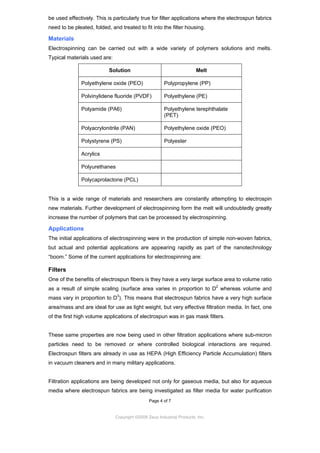
Electrospinning is a technique that uses electrical charges to draw thin fibers from liquids or melts. It can produce fibers as small as 10 nanometers in diameter. Common applications include filters, protective clothing, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery systems. Emerging applications include wearable power sources and wound dressings made from genetically engineered collagen. Electrospinning offers a versatile way to manufacture nanofibers and fabric structures with potential applications across many industries.