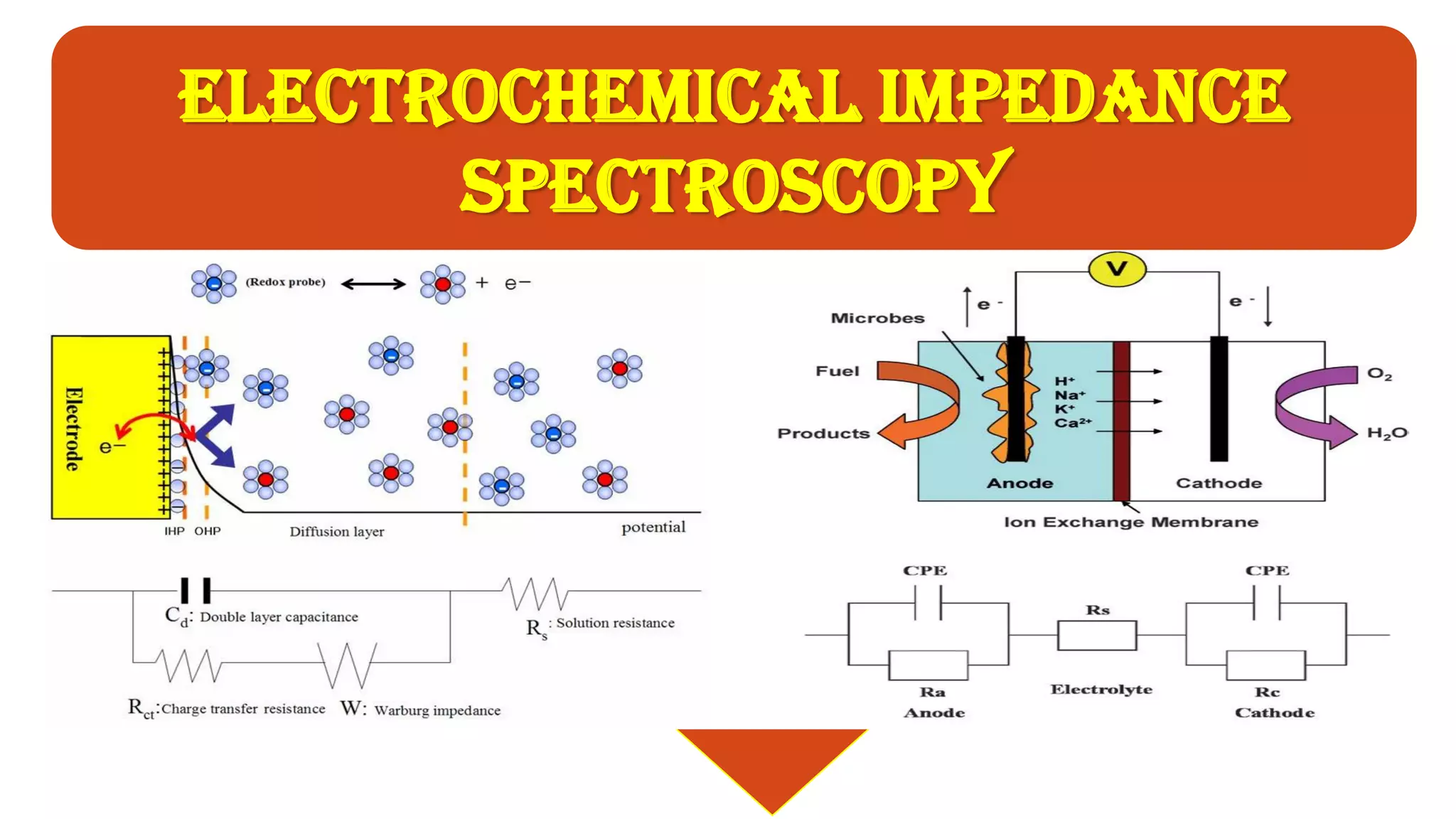
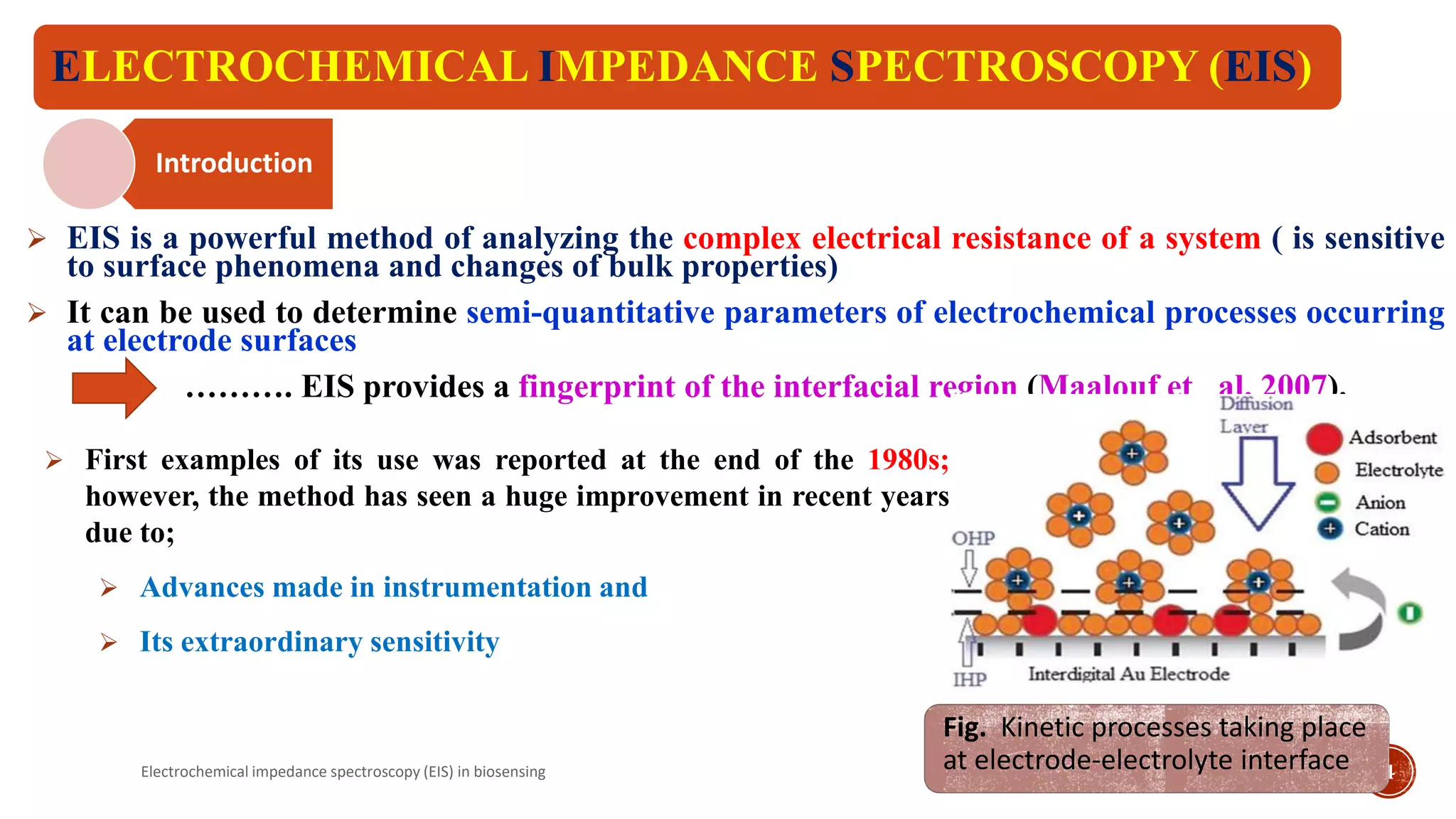
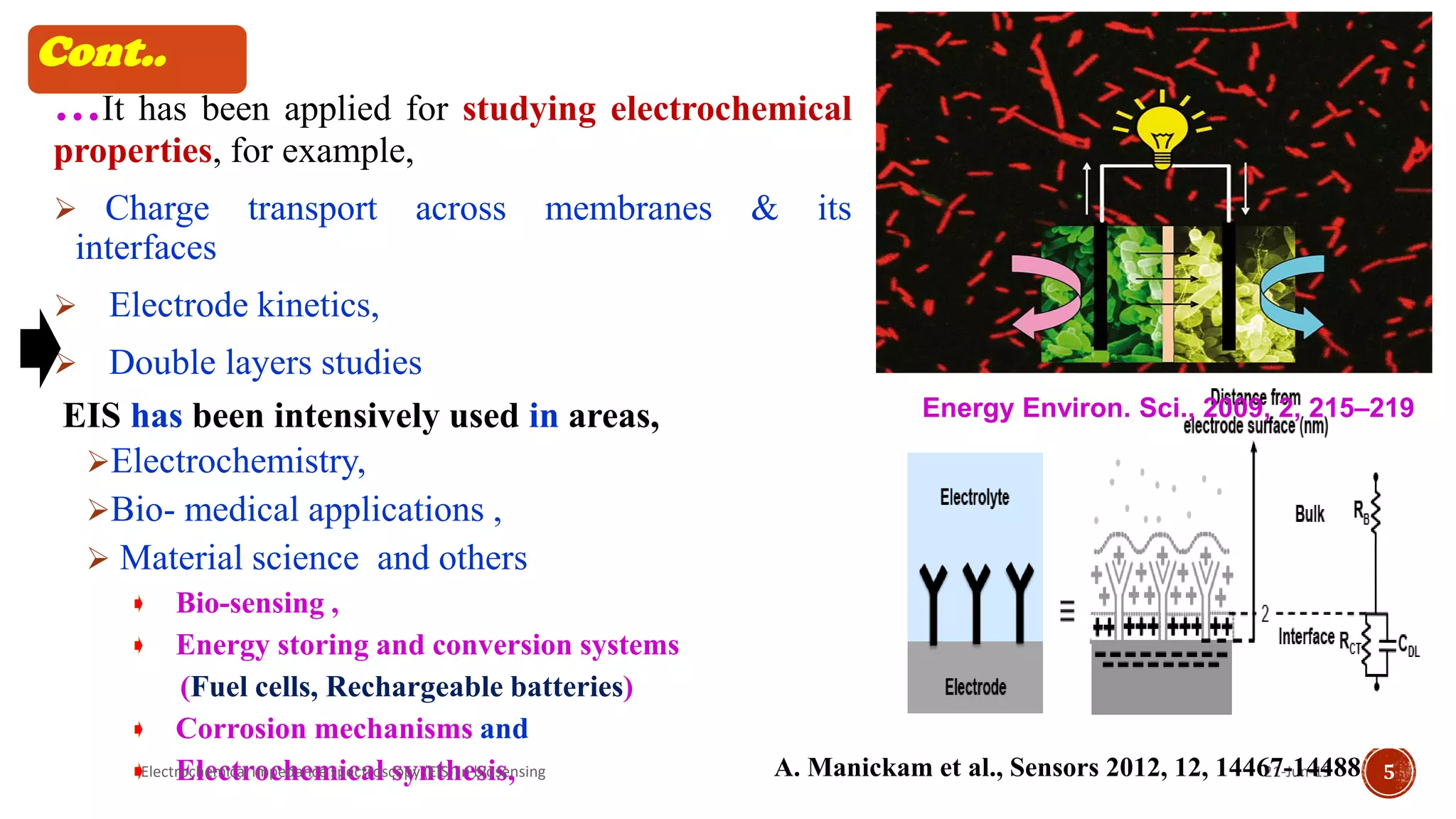
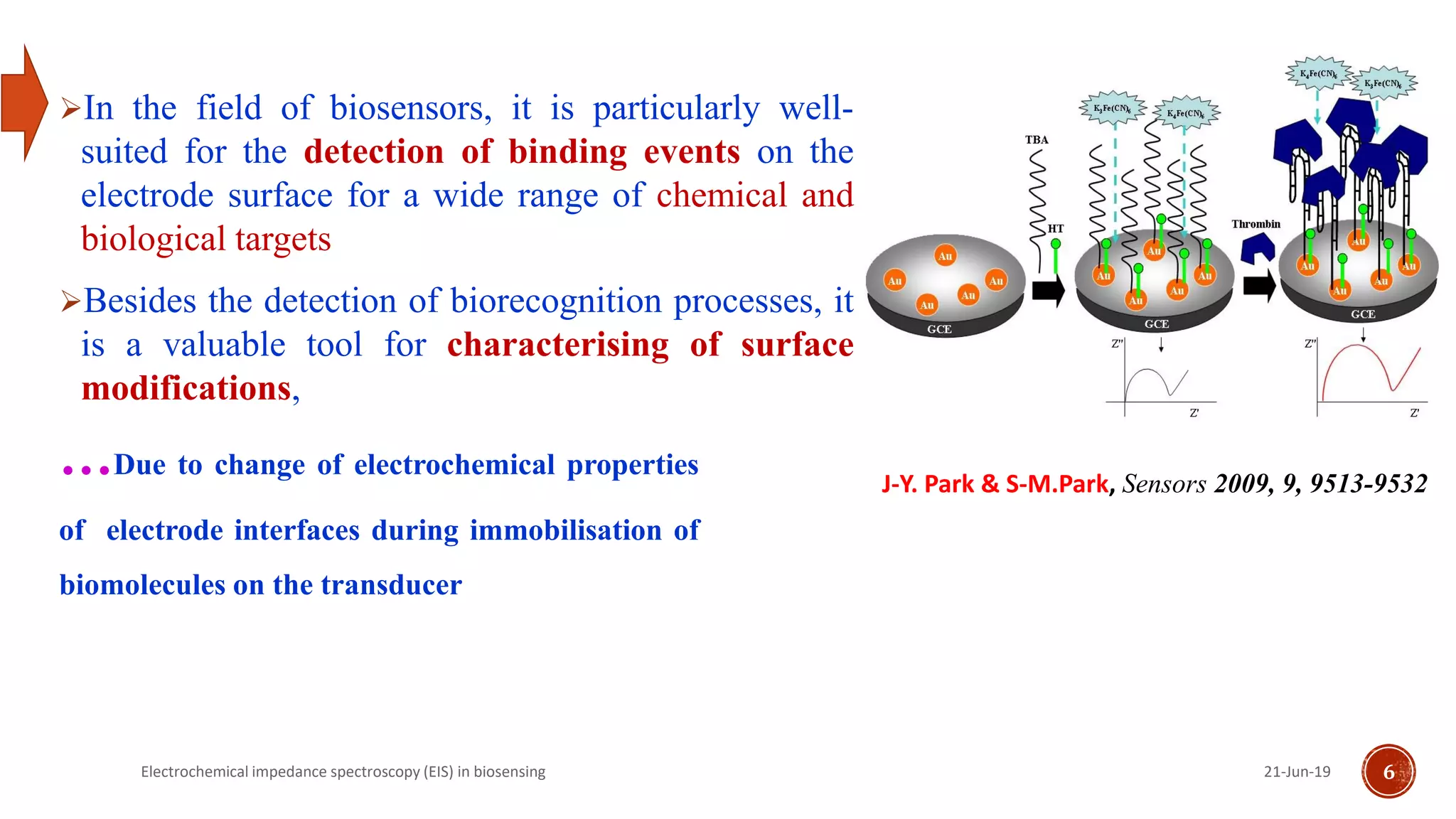
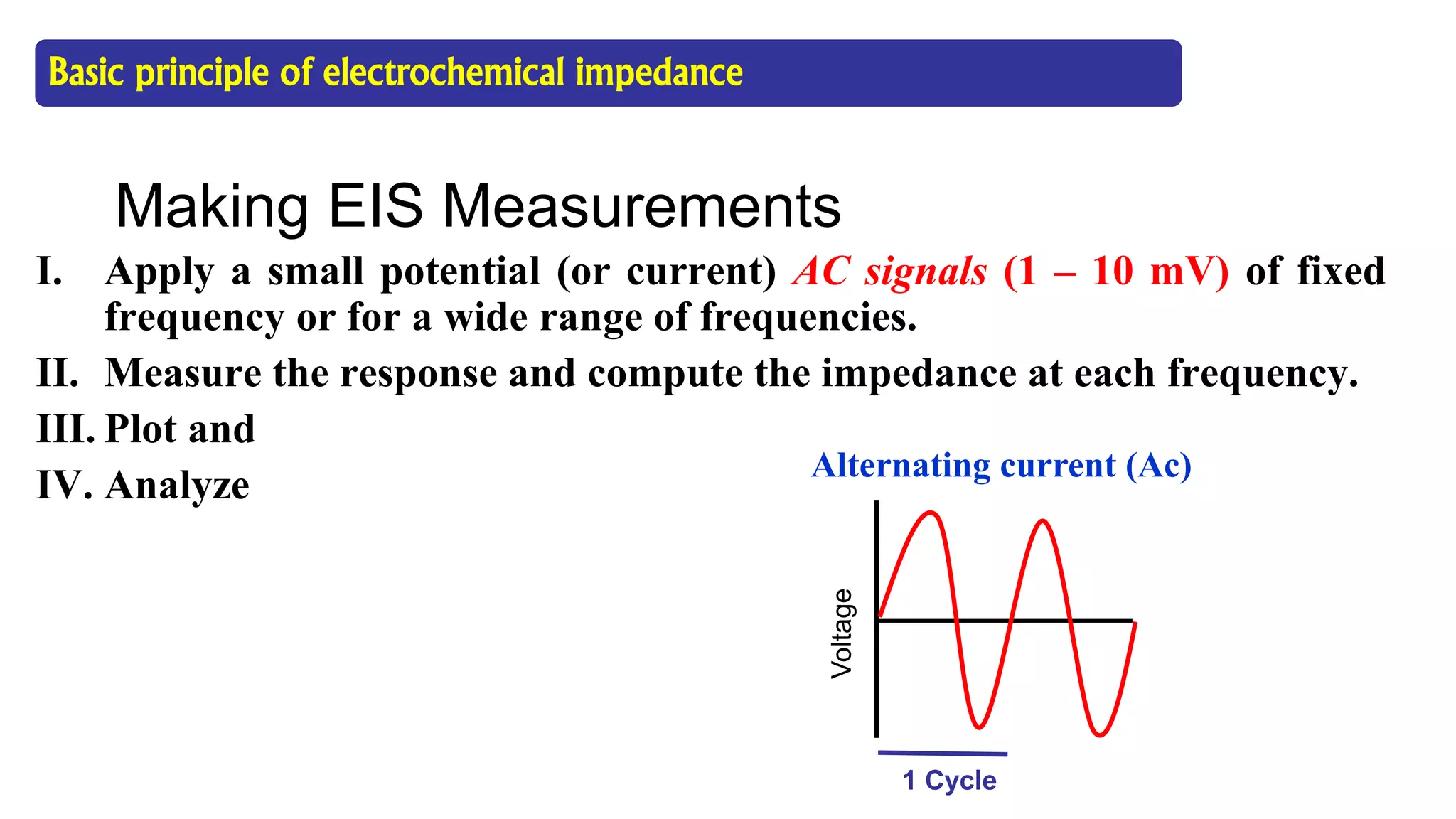
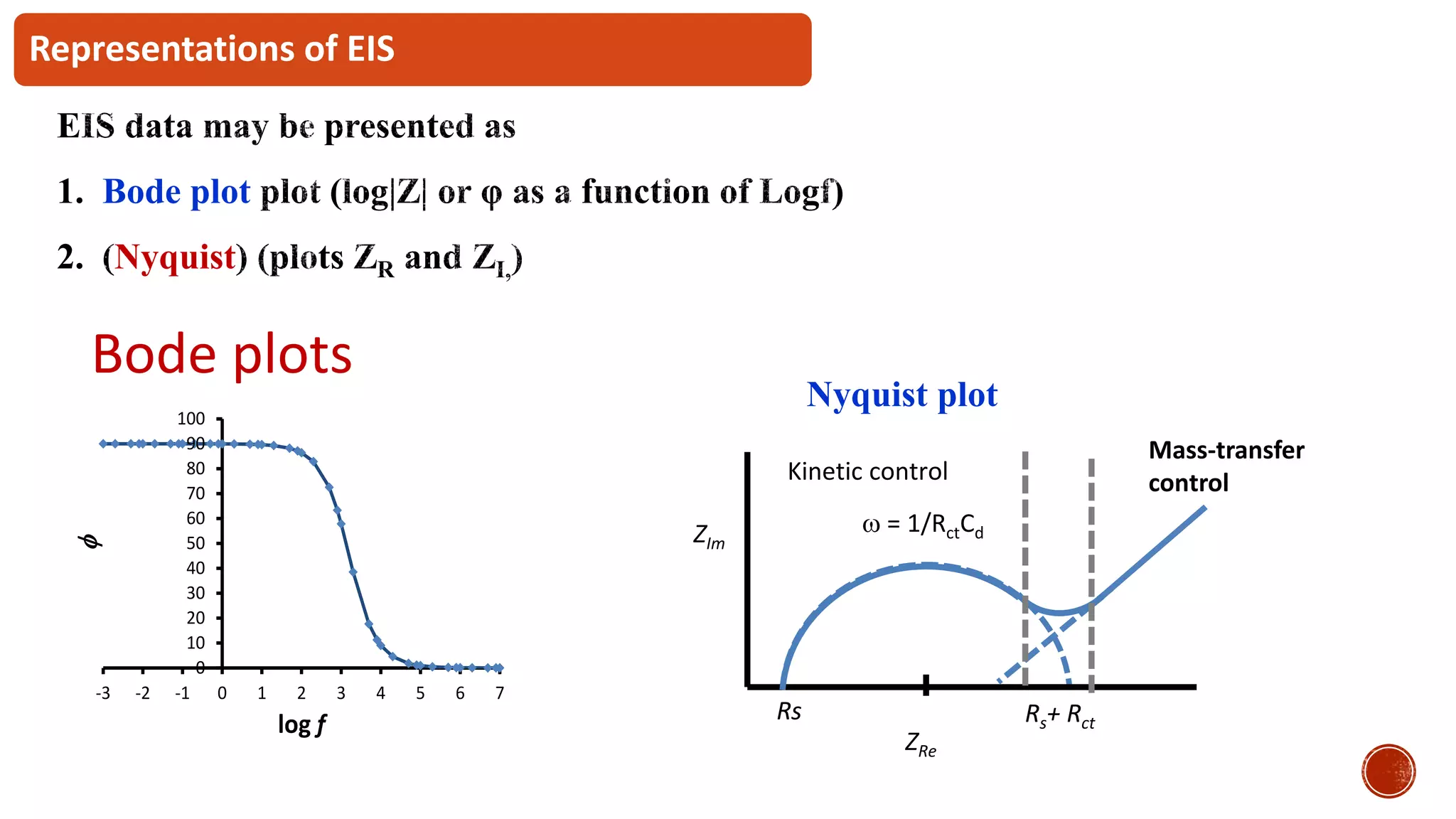
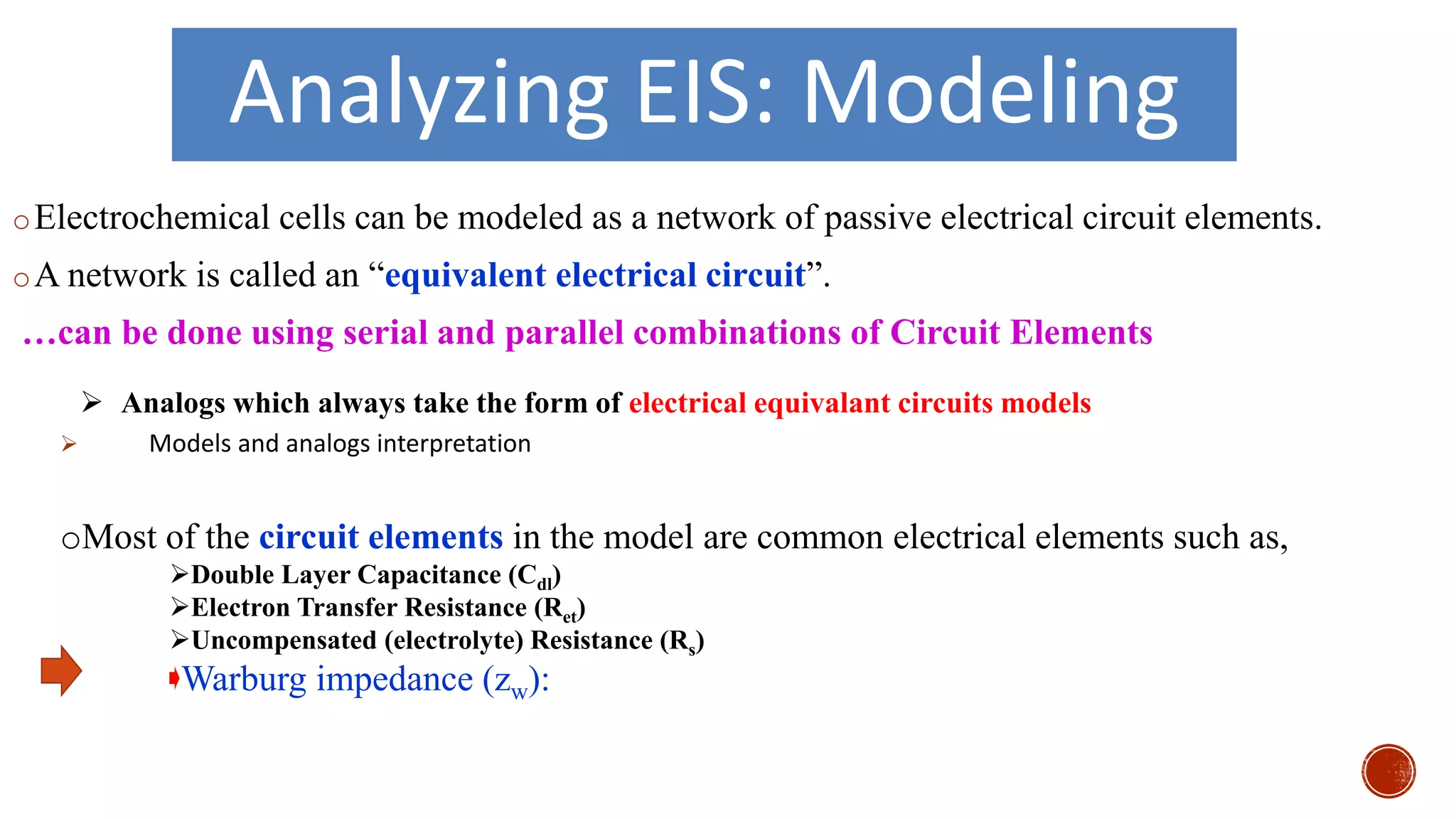
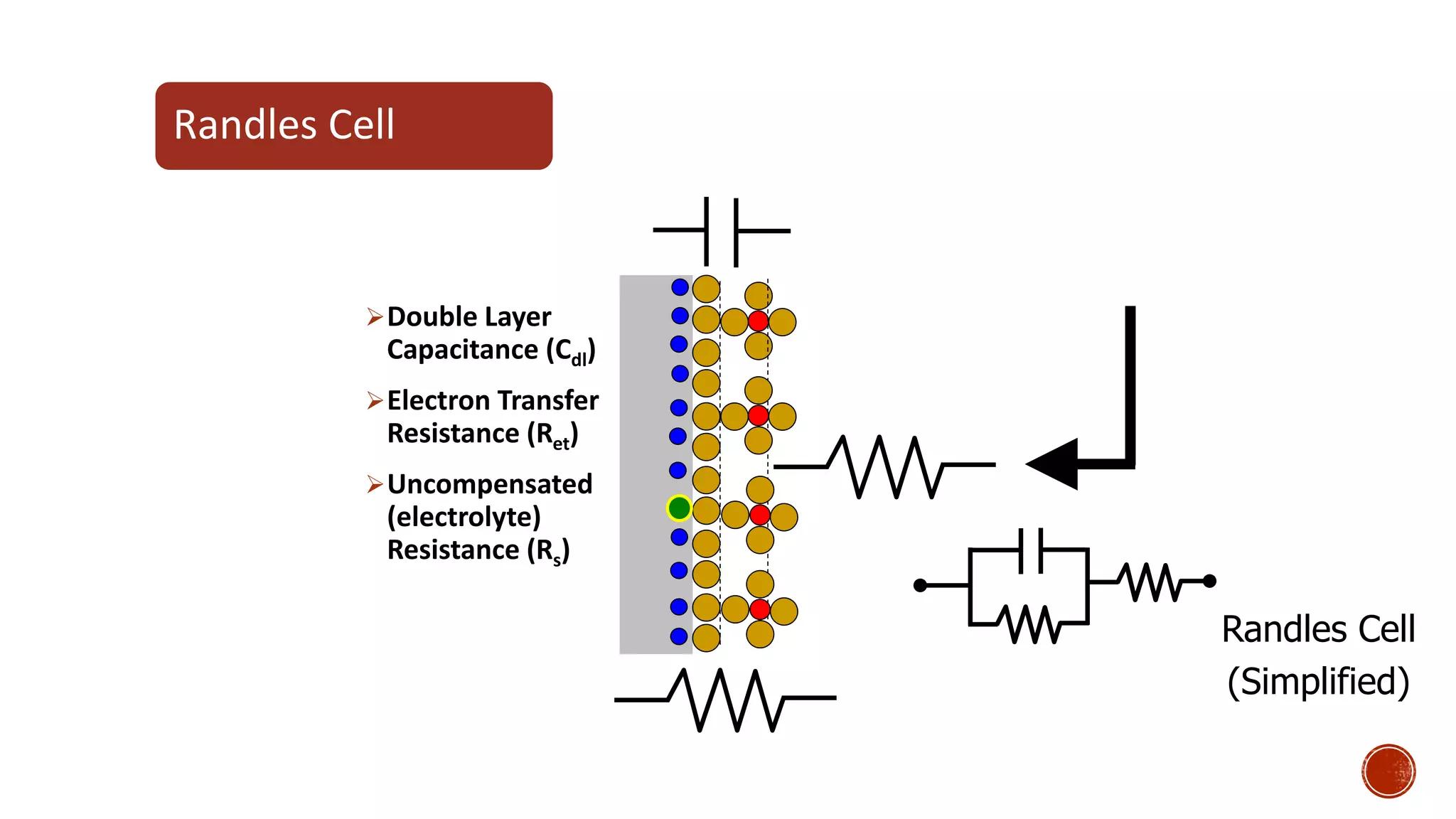
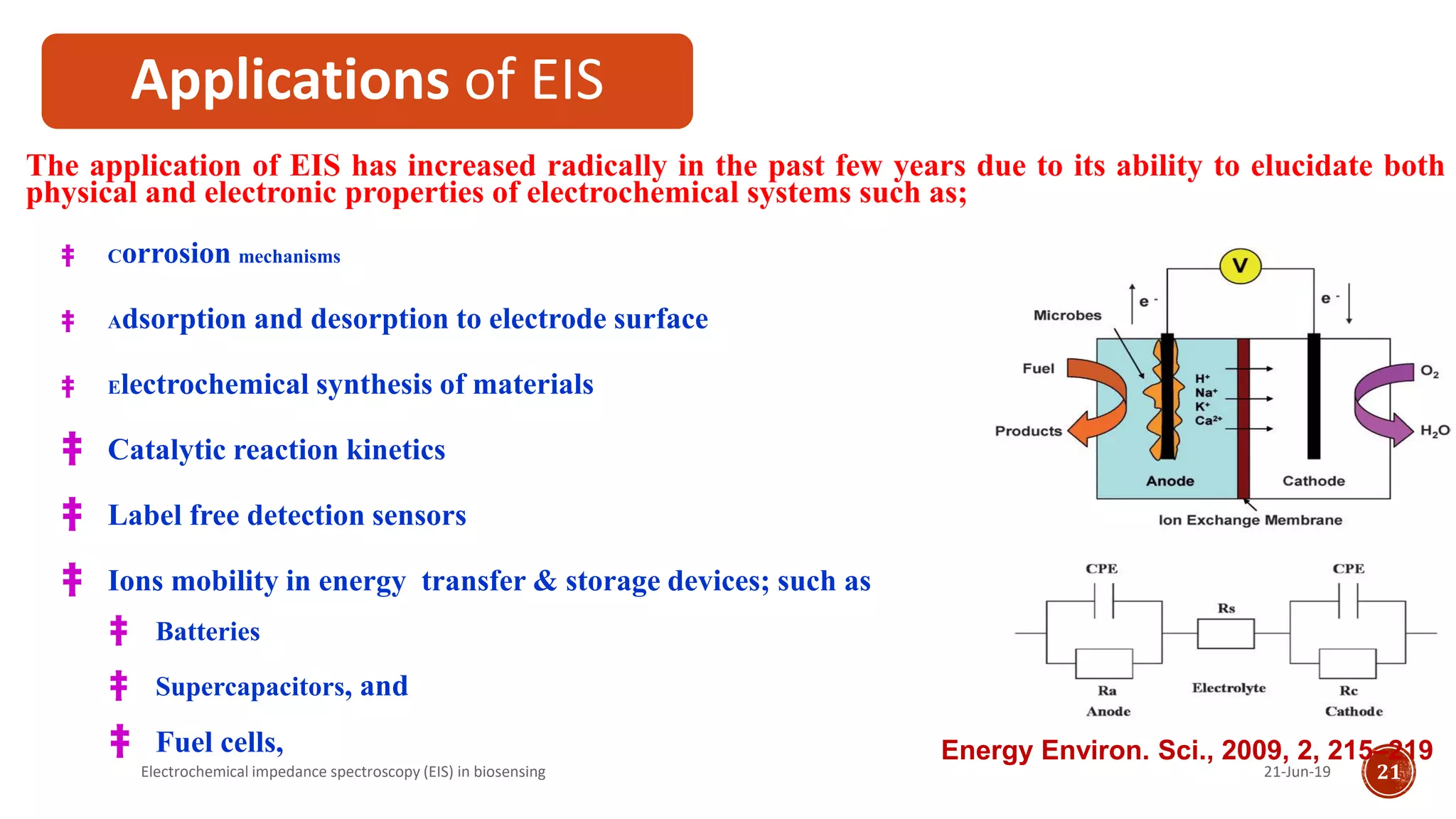
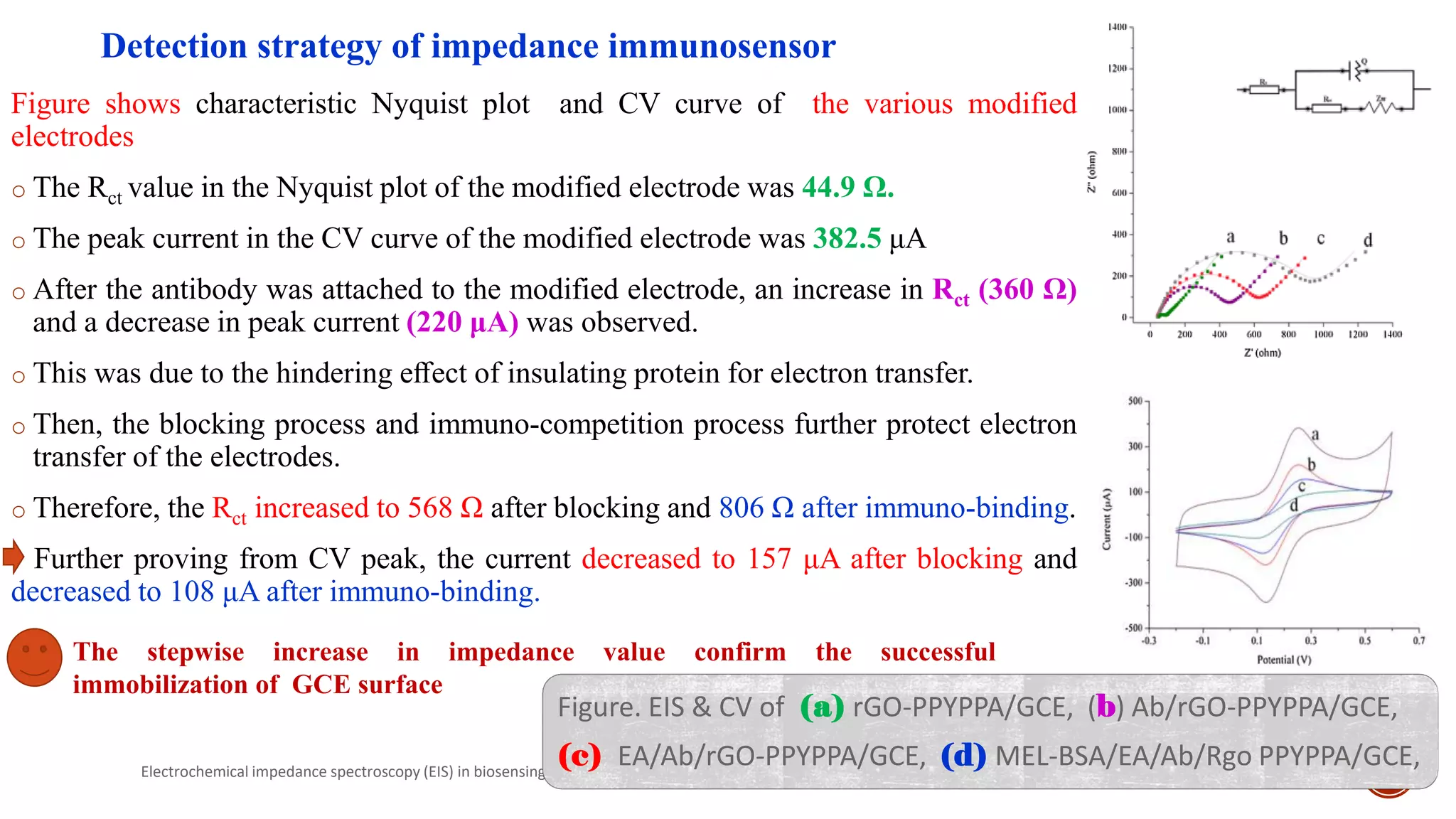
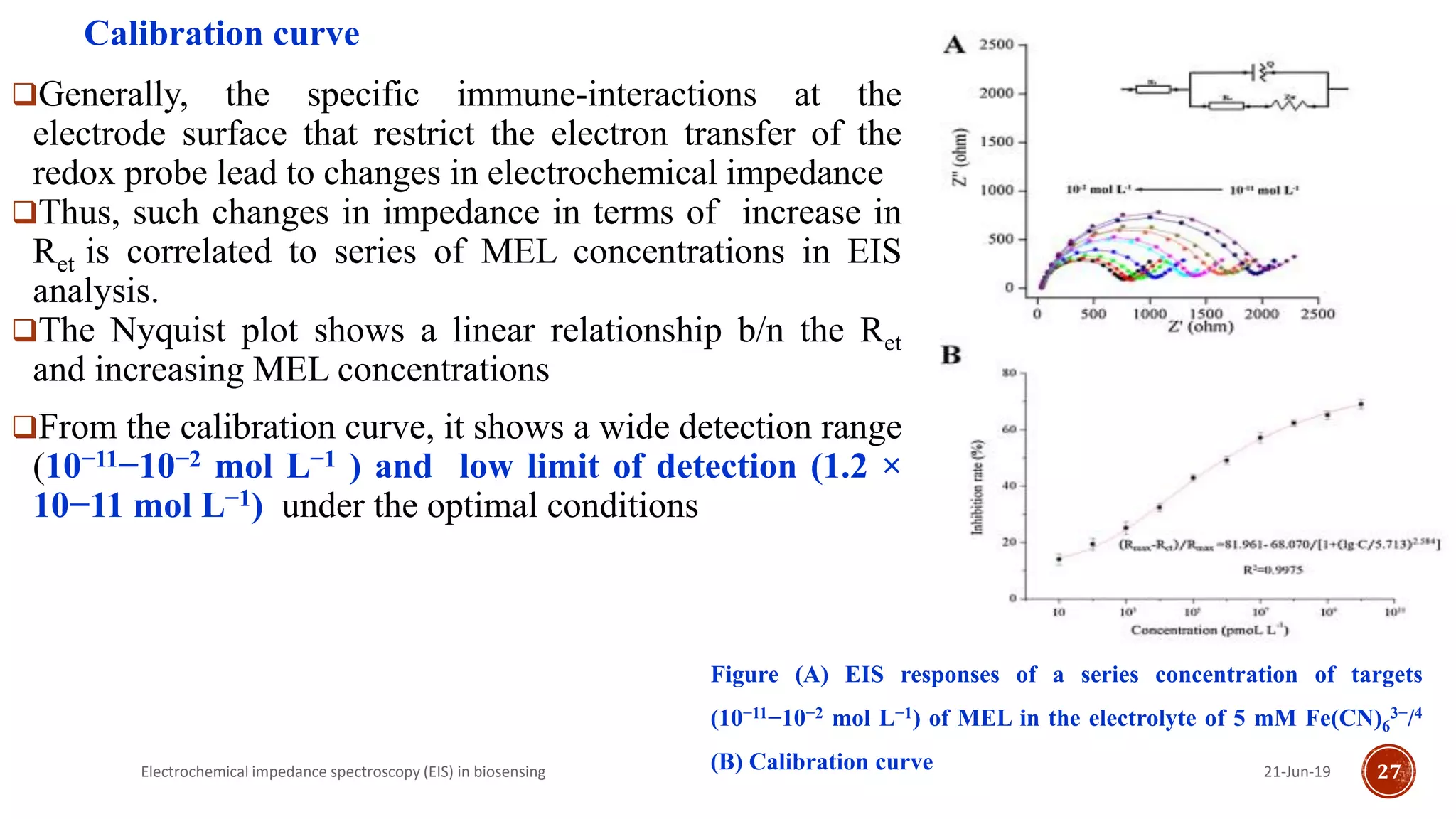
The document discusses electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) as a vital technique in biosensing, highlighting its principles, advantages, and applications in detecting binding events at electrode surfaces. EIS is praised for its high sensitivity and ability to analyze various biological and chemical targets, although it presents challenges such as expensive instrumentation and complex data analysis. Recent advancements in EIS technology have led to a surge in its use in biomedical applications, particularly in the detection of a range of analytes such as proteins and nucleic acids.


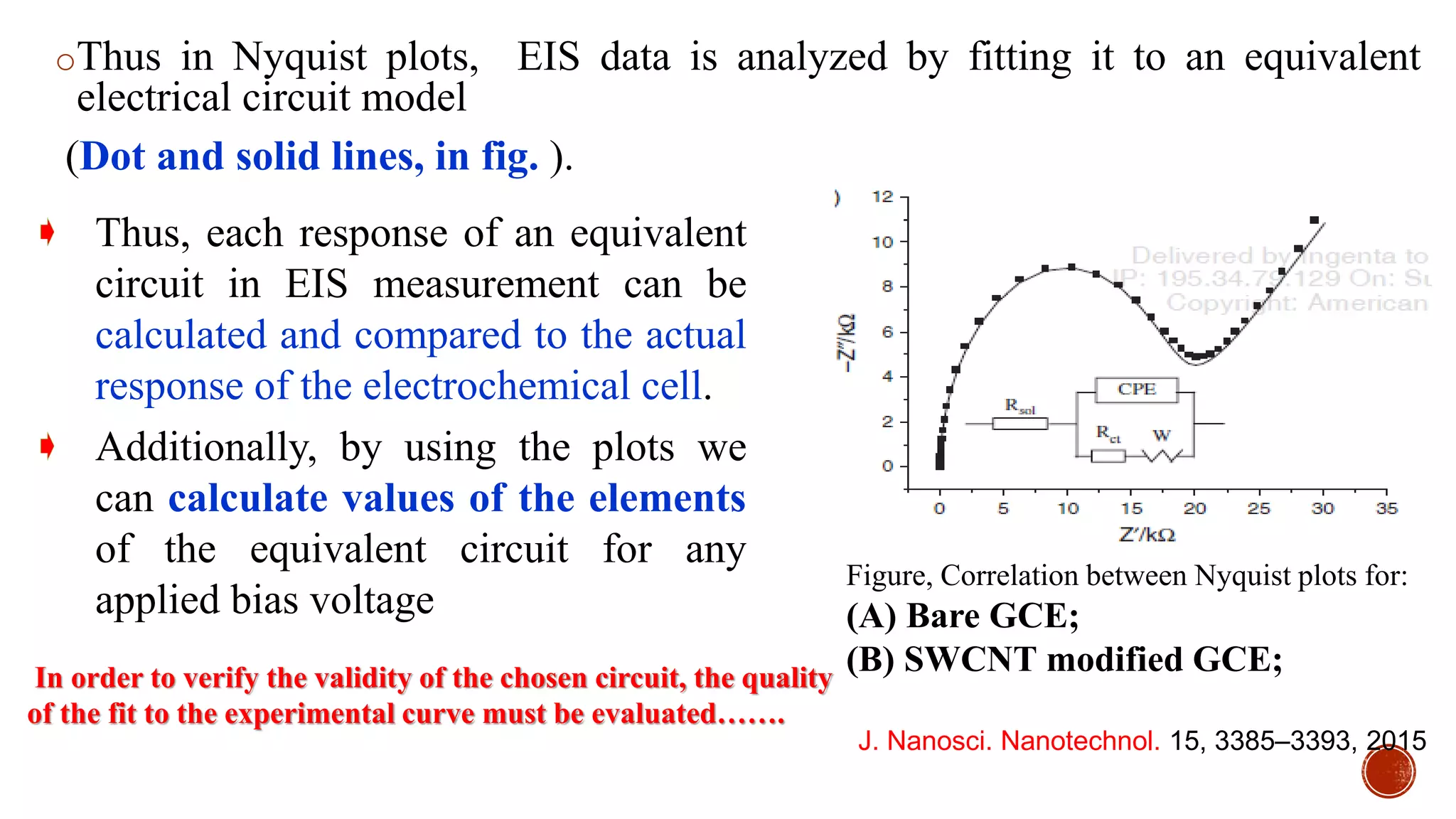



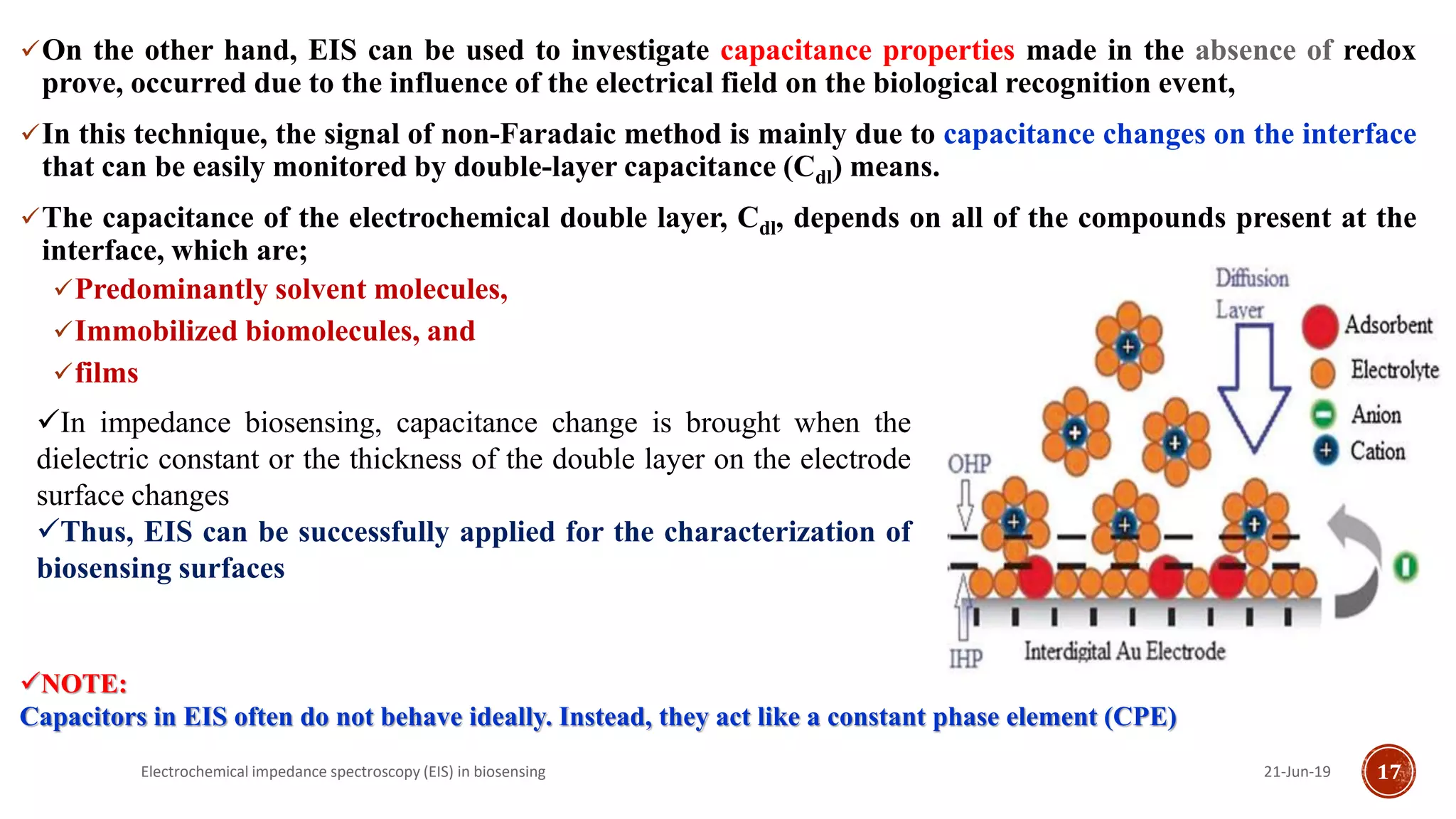
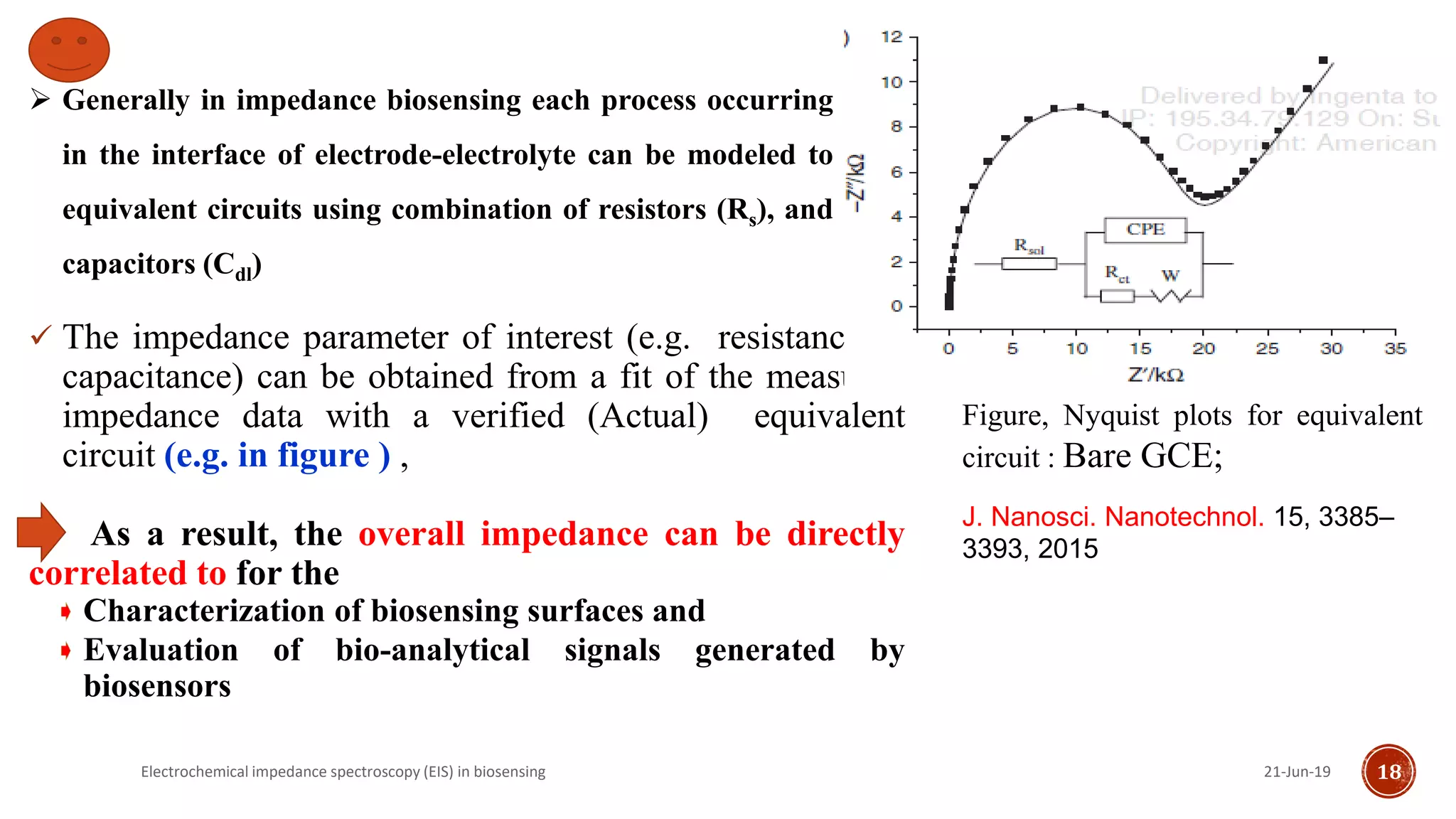
![Impedimetric immunosensors
It is a sensitive technique for label-free detection of antigen –
antibody binding
It is based on measurements of electrochemical faradaic
impedance in the presence of Fe(CN)6]3-/4- as a redox probe
In impedimetric immunosensors antibodies are immobilized on
the electrodes surface following the antigens is bound to form
immunocomplex
After immunocomplex formation, it create a barrier that prevents
(hinders) the redox probe from making contact with the electrode
surface
This results impedance changes due to electron transfer
resistance (Rct) changes that can be measured with the potentiotat
instrument.
Finally, the changes in electrochemical impedance can be
correlated to specific concentrations of target analyte
21-Jun-19Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in biosensing 23
Figure, Impedimetric immunosensors
Figure . Principle of the immunosensor
a) Bare ; (b) Electrode with antibody
immobilization; and (c) antibody bind with
Antigen](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eispptpresentationfinal-190621082409/75/Electrochemical-impedance-spectroscopy-EIS-23-2048.jpg)





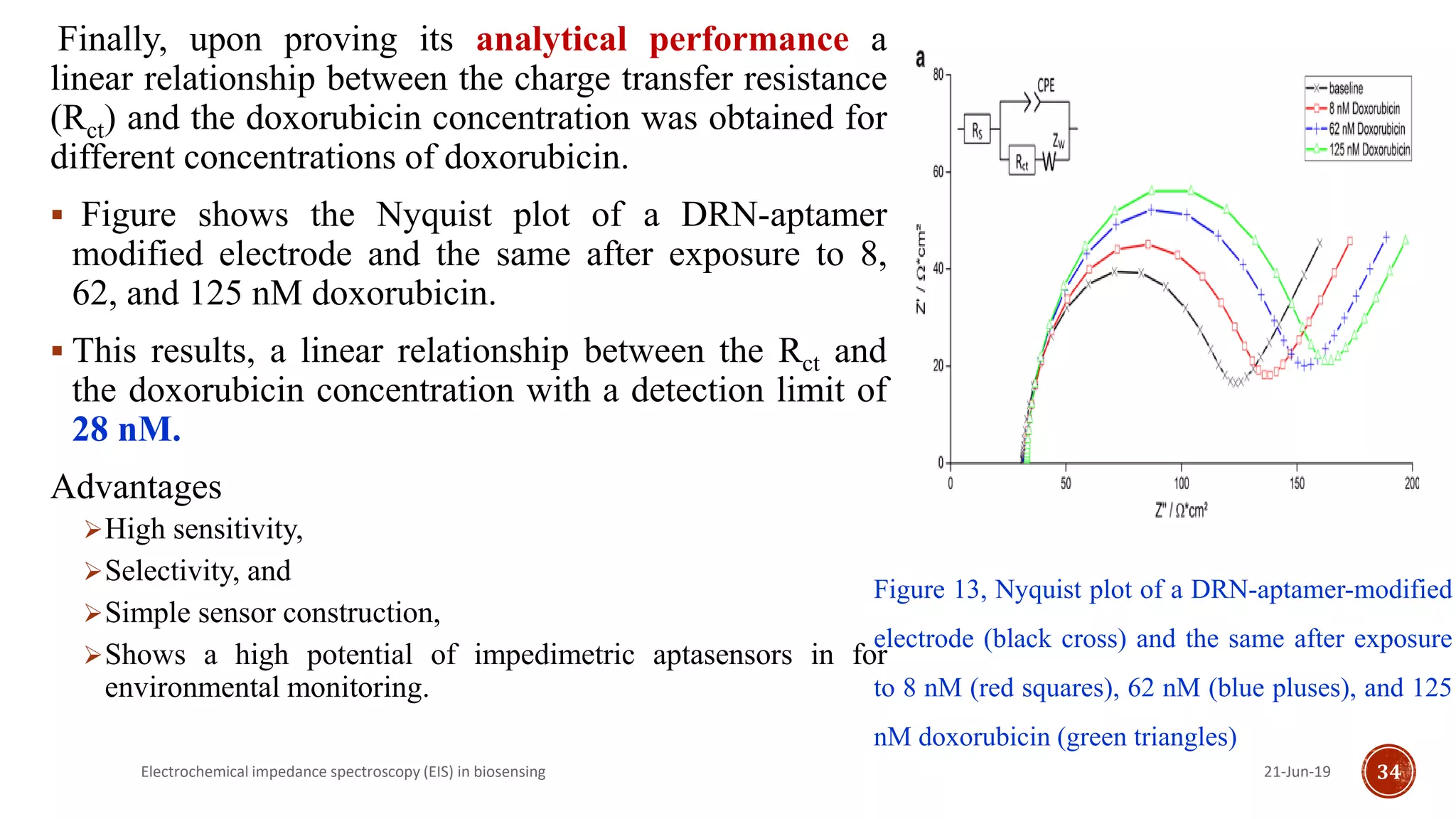
![ The change in impedance during the immobilization of the
DRN-aptamer was investigated by means of
electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS).
Upon binding of doxorubicin to the immobilized aptamer,
the impedance increases due to the hindrance of electron
transfer between electrode, and the redox probe of ferri-
/ferrocyanide [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-.
Fig.12 shows a comparison among, the impedance
spectrum of a
Bare (black cross),
DRN-aptamer-modified gold electrode (red plus) and
MCH-coated gold electrode (blue triangles)
21-Jun-19Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in biosensing 32
Figure 12, Nyquist plot of a blank (black cross) electrode, a DRN-aptamer-modified electrode (red plus),
and MCH-modified electrode (blue triangles) measured in FeBB – the colored solid lines represent the fits
to the equivalent circuit
daunorubicin-binding aptamer (DRN-aptamer)
6-Mercapto-1-hexanol (MCH, 99%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eispptpresentationfinal-190621082409/75/Electrochemical-impedance-spectroscopy-EIS-32-2048.jpg)