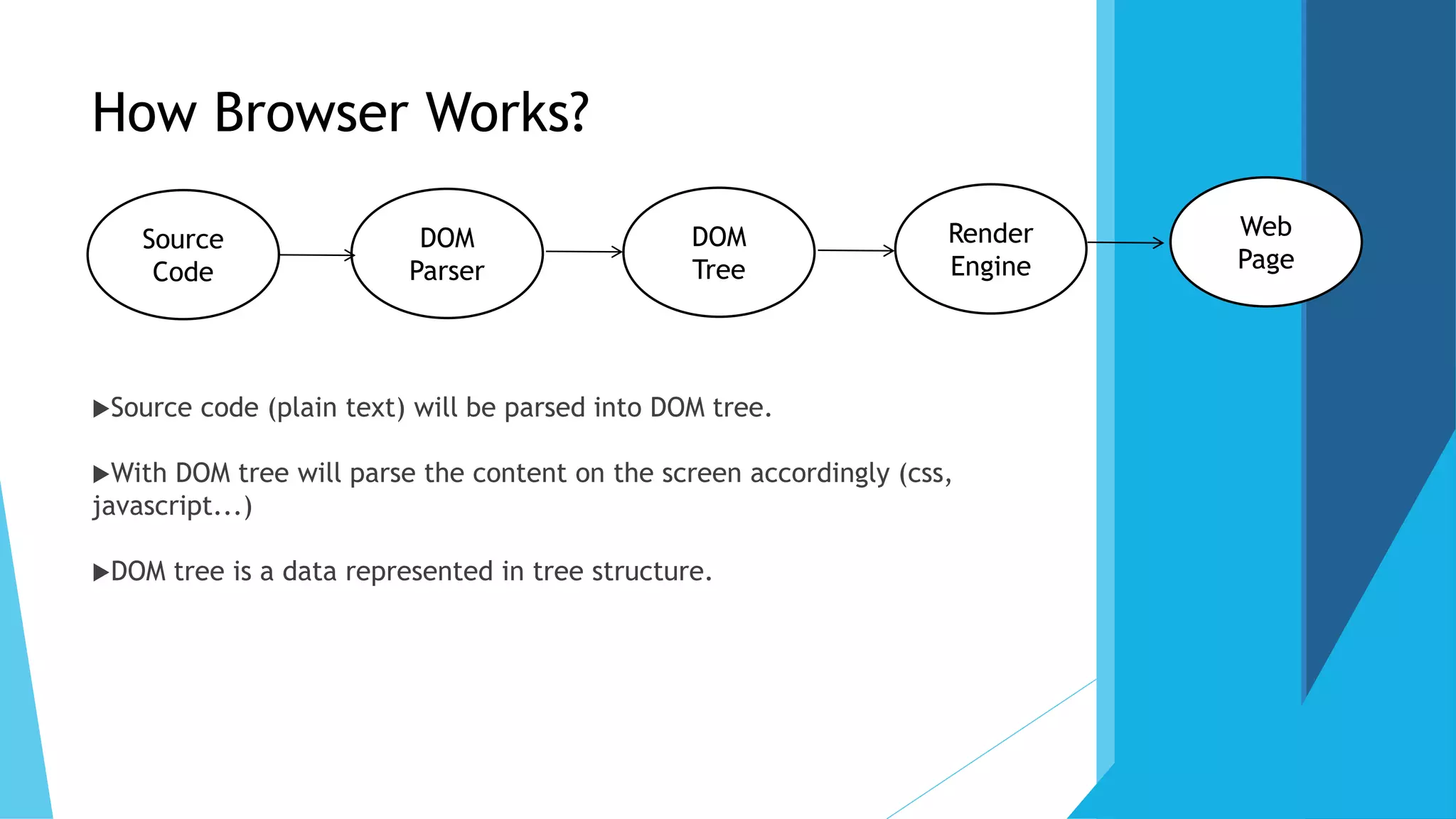
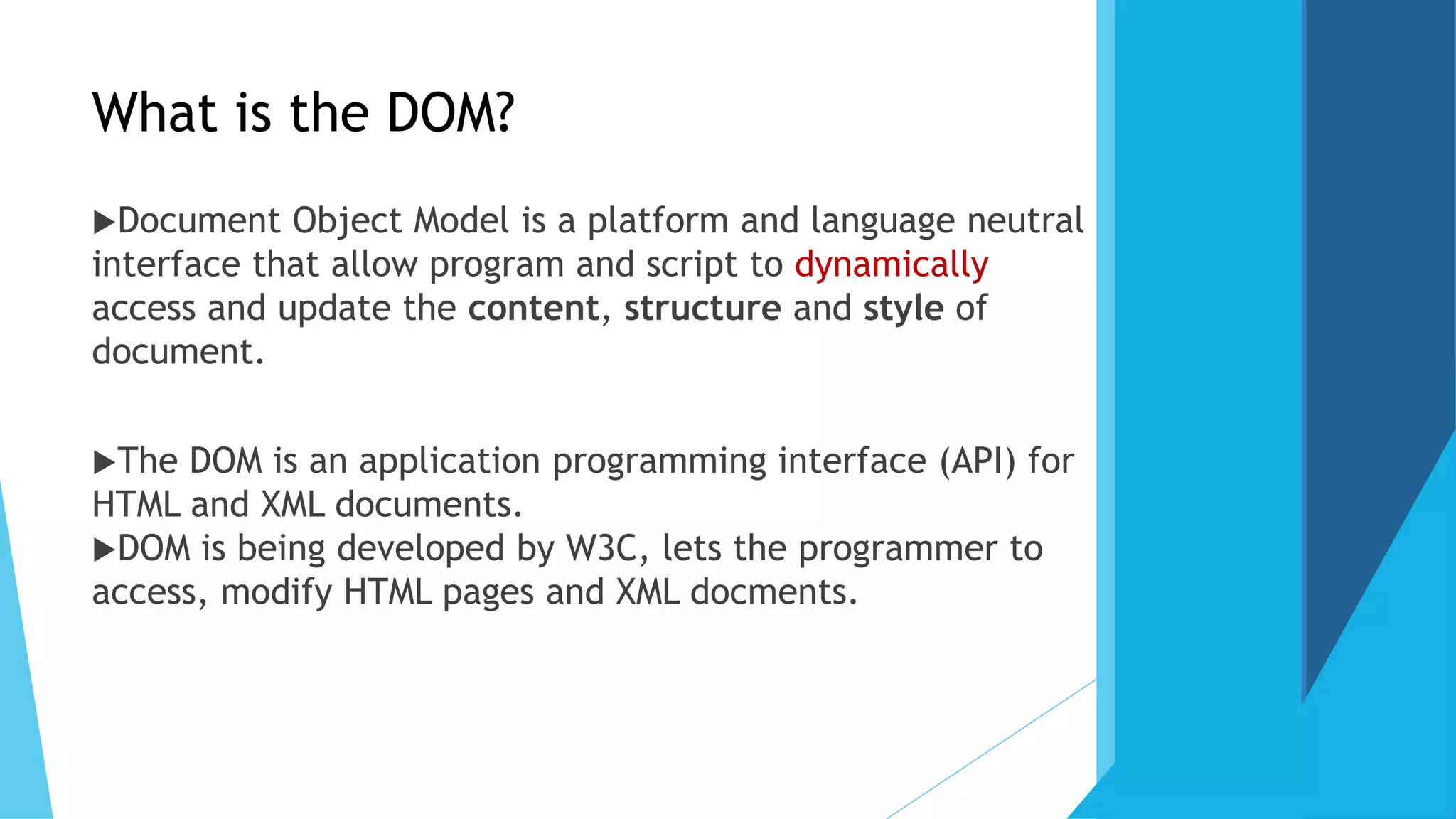
The document discusses the Document Object Model (DOM), which defines a standard for accessing and manipulating HTML and XML documents. It allows programming interfaces to dynamically access and update the content and structure of documents. The DOM represents the page as nodes and objects. It describes the DOM tree structure with parent-child relationships, and methods for accessing nodes by name, ID, tag name, or relative positioning. Examples are given for adding a new text node to the DOM tree. Advantages are robust APIs and easy data modification. Disadvantages include storing the entire document in memory.


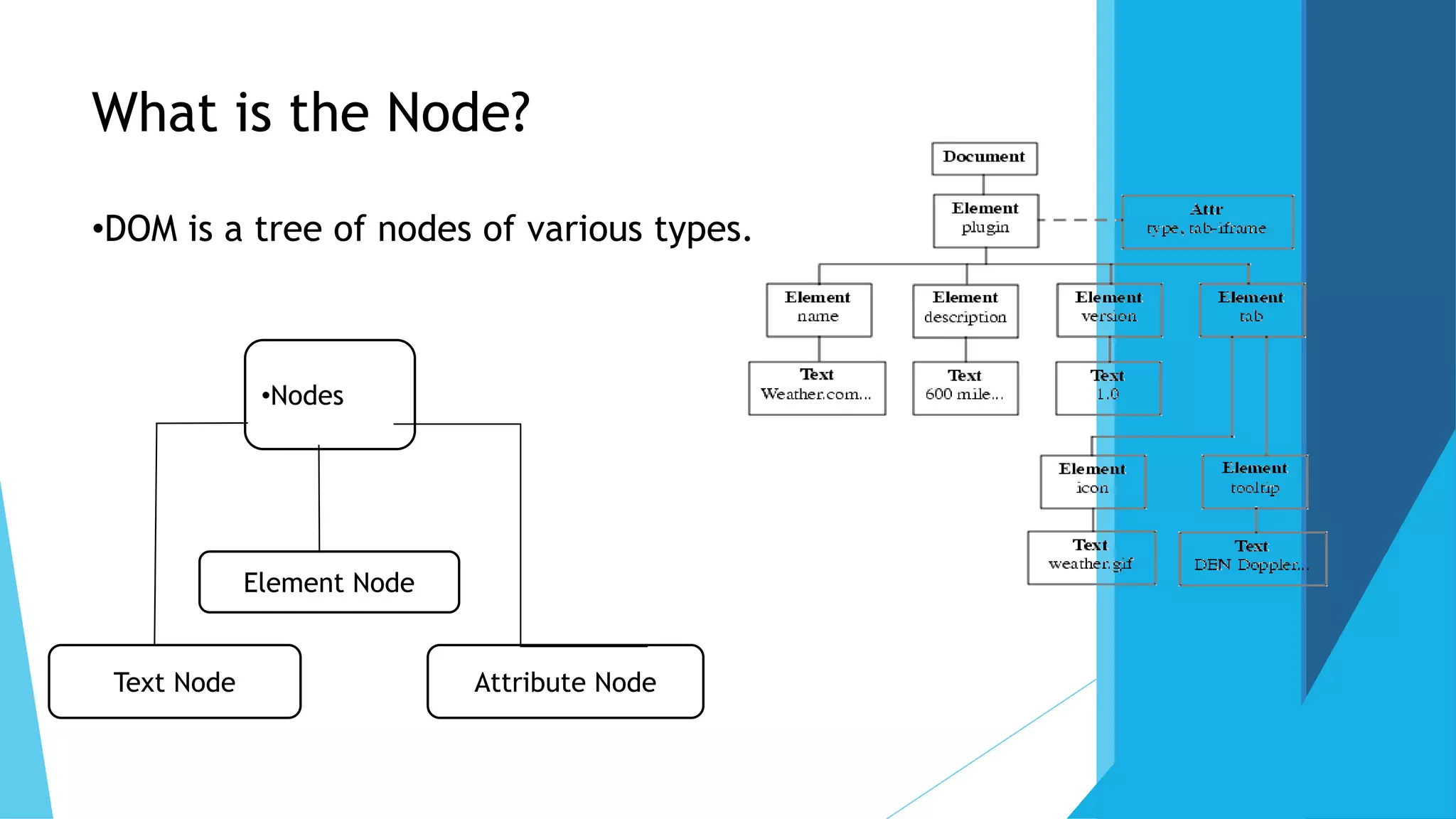
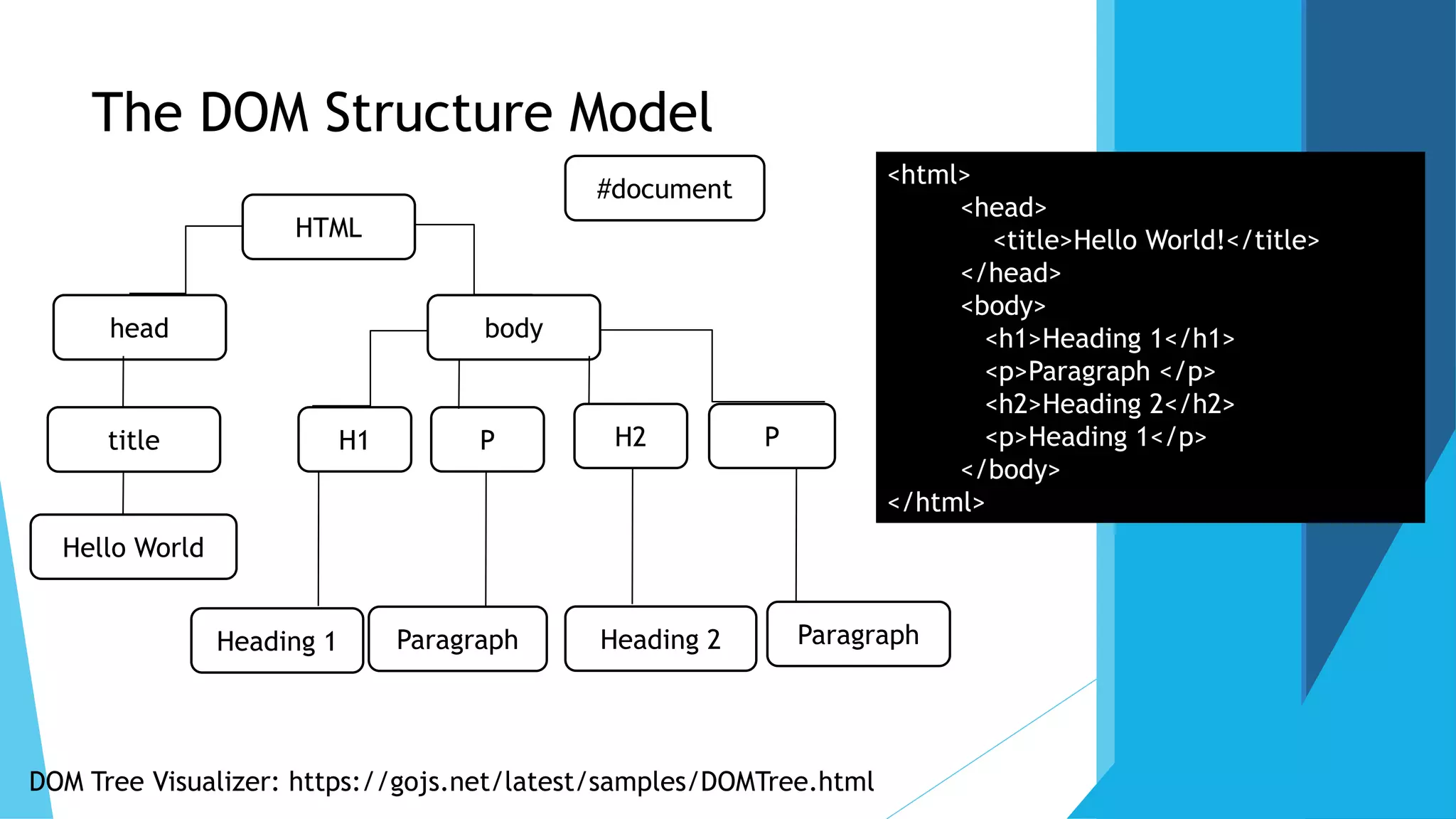
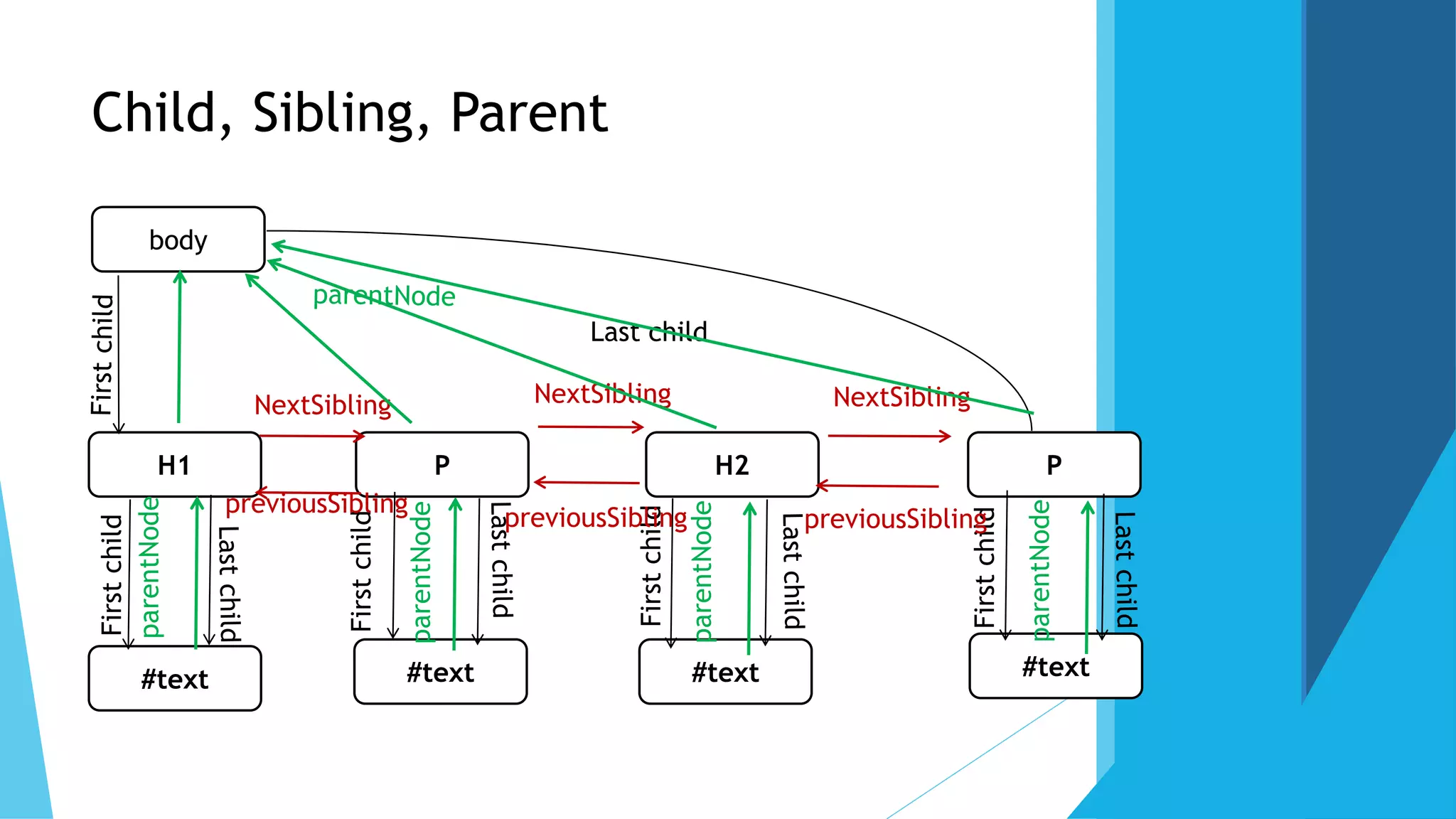
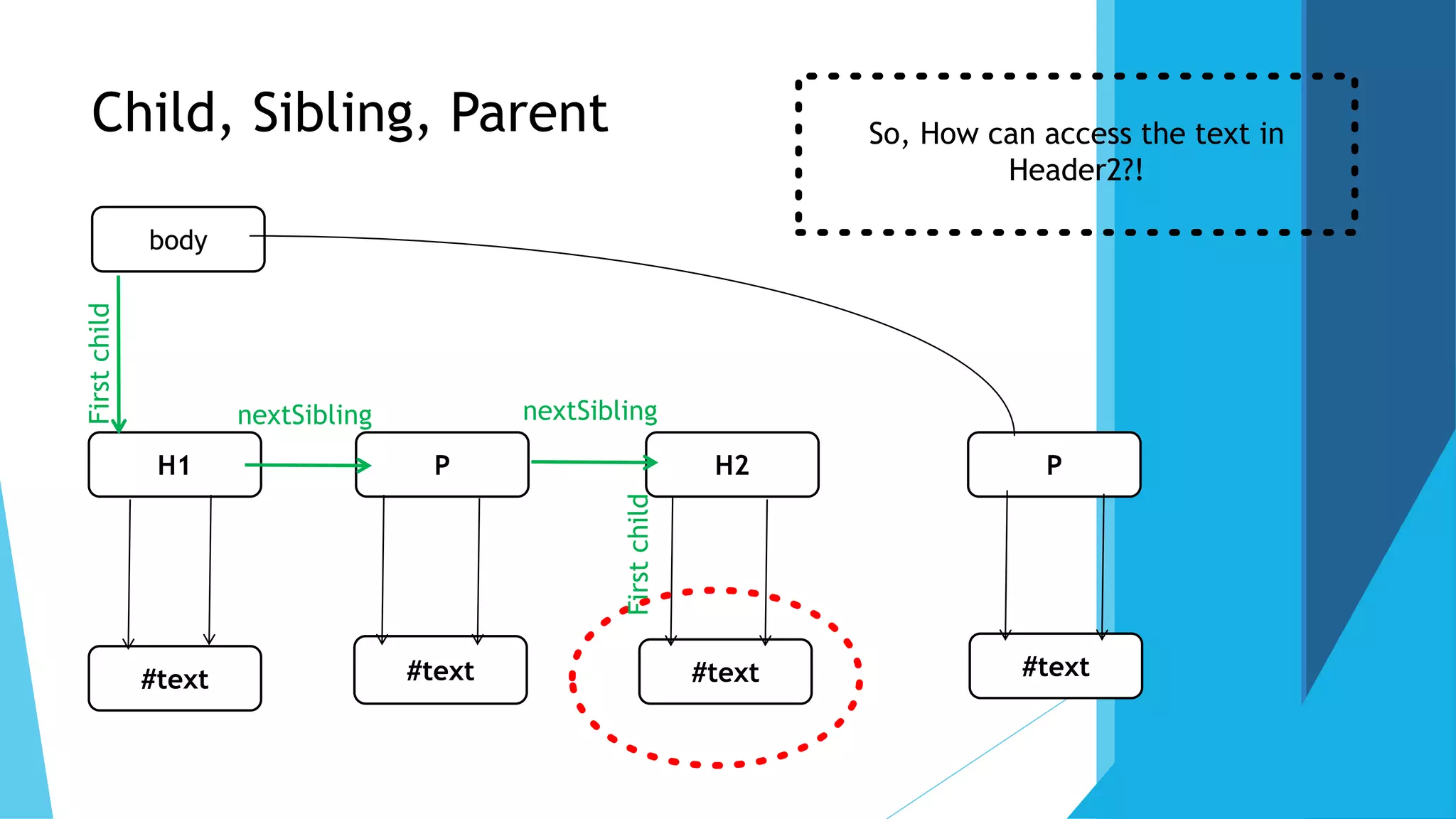
![How can access the nodes?
By their name or Id (it will allow you to work with one element, and it's the
easiest way)
GetElementByName(NodeName)
GetEllemtById(IdName)
By Tag Name (GetElementsByTagName), it will return array of nodes
By their relation to parent, child, sibling
(nextSibling,previousSibling,parentNode,lastchild, firstchild, childNode) , childNode[0] ==
first child](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-170226122602/75/Introduction-to-the-DOM-10-2048.jpg)