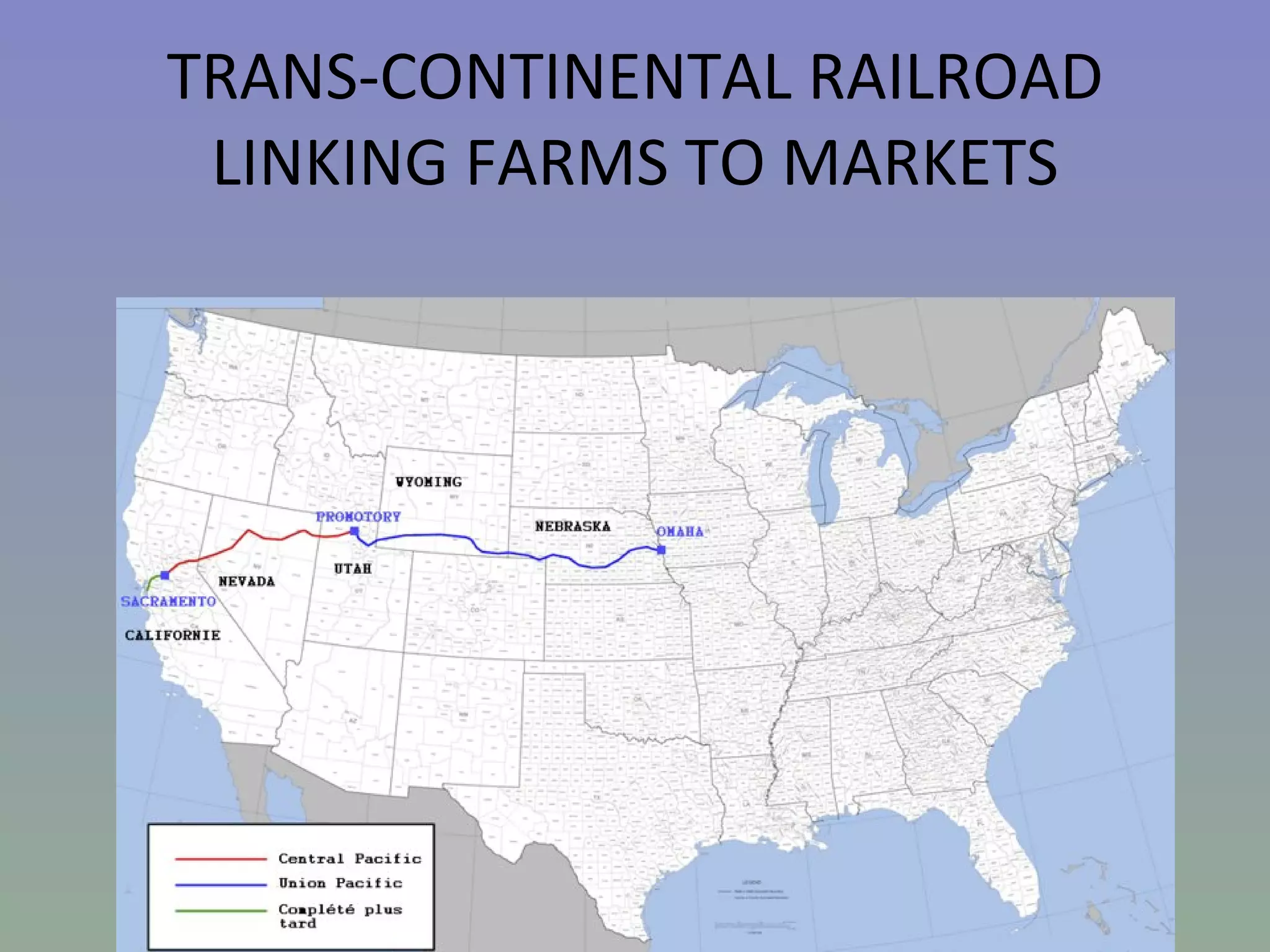
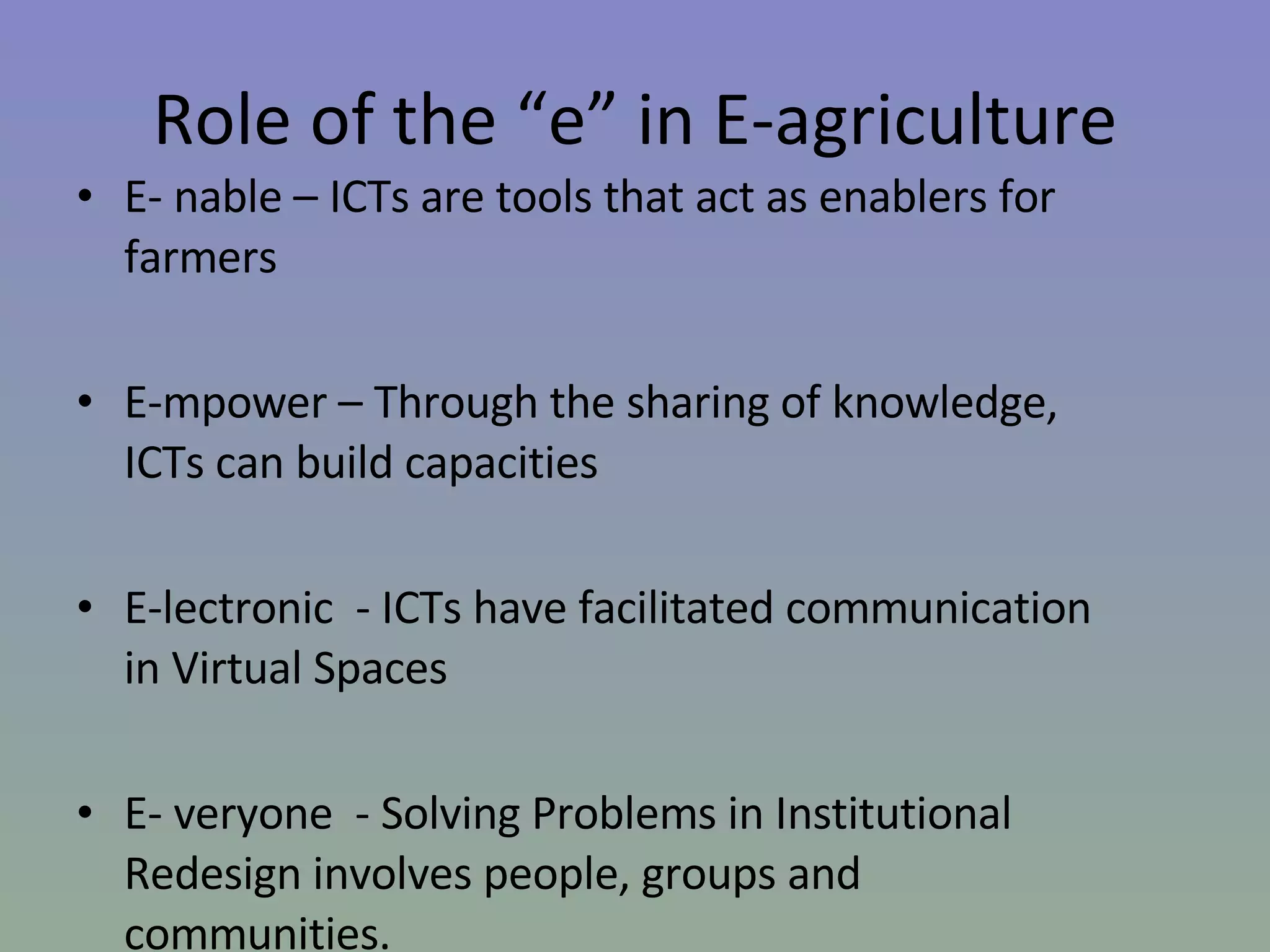
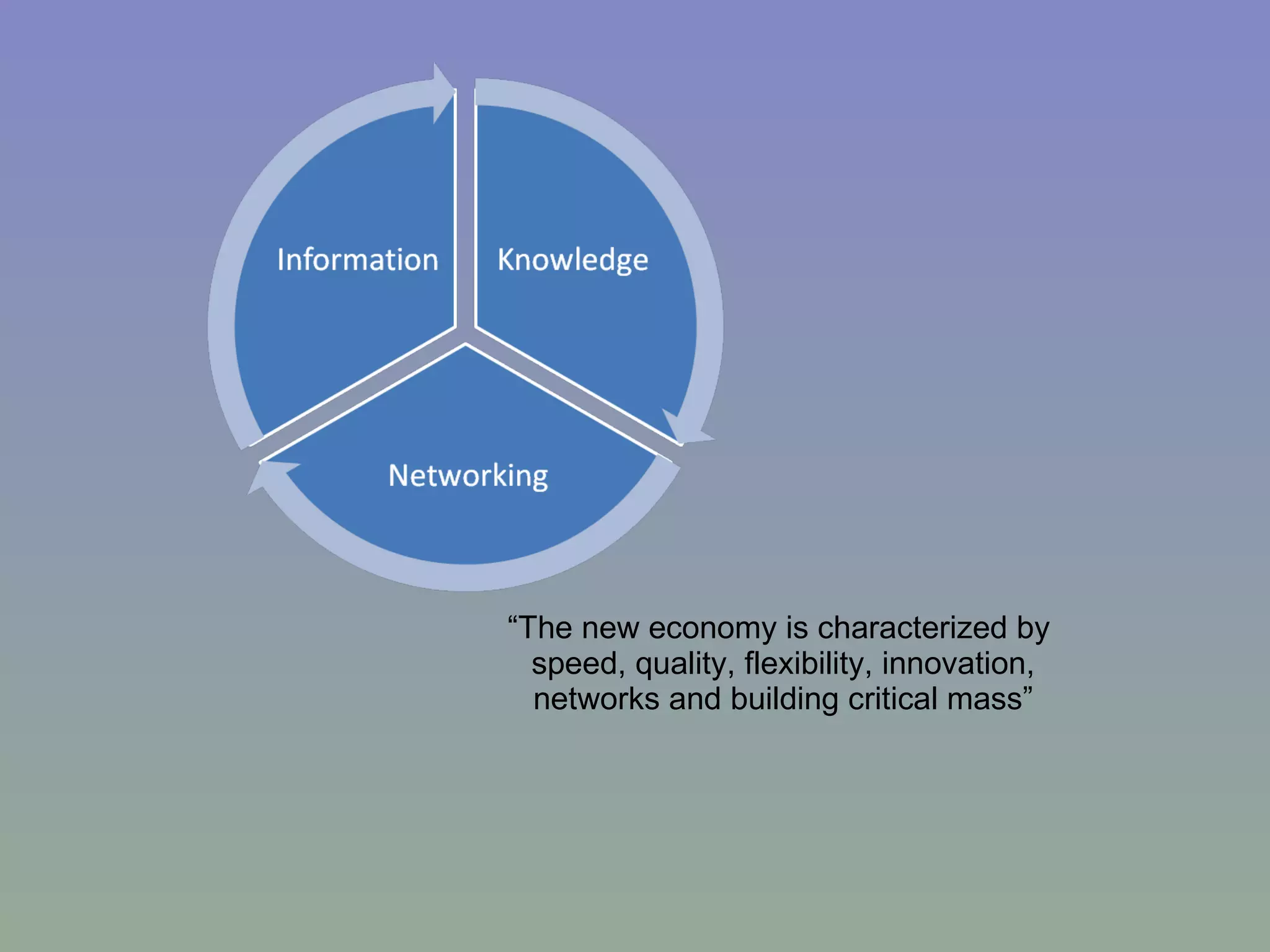
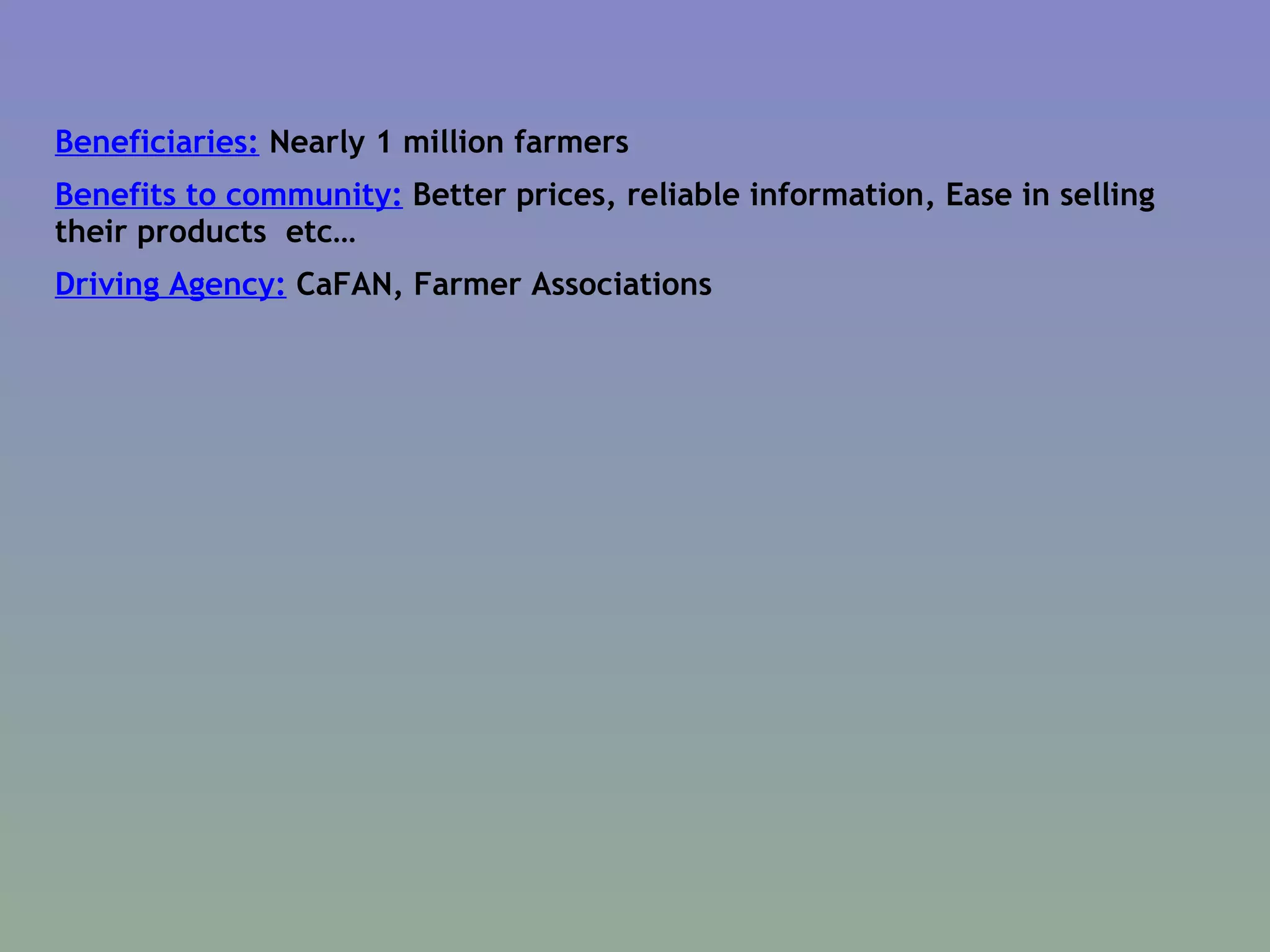
The document discusses the evolution of agricultural technology from historical innovations like the steel plough and windmill to contemporary ICT solutions for farmers, emphasizing their role in enhancing agricultural productivity and market access. It also highlights various initiatives across the Caribbean and other regions that leverage digital technology to empower rural farmers by providing timely information and improving communication networks. Key themes include the need for community involvement, public-private partnerships, and adapting to a rapidly changing socio-economic landscape driven by innovation.