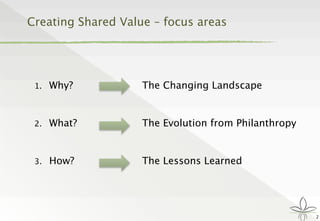
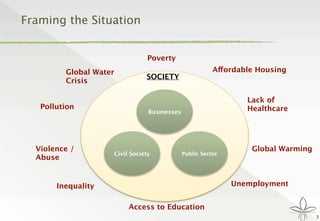
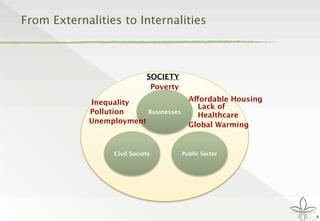
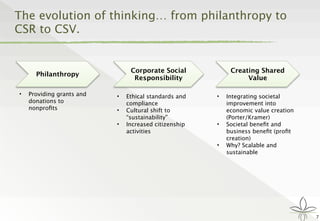
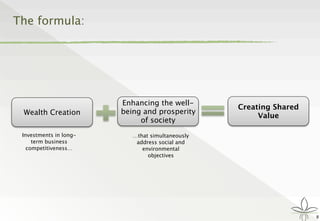
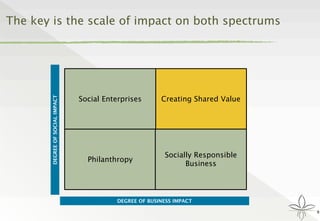
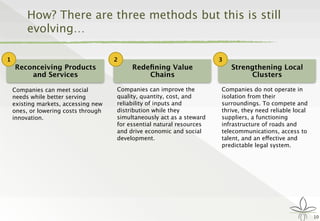
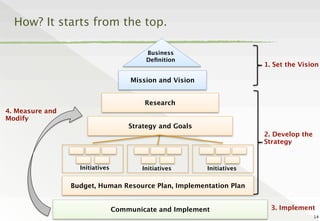
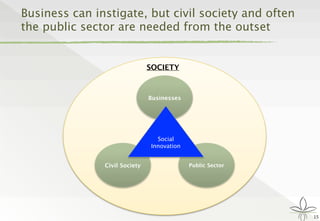
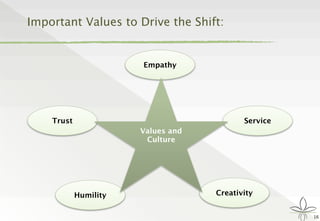
The document discusses the transition from traditional philanthropy to the concept of Creating Shared Value (CSV), emphasizing the integration of societal improvement into economic value. It highlights the need for businesses to adapt their strategies to address social and environmental challenges while creating profit, calling for collaboration with civil society and the public sector. The key takeaway is the importance of empathy, partnerships, and a commitment to redefining business goals to achieve both social and economic outcomes.