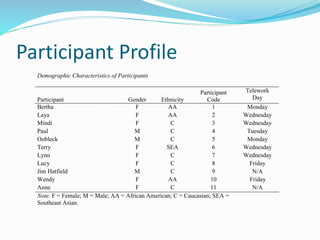
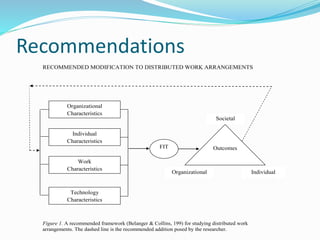
Kristin Albright Waters will defend her doctoral dissertation on April 1, 2016. Her dissertation examines the lived experiences of employees who telework through a case study of employees at a higher education institution. She investigated what the experiences of teleworking employees are and whether they experienced "fit" as defined by the Concept of Fit theoretical framework. Her findings showed that participants had both similar and unique individual experiences of teleworking and that overall they did experience fit as outlined by the framework, though they were unaware of the framework. She provides recommendations for modifying the framework and implications for future research, such as further analyzing the framework, gender roles, and supervisory styles.