1) Eccentric connections experience both direct axial forces and bending moments due to eccentric loads. This results in more complex stress distributions compared to concentric connections.
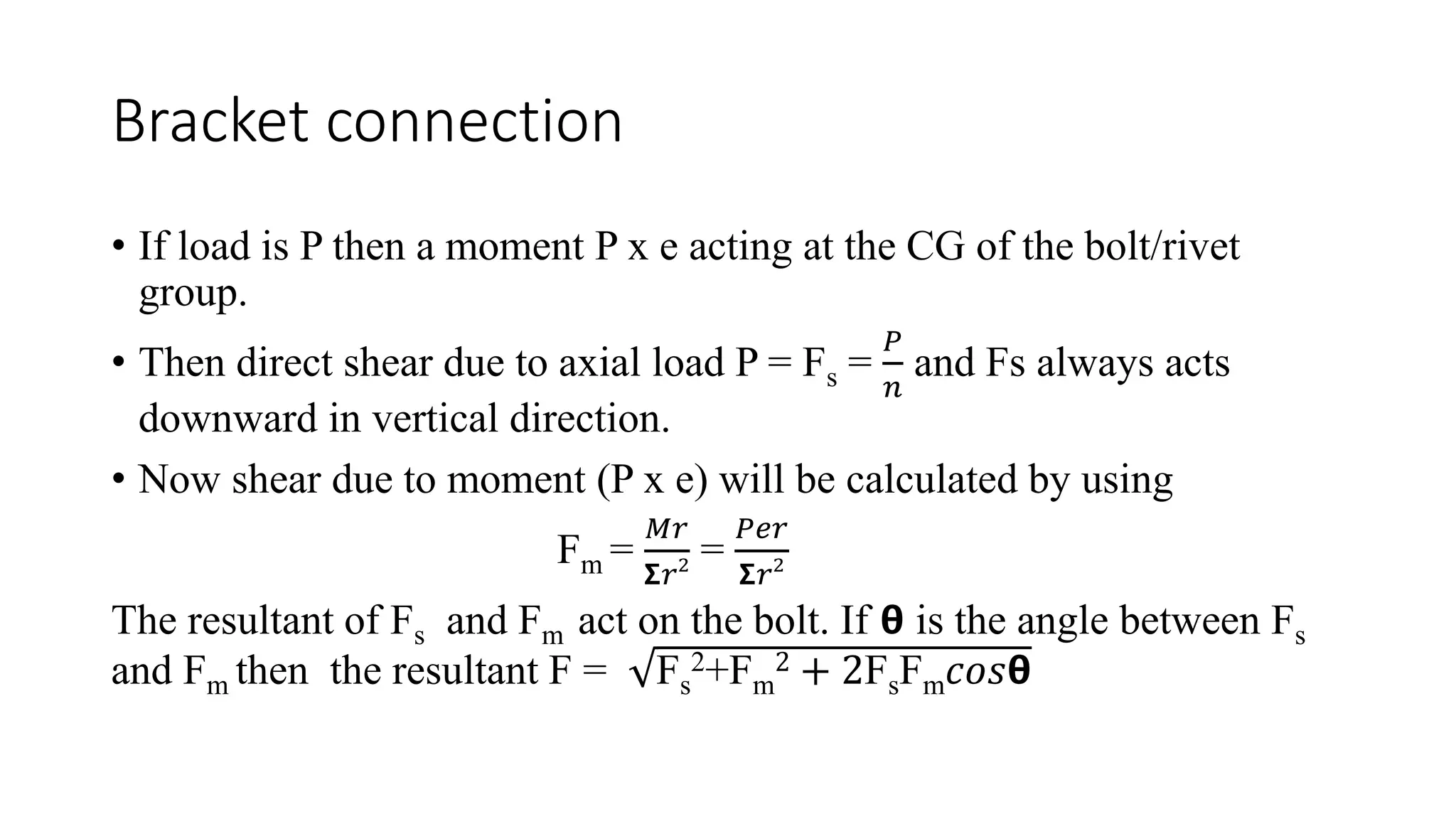
2) For bracket connections with eccentric loads, the direct shear stress and bending stress due to the moment must be calculated and combined using the Pythagorean theorem.
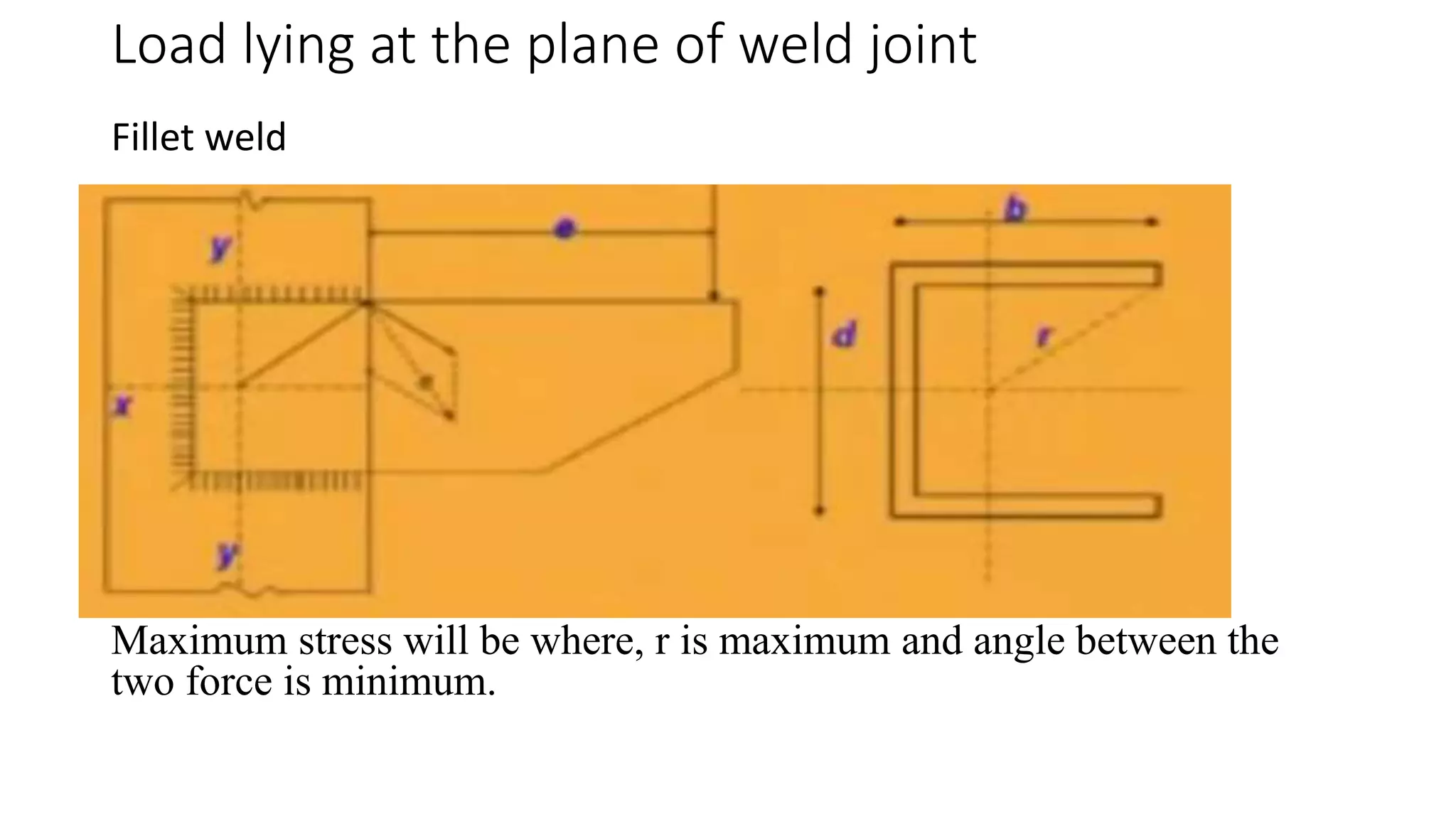
3) For welded joints with eccentric loads, both the direct shear stress and bending stress in the weld must be determined and combined, considering the weld geometry, load magnitude and eccentricity. The resultant stress must satisfy allowable stress criteria.