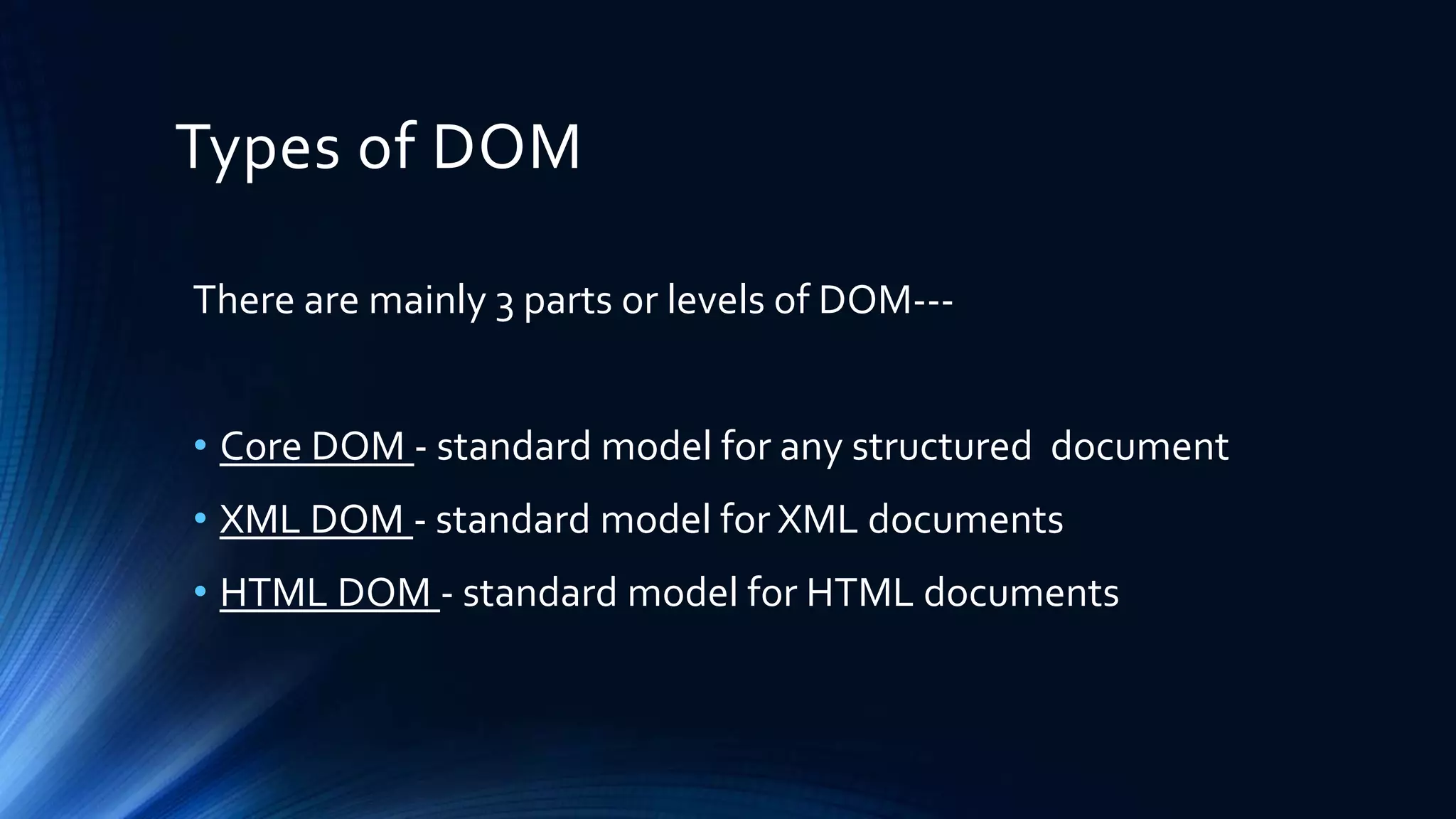
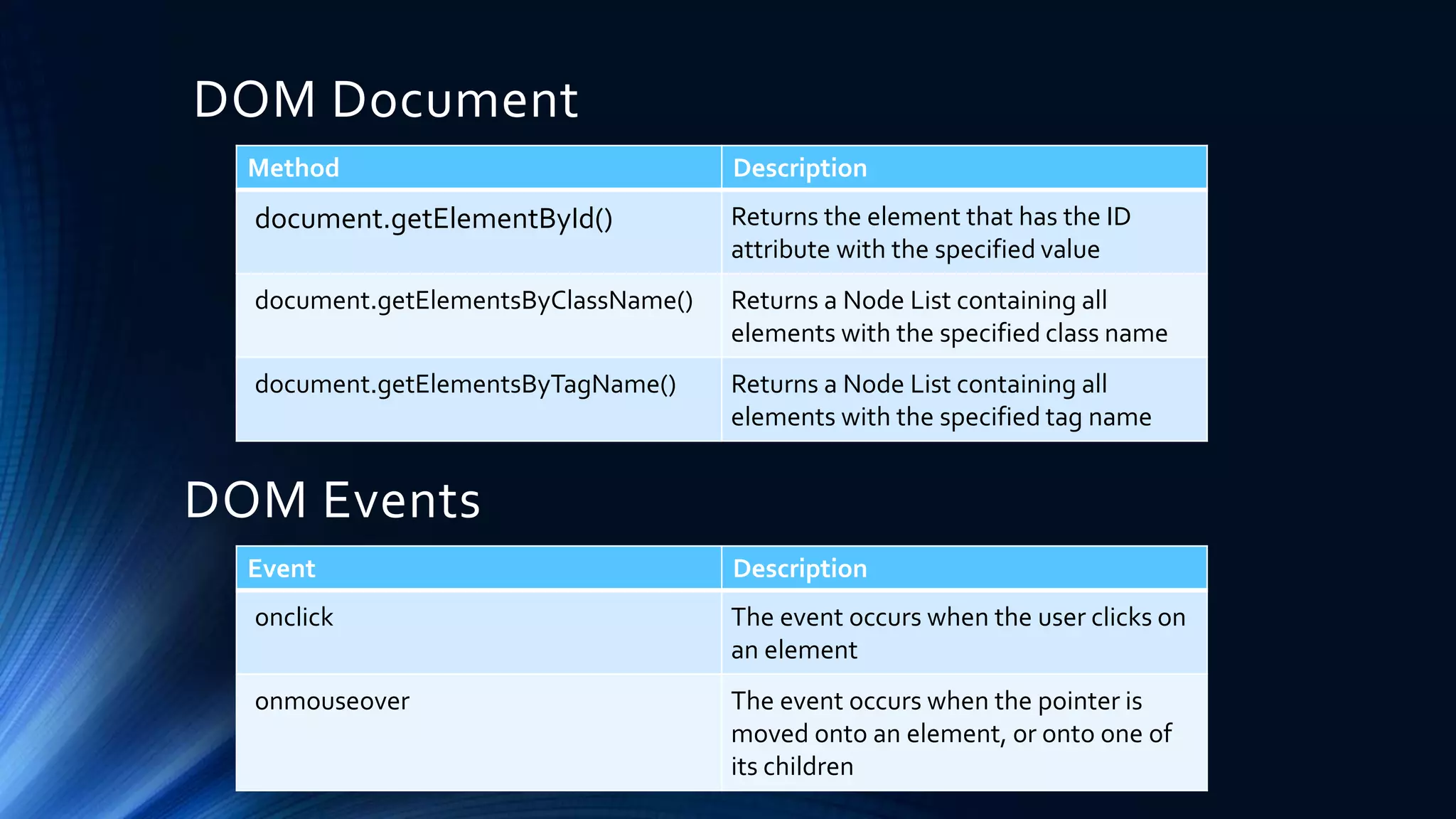
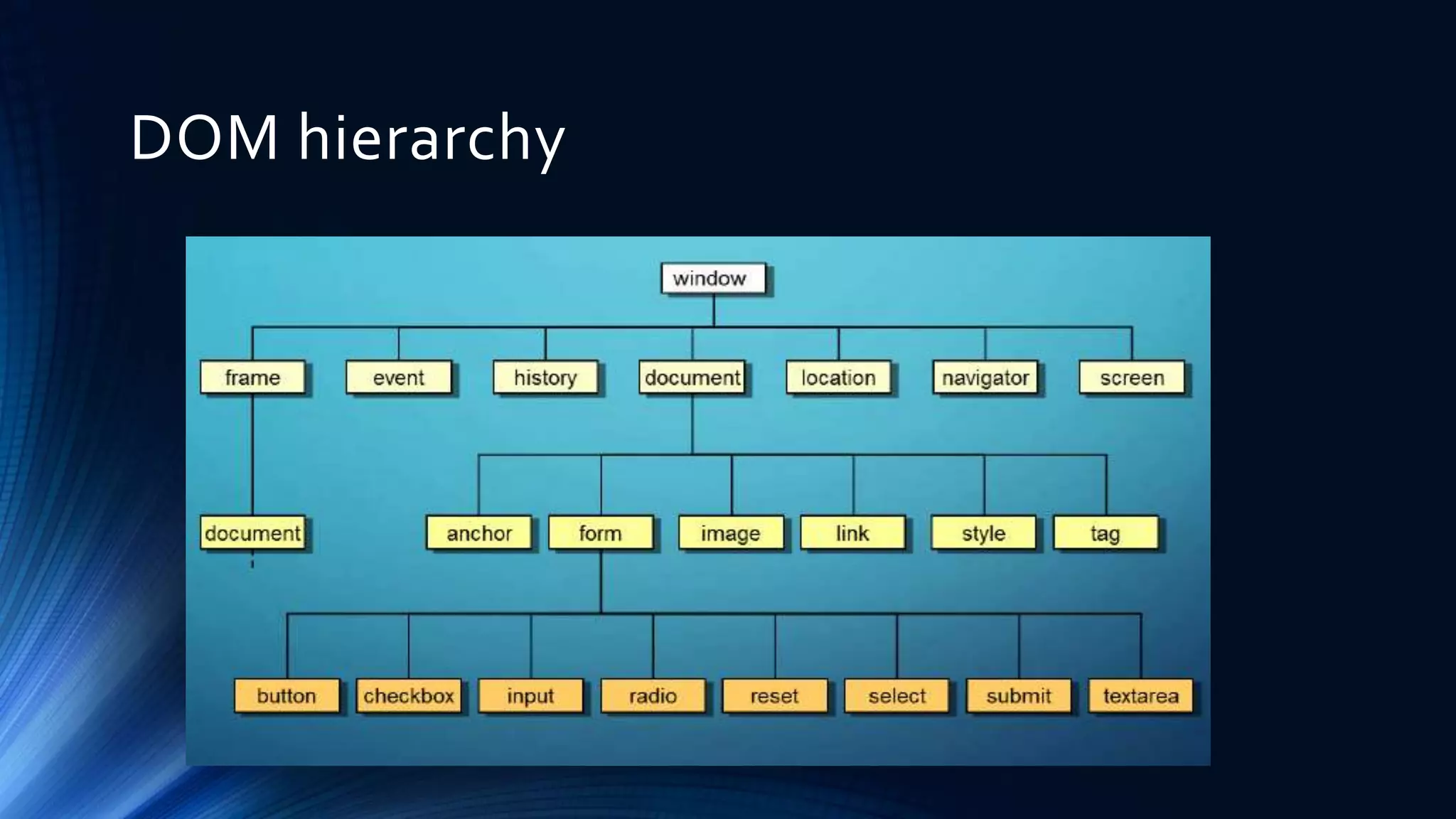
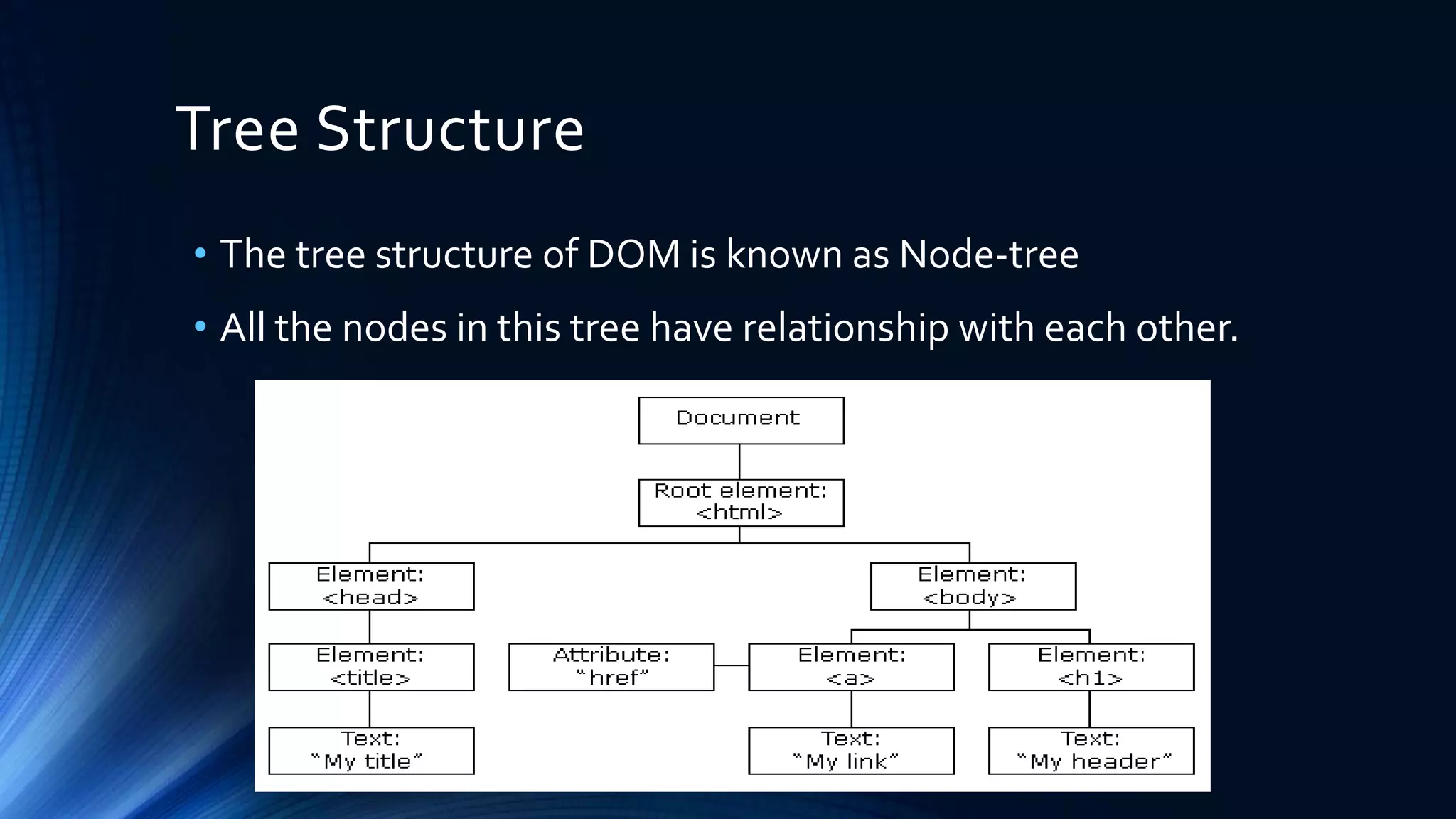
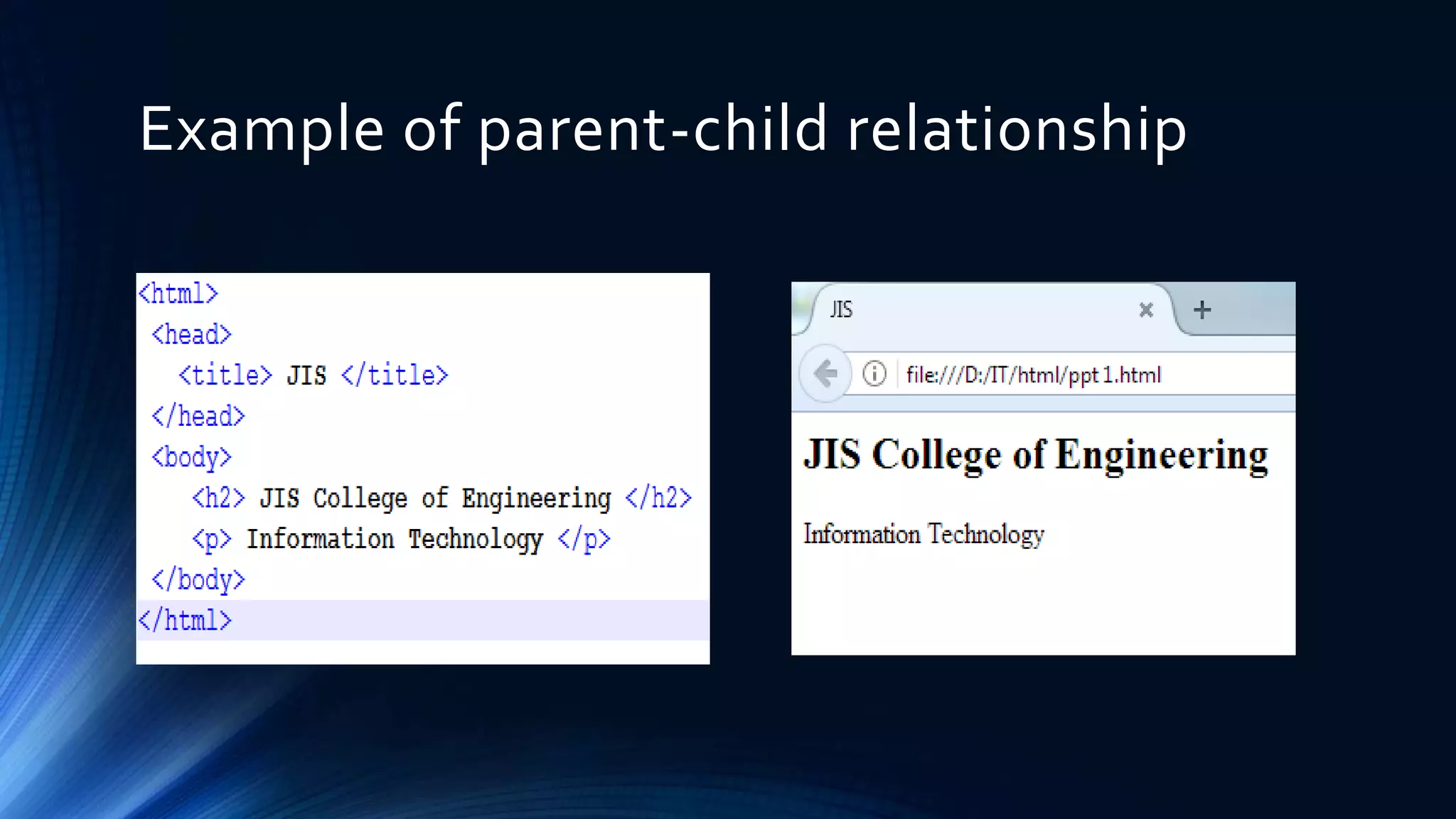
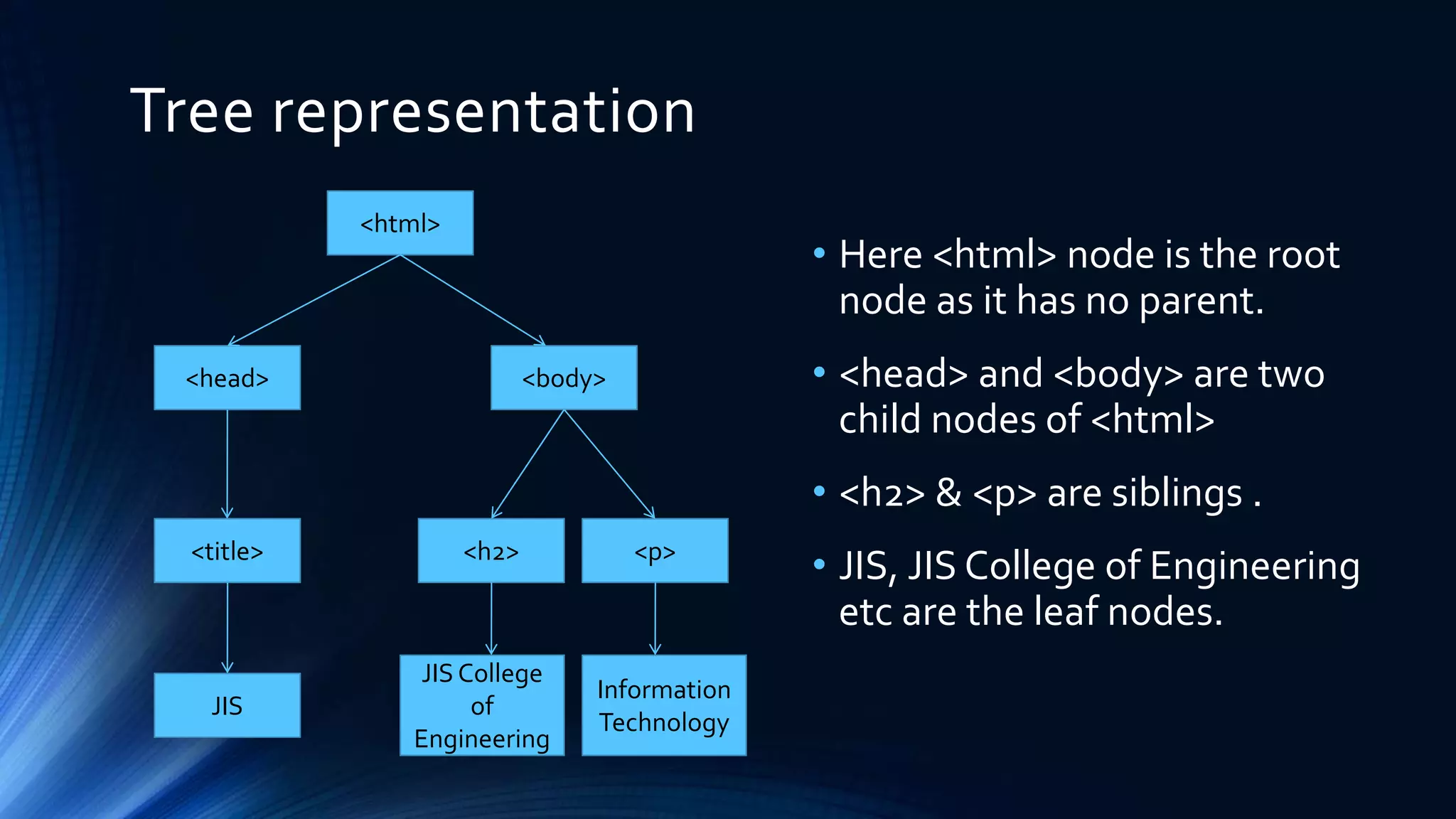
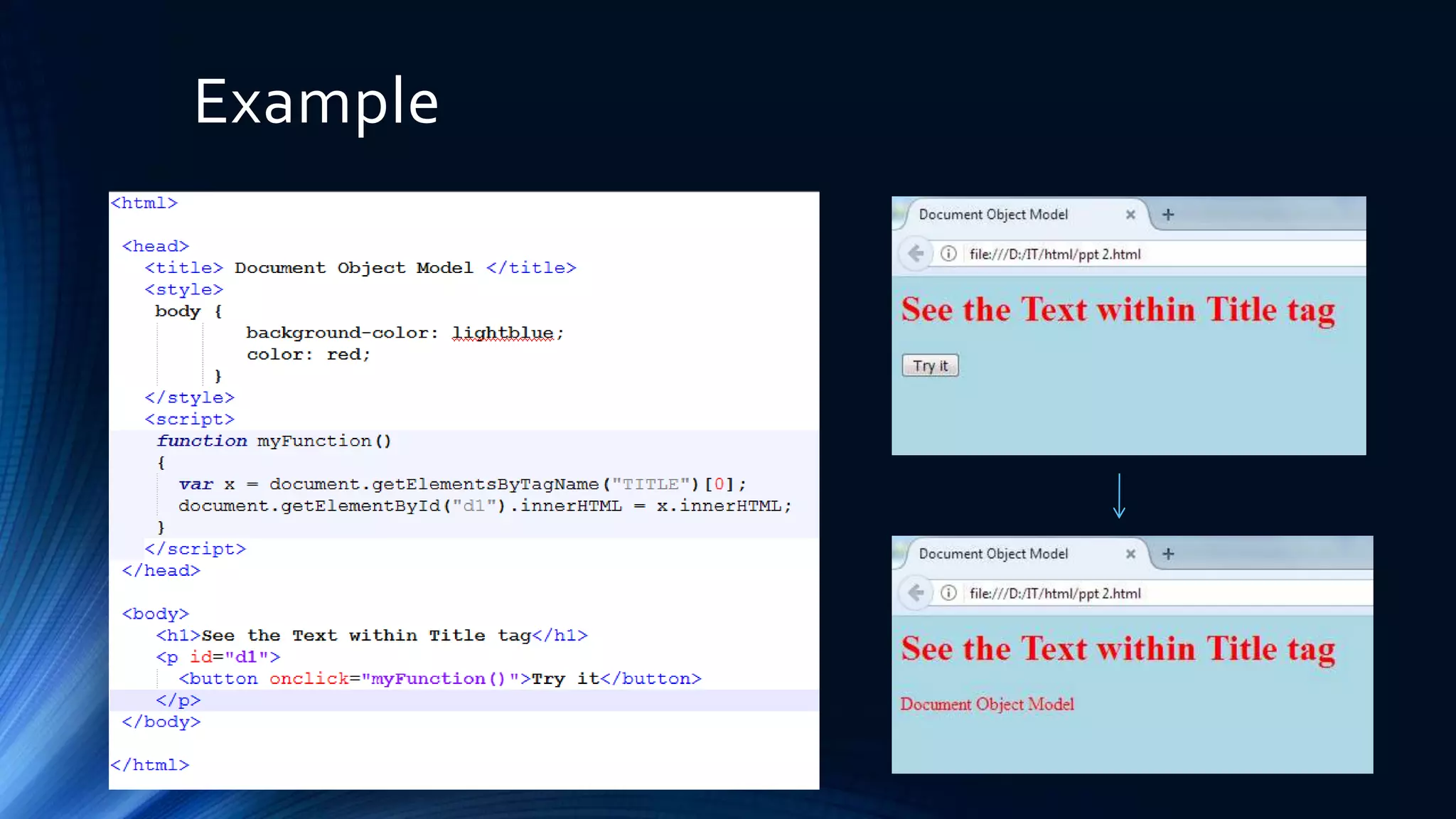
The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML that defines the logical structure of documents and how they can be accessed and manipulated. It consists of three types: Core DOM, XML DOM, and HTML DOM, each serving as a standard model for structured documents. The document outlines its hierarchy, tree structure, and methods for accessing nodes, along with advantages and disadvantages of using the DOM.