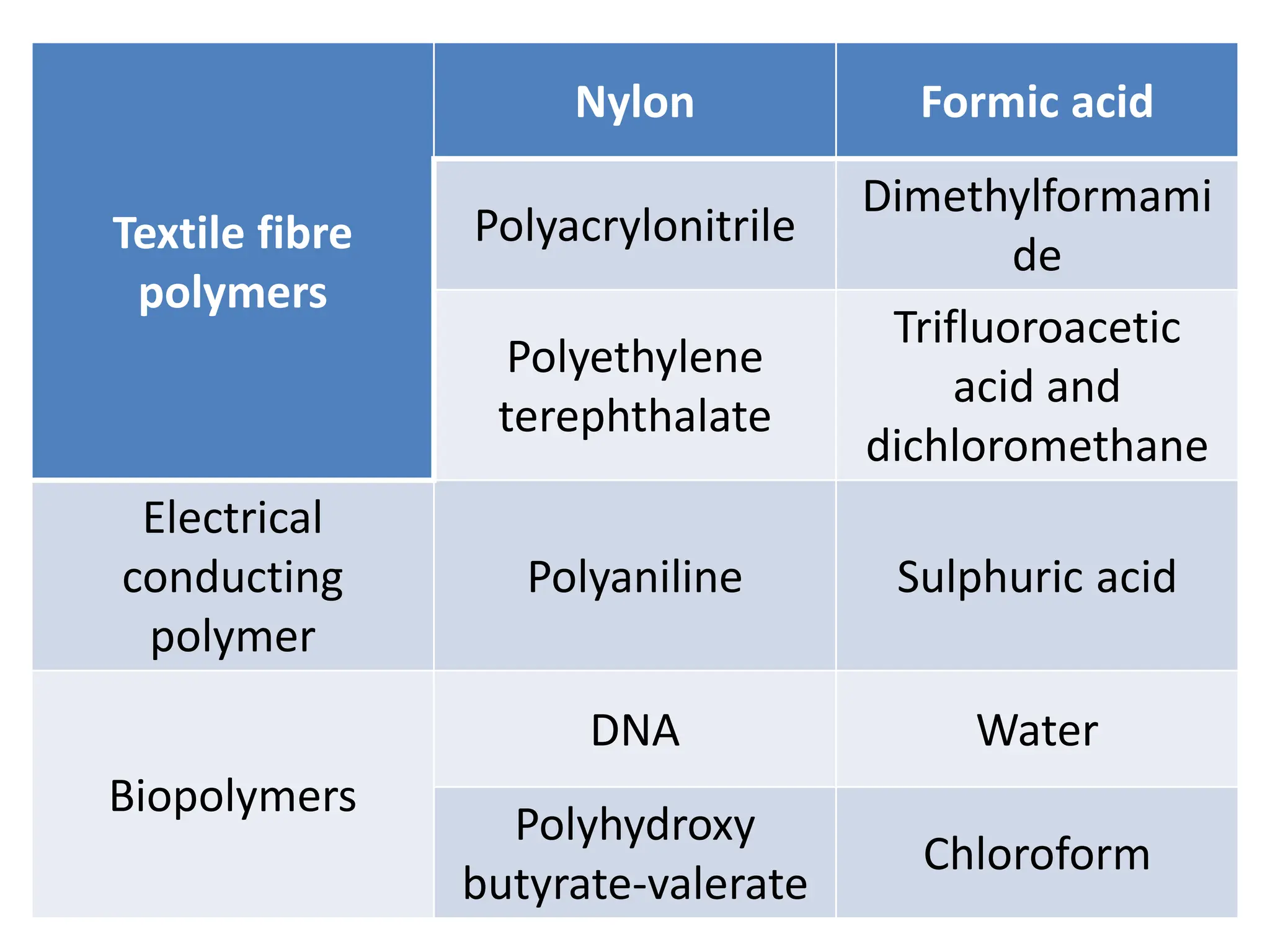
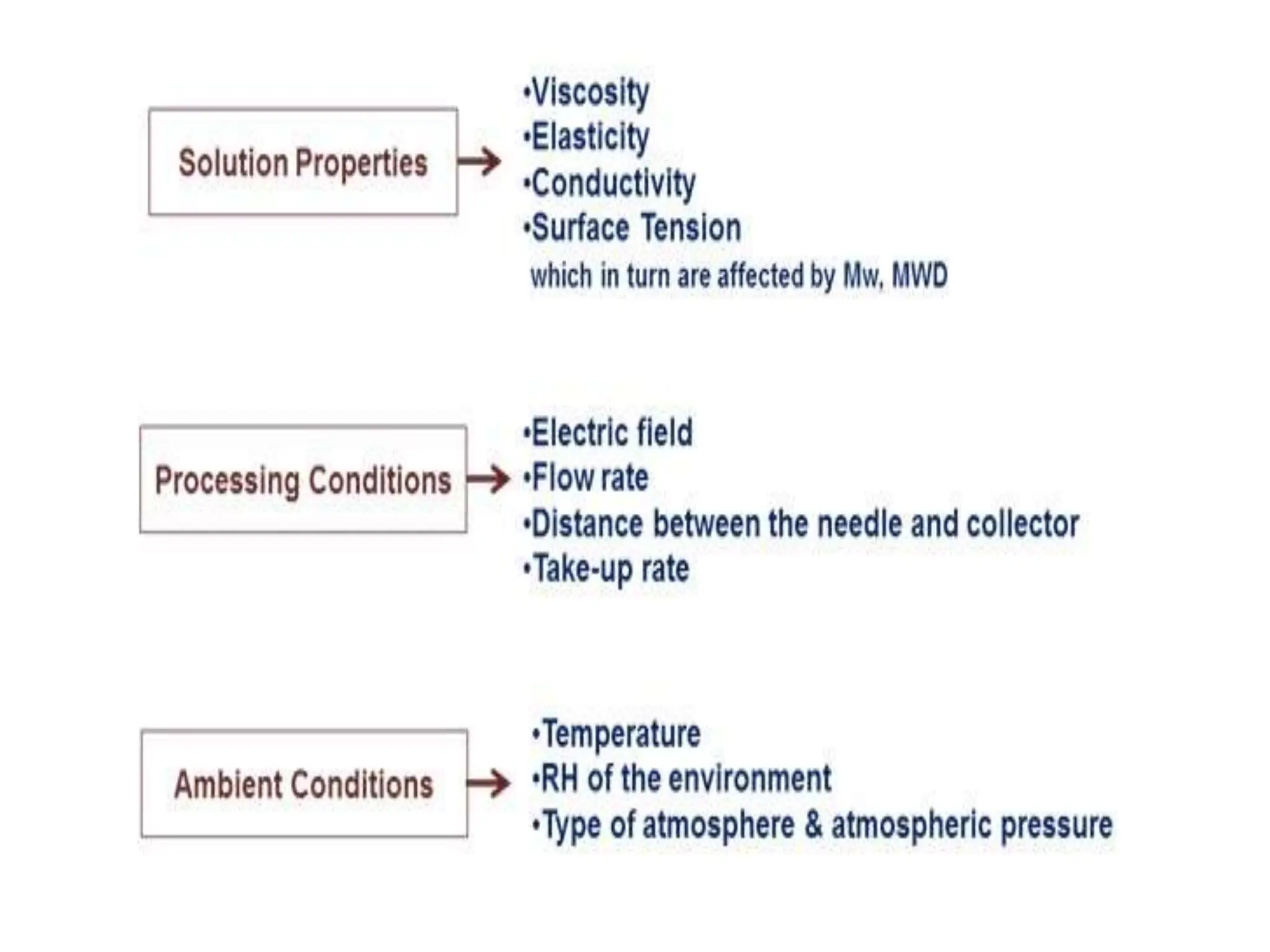
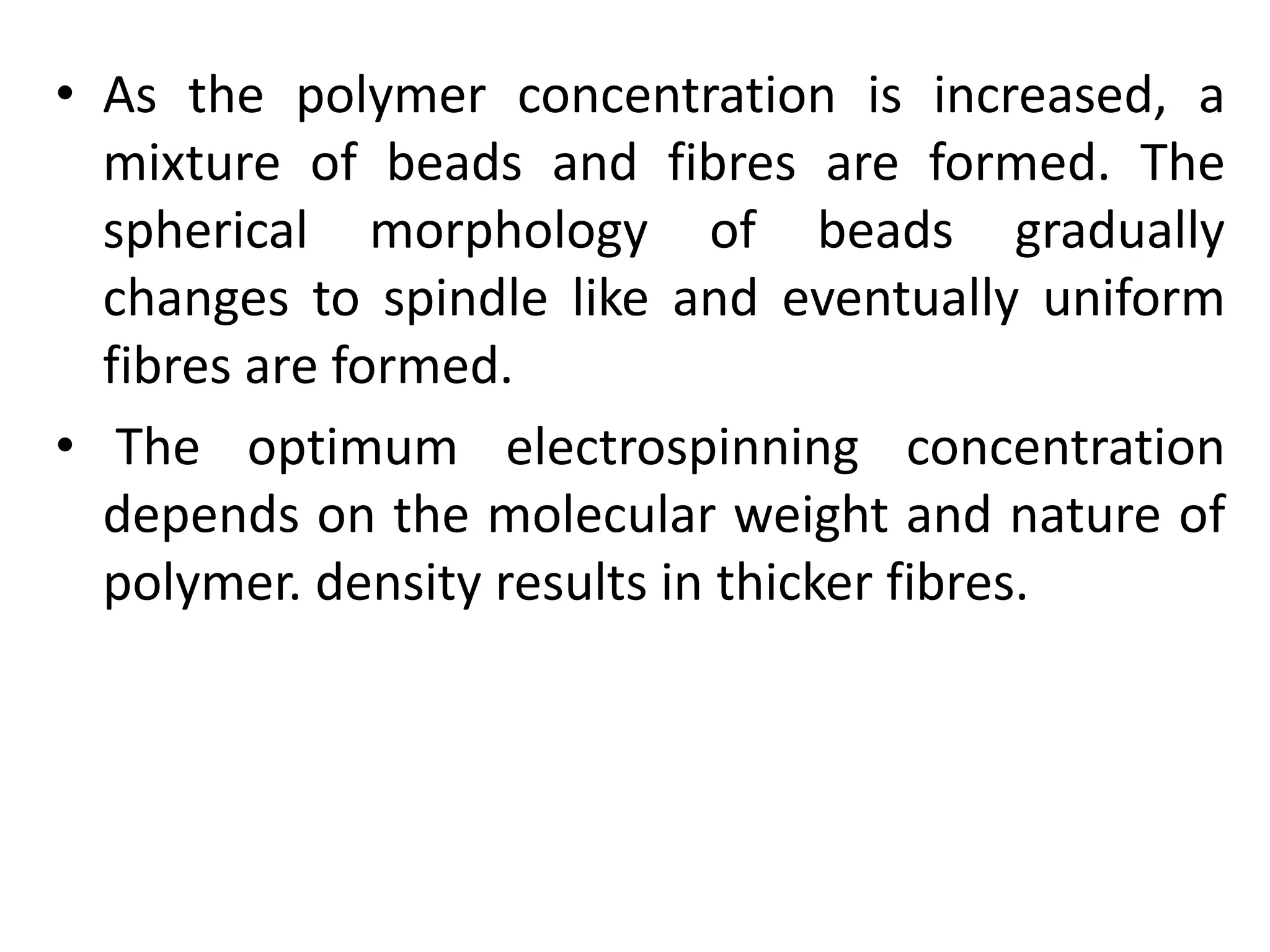
Nanofibres are fibres with diameters less than 500 nm that have unique properties like large surface area and superior mechanical performance. Electrospinning is the most efficient technique to produce polymer nanofibres, using a high voltage electric field to draw charged polymer jets into fibres. The electrospinning process is influenced by solution properties like polymer concentration and molecular weight, as well as processing parameters like voltage and flow rate. By varying these parameters, electrospun nanofibre webs with controlled morphology, diameter, and porosity can be produced.