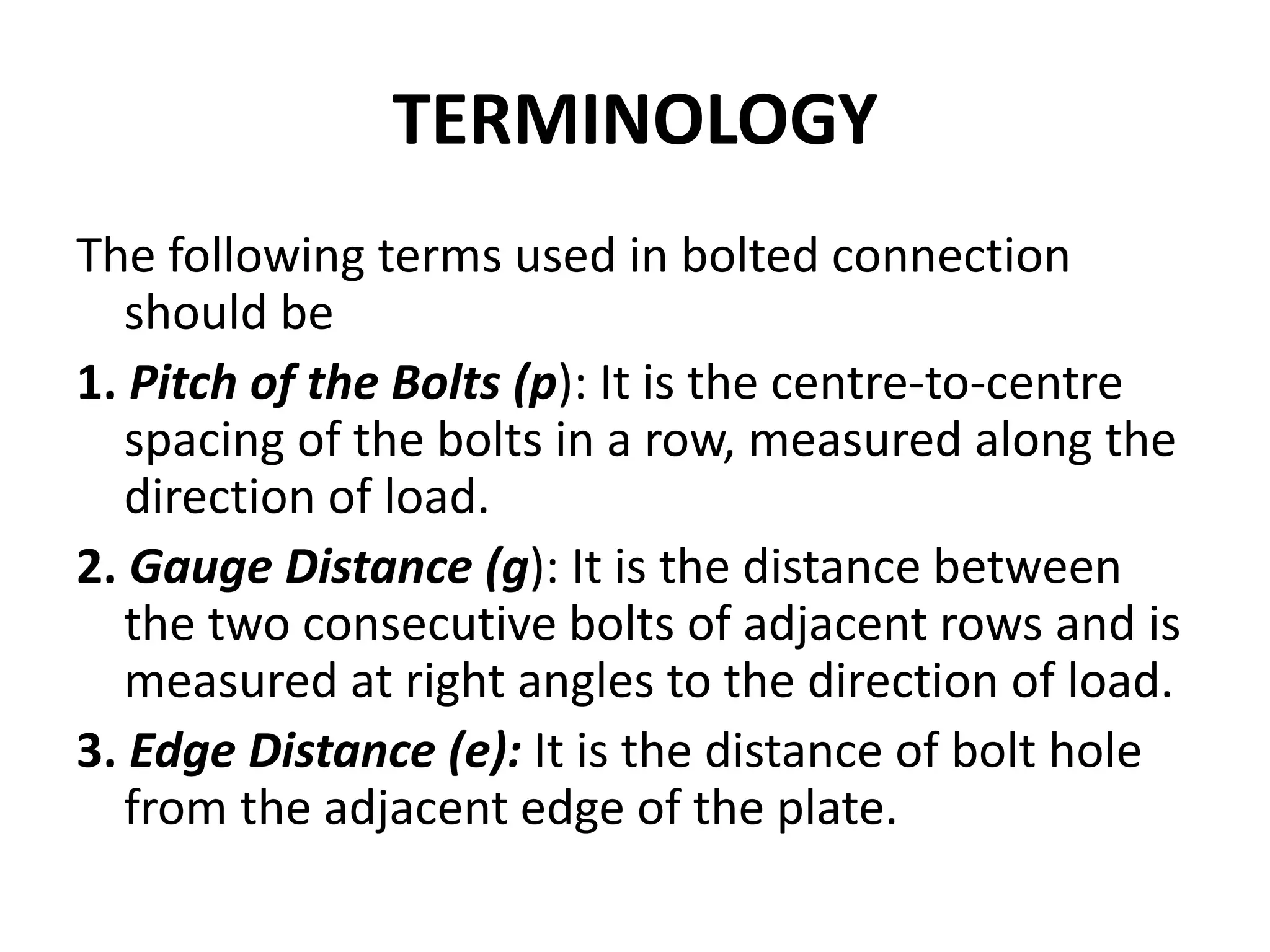
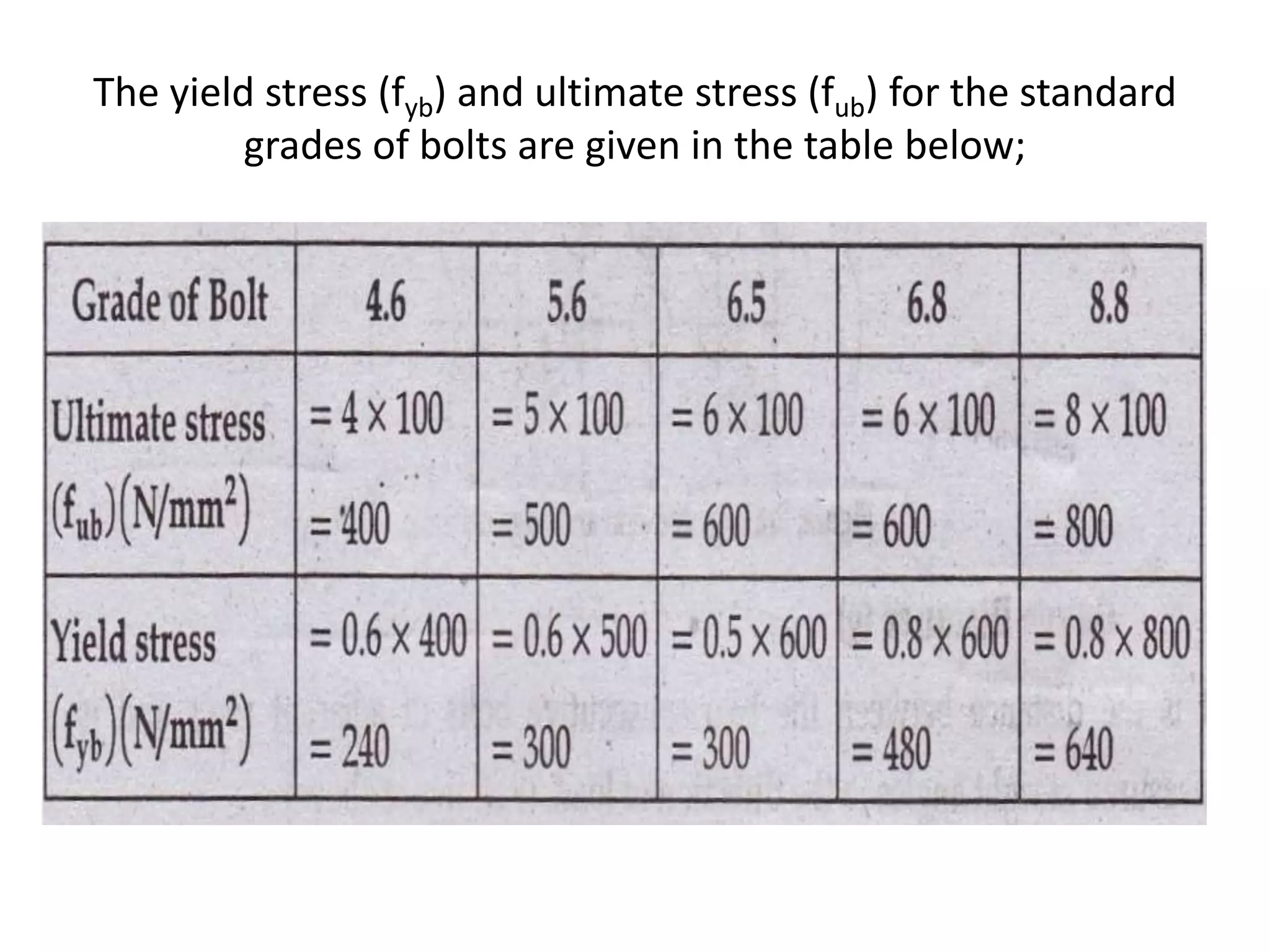
This presentation summarizes different types of bolted connections. It discusses bearing bolts, which can be unfinished or finished. Unfinished bolts have rough shanks while finished bolts have circular shanks from turning. It also defines terminology used in bolted connections like pitch, gauge distance, and edge distance. Finally, it discusses grade classifications for bolts based on their strength and specifies requirements for bolted connections according to Indian codes and standards, distinguishing between lap joints and butt joints.