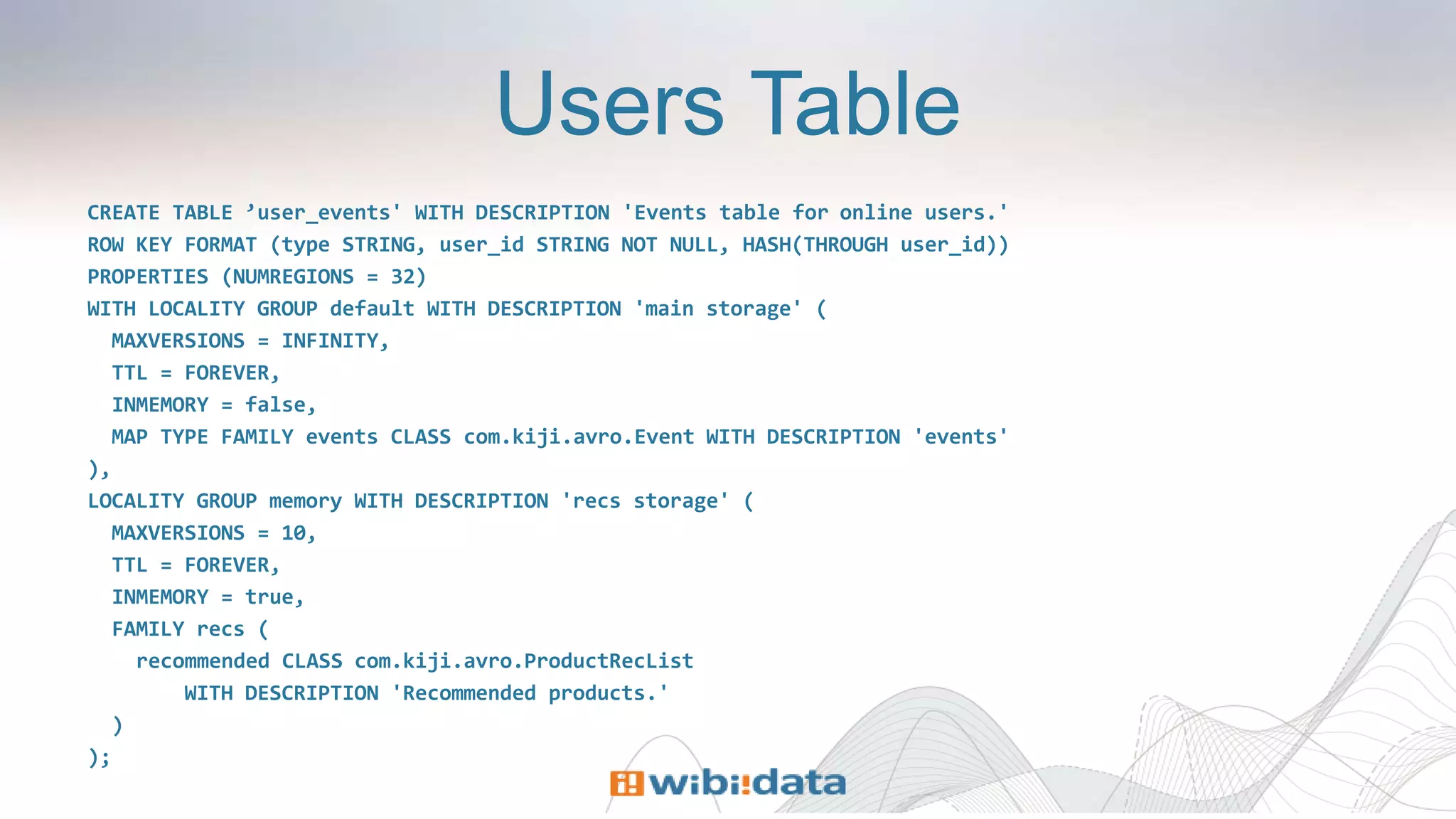
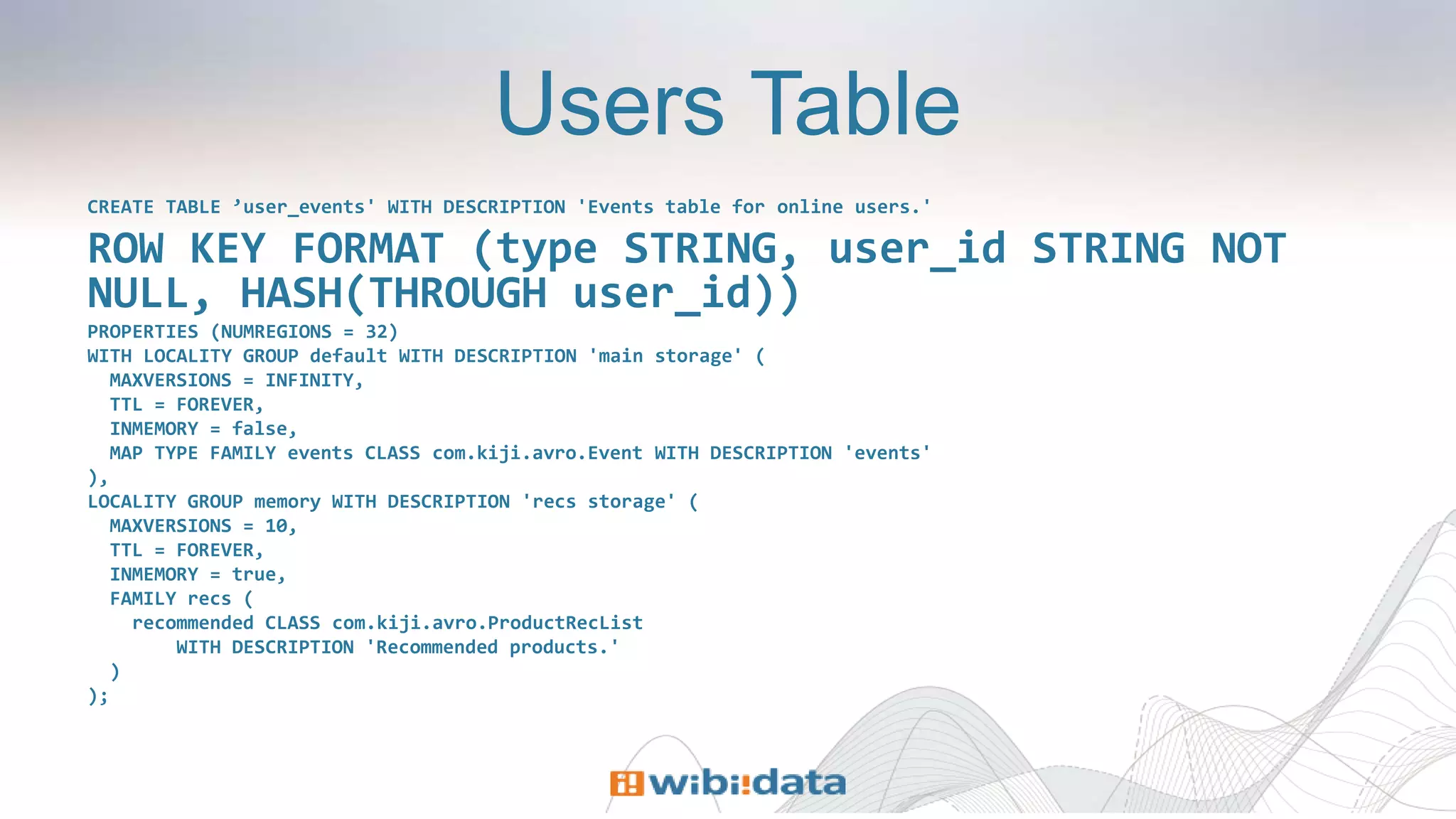
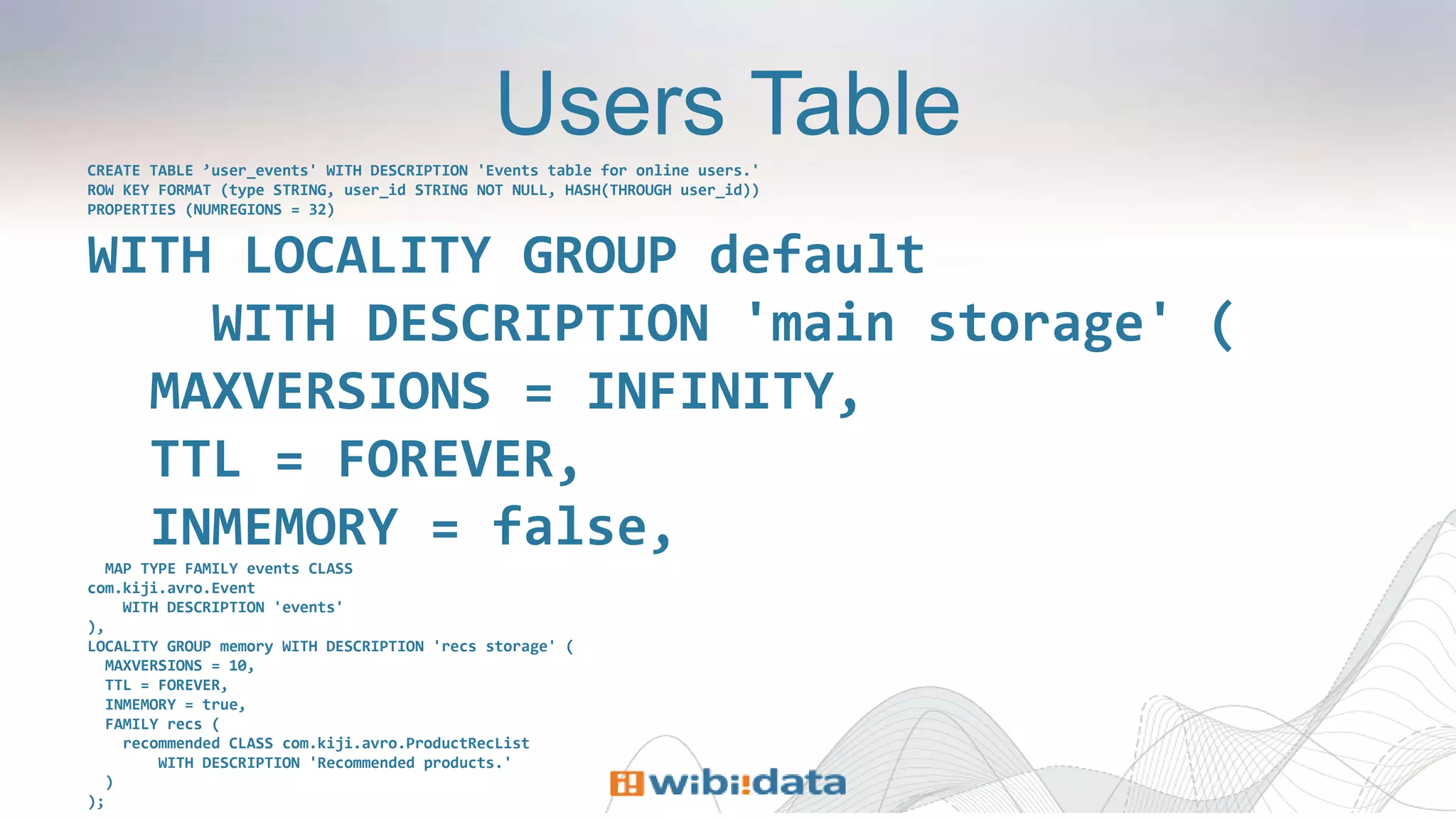
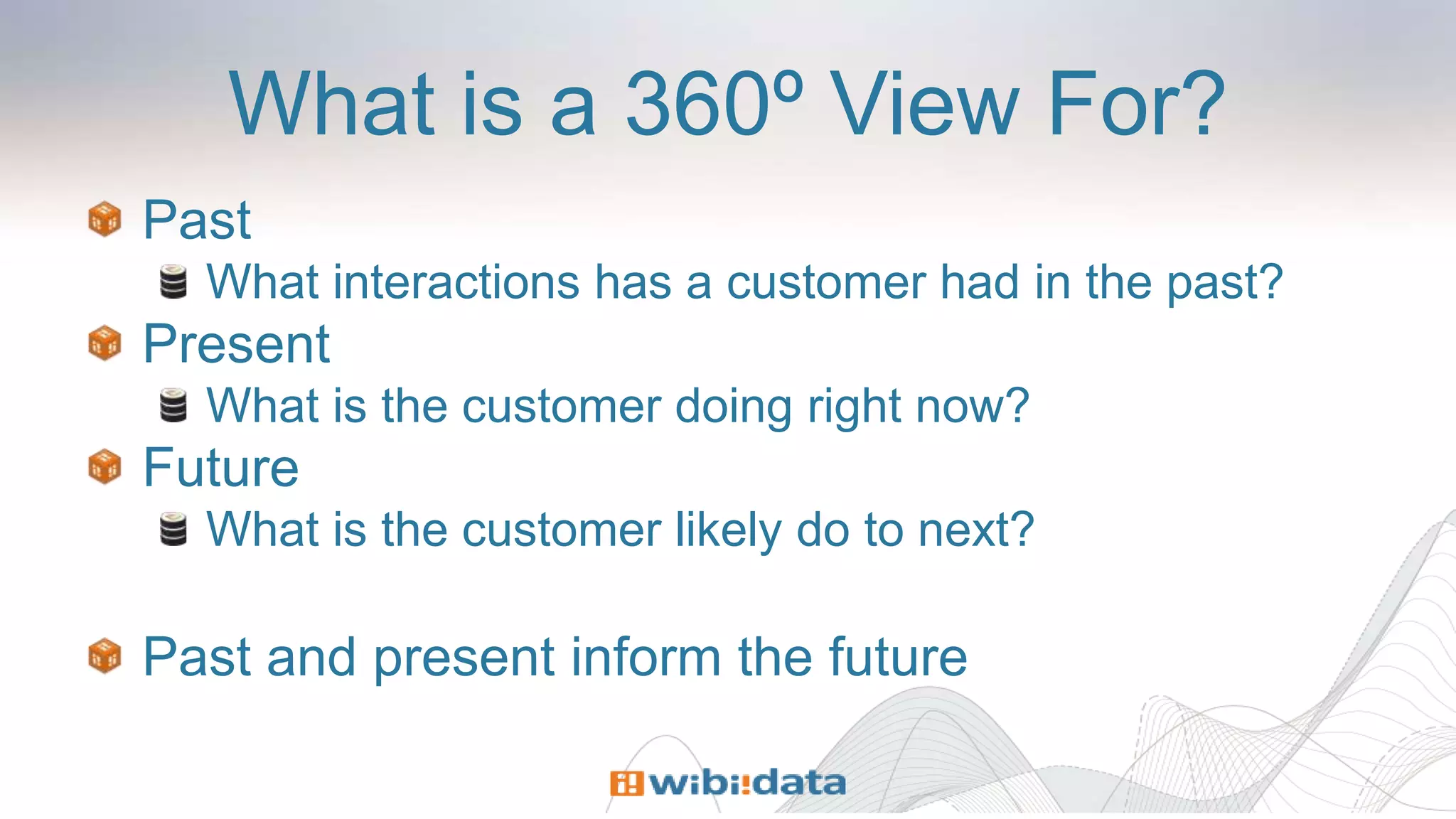
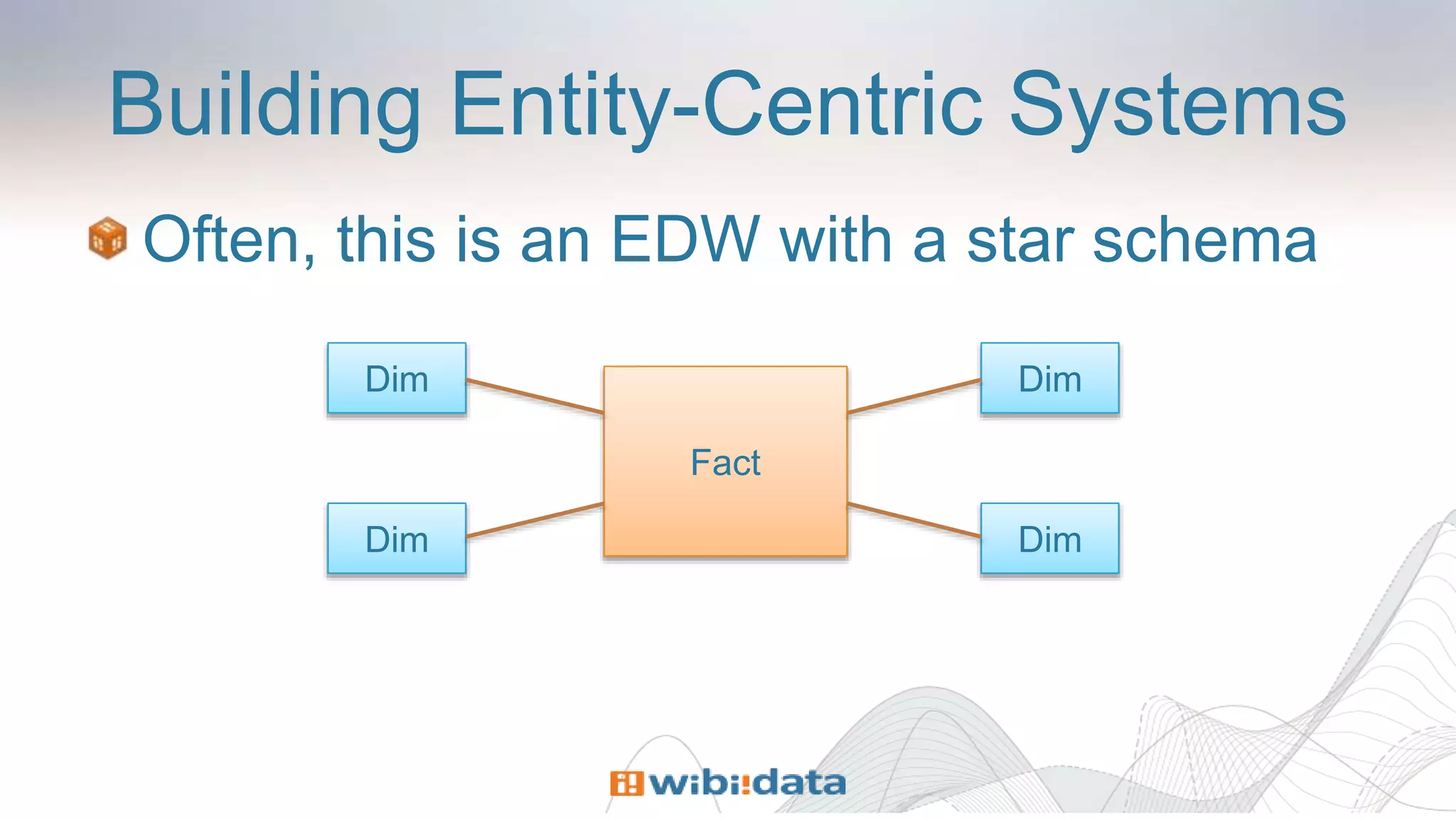
The document discusses designing entity-centric systems for achieving 360-degree views of customer interactions using HBase and Kiji, emphasizing the importance of storing both static and event-oriented data. It outlines the challenges of traditional star schemas and highlights the benefits of HBase, including improved performance for single-row lookups and flexibility in schema management. Additionally, it describes how to define row keys, handle known users, store event series, and evolve entity-centric systems over time.











![Choosing a Row Key
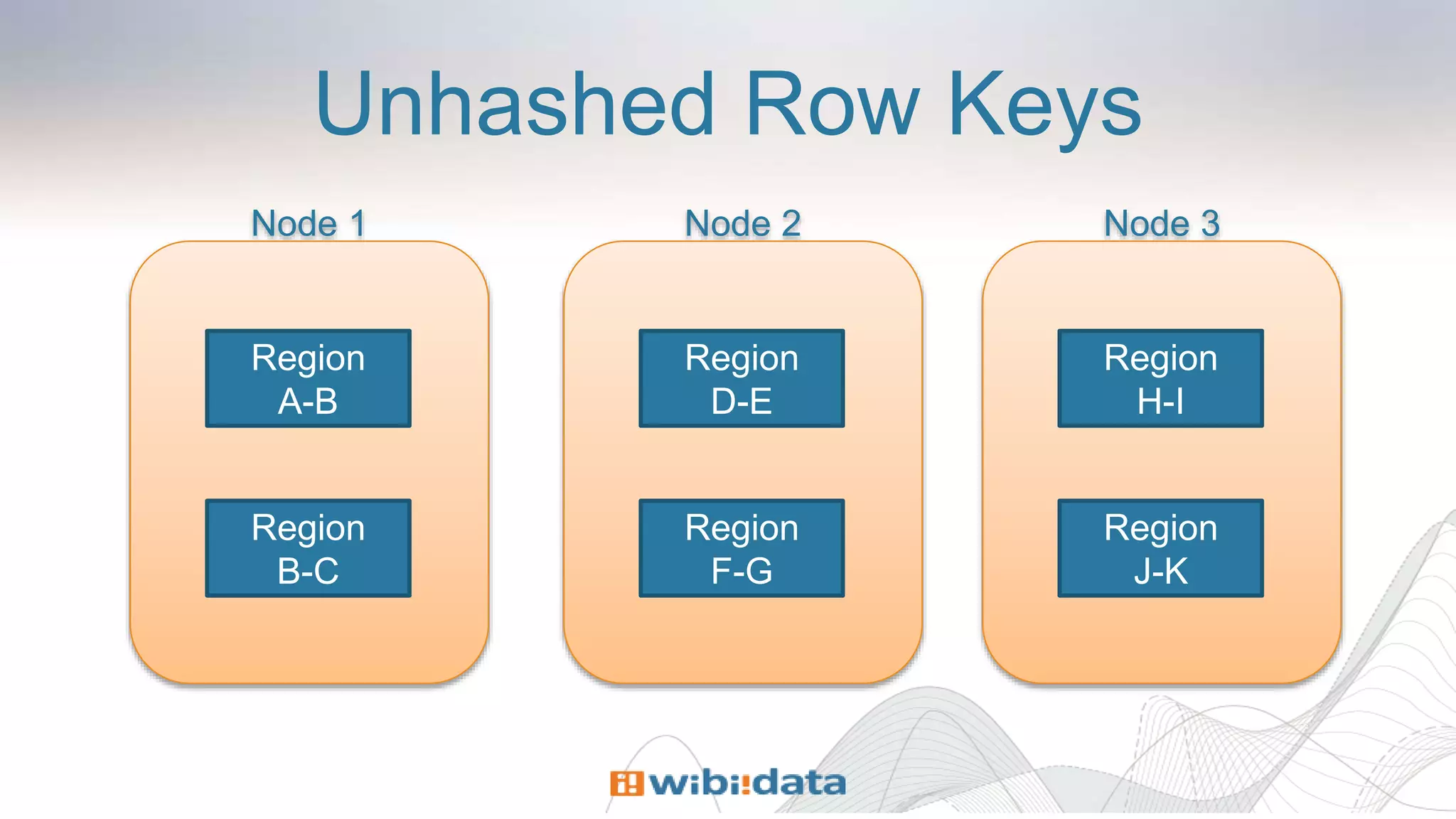
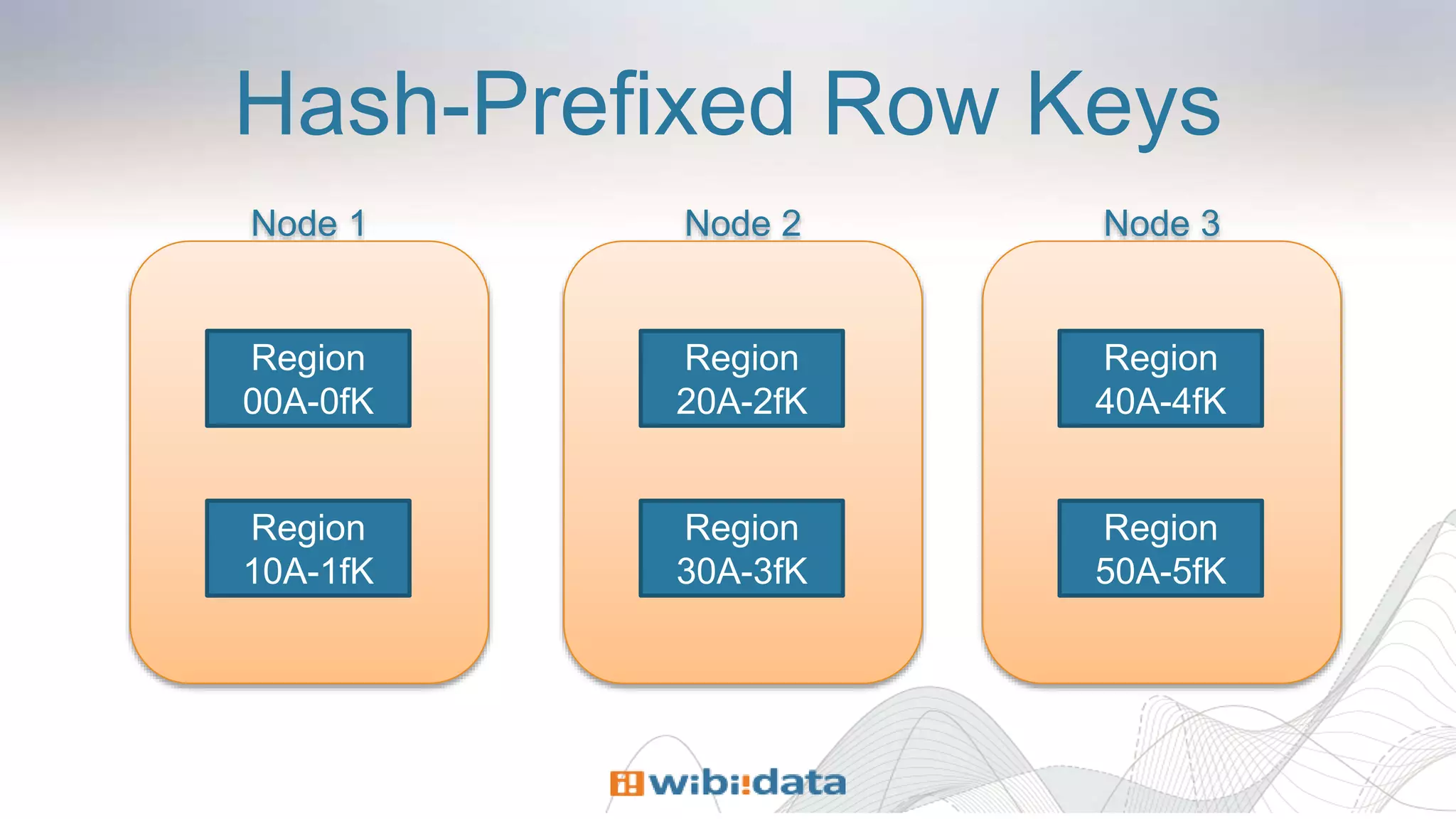
Row keys in Kiji are componentized
[ ‘component1’, ‘component2’, 1234 ]
More efficient than byte arrays
Consider ‘1234567890’ versus [ 1234567890 ]
Good for scanning areas of the keyspace](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecosystem-session4-140616155127-phpapp02/75/Design-Patterns-for-Building-360-degree-Views-with-HBase-and-Kiji-19-2048.jpg)
![A Common Use for
Components
Known users IDs versus unknown IDs
On a website, how do you differentiate
between a logged-in or cookie’d user versus a
brand new visitor
[ ‘K’, ‘user1234’ ] or [ ‘U’, ‘unknown2345’ ]
Physically and logically separate rows
Run jobs over all known or unknown users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecosystem-session4-140616155127-phpapp02/75/Design-Patterns-for-Building-360-degree-Views-with-HBase-and-Kiji-20-2048.jpg)