Learning Python as a beginner doesn’t have to be overwhelming, and that’s exactly what Docketrun’s Python Course for Beginners aims to solve. Rather than dumping syntax rules or complex algorithms from day one, this course starts from the mindset of someone who's completely new to programming. The structure is clean, logical, and progressive — guiding you step-by-step from the basics all the way up to writing simple, working programs. It doesn’t assume you already know how code works. Instead, it explains programming concepts in plain language, often using real-life examples to relate abstract logic to everyday thinking. Variables, loops, and functions are introduced not just with definitions, but with purpose — why you use them, where they fit into problem-solving, and how they form the building blocks of everything more advanced.
The course places strong emphasis on practical application. Every module introduces a topic, walks you through an example, and then challenges you with a hands-on exercise. Rather than passive learning, it encourages active doing. The syntax of Python is beginner-friendly, and Docketrun leverages that simplicity to build confidence fast. Instead of just saying “here’s how a loop works,” it asks you to build small projects with loops. For example, creating a number guessing game, building a simple calculator, or automating text-based tasks. These aren’t toy problems—they’re mini applications that teach you to think like a developer. And that’s the shift that separates a casual learner from someone building real skill.
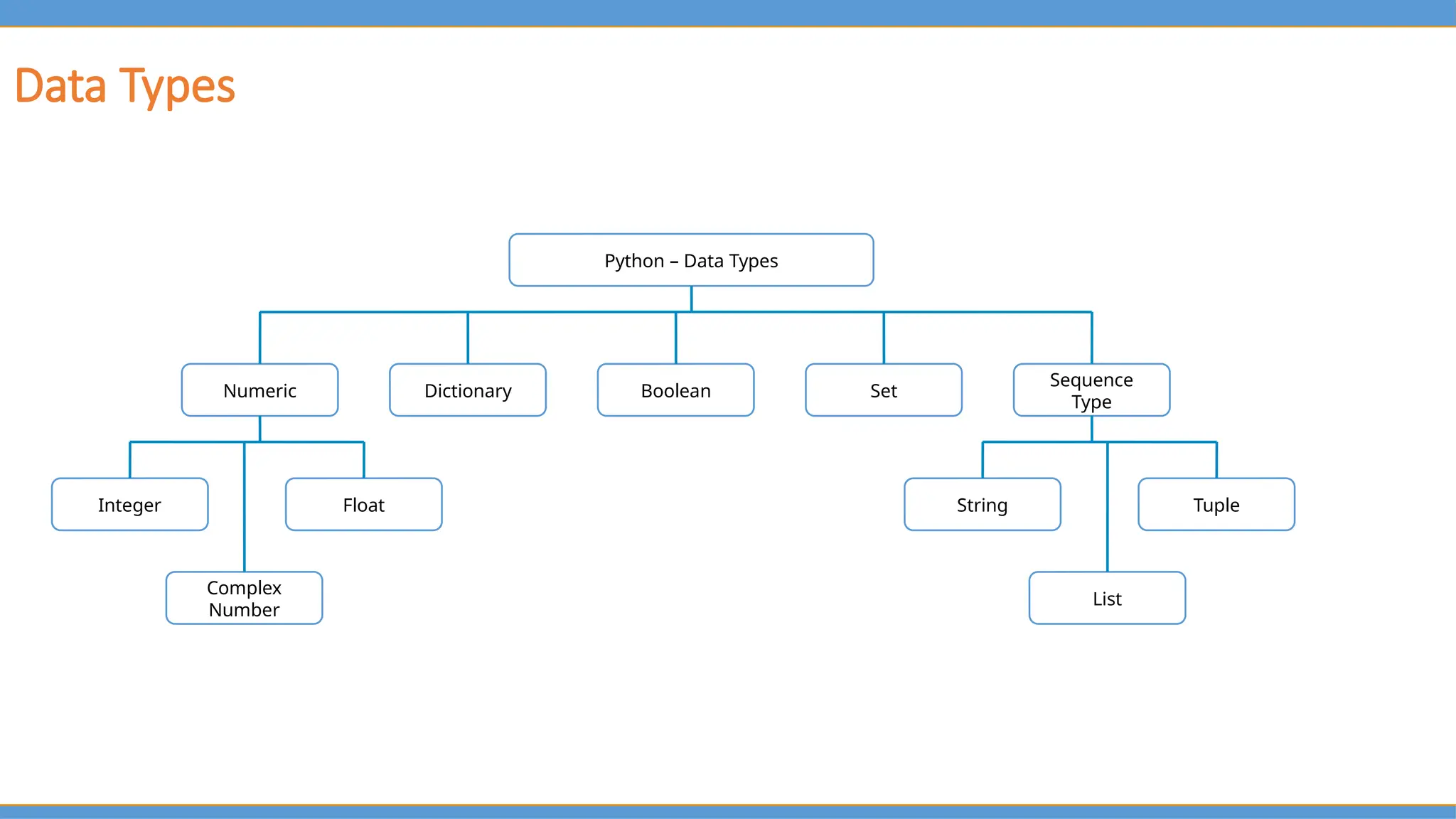
Another strength is how it covers the foundational logic behind programming, not just Python as a language. Things like conditional statements, error handling, input/output, and data types are explained with clarity, but also with a focus on how they work together to solve problems. That’s important because once you understand those, you’re not just learning Python — you’re learning how to code. And because Python is used in data science, automation, web development, and AI, that foundation gives you the flexibility to explore any of those paths later.
One of the smartest decisions the course makes is avoiding unnecessary complexity early on. It doesn’t jump into object-oriented programming or advanced libraries in the first week. Instead, it focuses on repetition, clarity, and real feedback. You’ll write dozens of small programs before ever seeing a class or decorator. That might seem slow, but it builds rock-solid understanding, which later makes learning more advanced topics much easier. The course also includes quizzes, short challenges, and debugging sessions so you build not just skill but instinct — learning to fix your own code and think through problems logically.
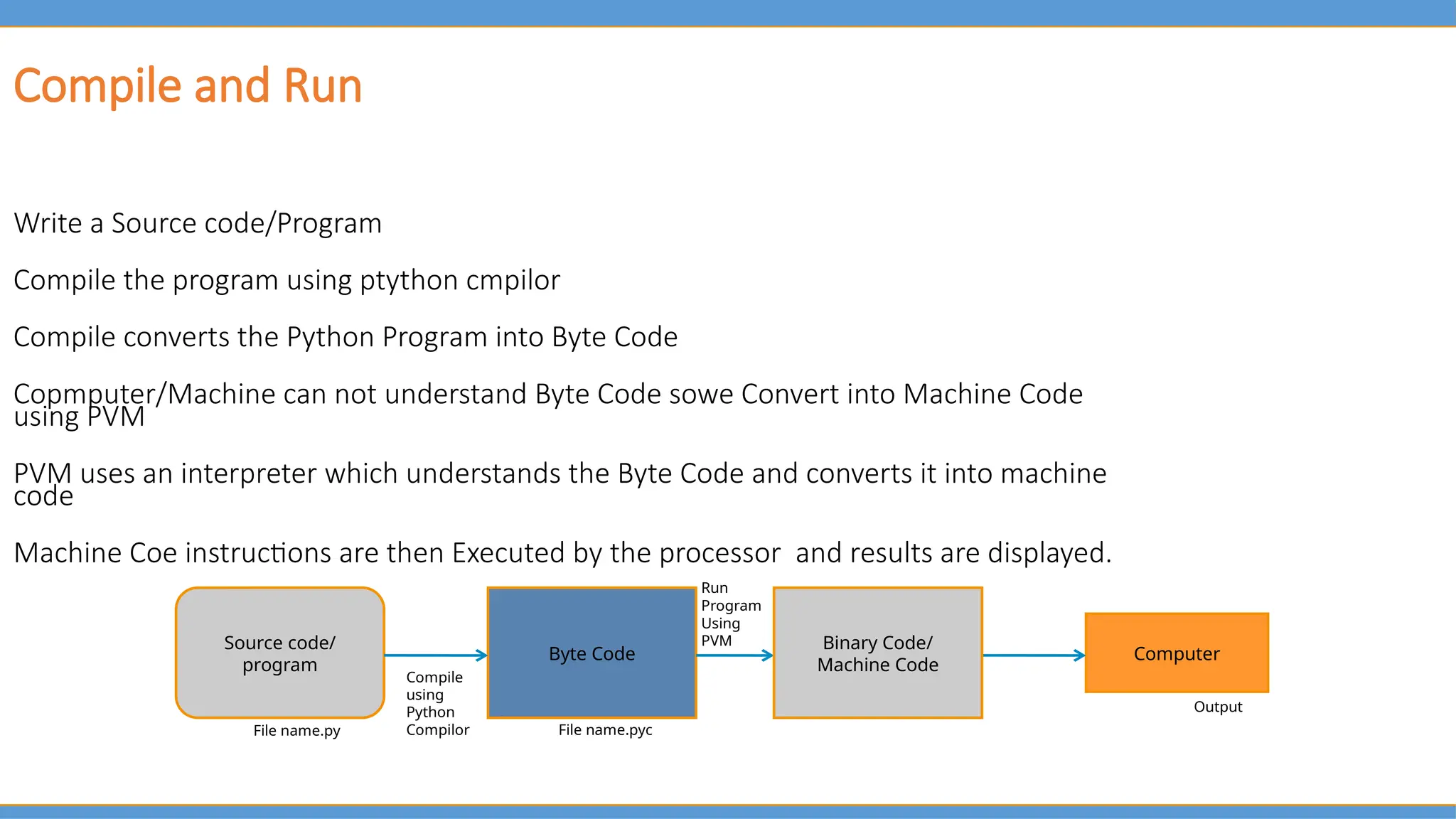
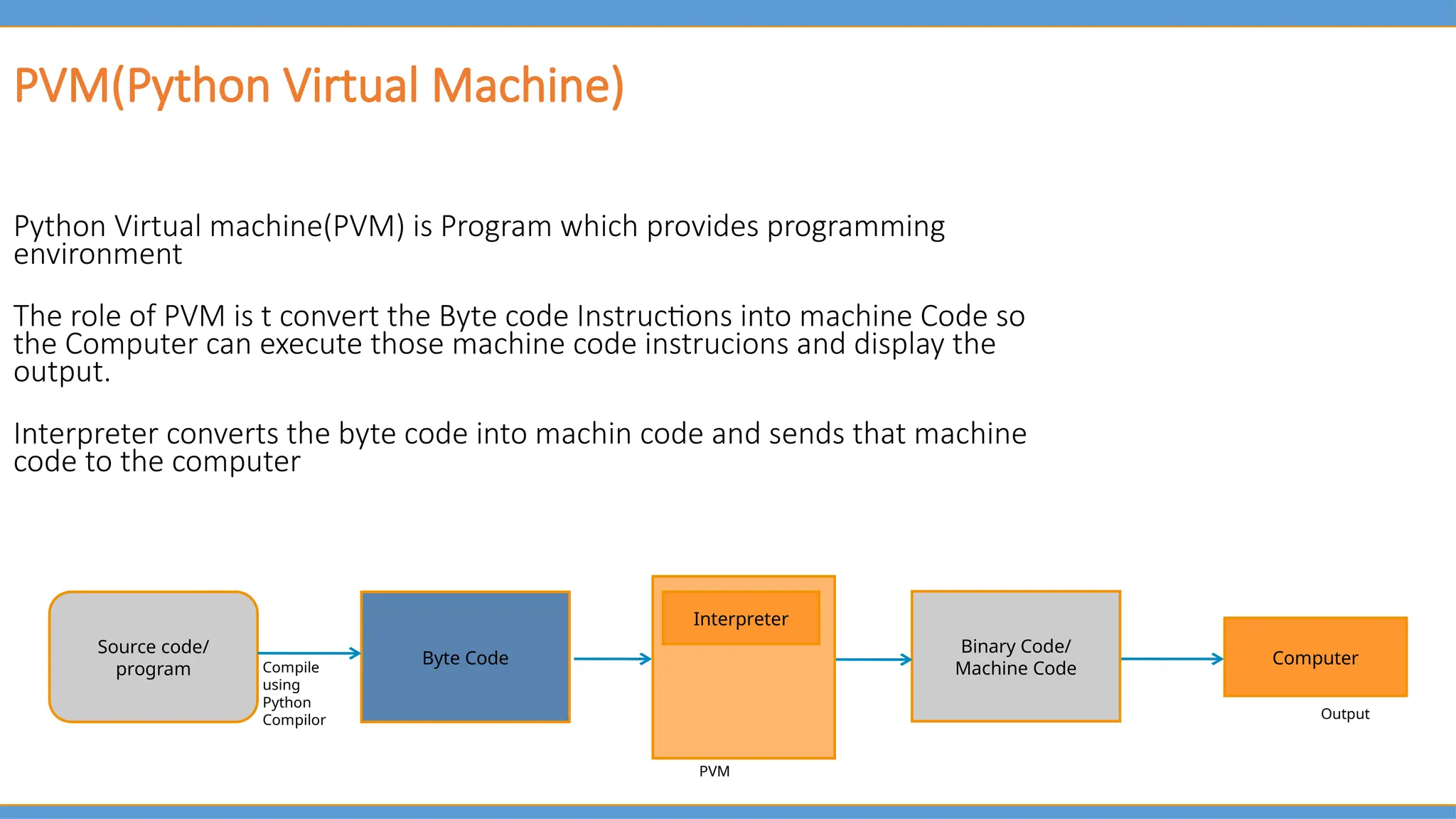
For someone who’s never coded before, another standout feature is the explanation of how Python runs under the hood. You’ll learn about the Python interpreter, how memory works, and why indentation matters—not just that it does.


![Application For Python
Web Application – Django, Pyramid, Flask, Bottle
Desktop[ GUI Application – Tkinter]
Console Based Application
Games and 3D Application
Mobile Application
Scientfic and Numeric
Data Science
Machine Learning – scikit-learn and TensorFlow
Data Analysis – Mataplotib, Scaborn
Business Application](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docketrunspythoncourse-250713173548-d56f84f8/75/Docketrun-s-Python-Course-for-beginners-pptx-3-2048.jpg)




![List
Lists are mutable sequences that can hold multiple items.
You can manipulate lists using various built-in methods.
Common List Operations:
Adding items: append(), extend()
Removing items: remove(), pop()
Accessing items: list[index]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docketrunspythoncourse-250713173548-d56f84f8/75/Docketrun-s-Python-Course-for-beginners-pptx-12-2048.jpg)

![String
Strings are sequences of characters.
Python provides several methods for manipulating strings.
Common String Operations:
Accessing characters: string[index]
Slicing: string[start:end]
String methods: upper(), lower(), replace()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docketrunspythoncourse-250713173548-d56f84f8/75/Docketrun-s-Python-Course-for-beginners-pptx-14-2048.jpg)









![Basic Regex Syntax
Pattern Meaning Example Match
d Digit (0-9) 2, 98
w
Word character (a-z, A-Z, 0-9,
_)
hello_123
. Any character except newline a.c matches abc, axc
+ One or more a+ matches a, aa, aaa
* Zero or more lo* matches l, lo, loo
[] Character set [aeiou] matches vowels
^ Start of string ^Hi matches "Hi there"
$ End of string end$ matches "The end"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/docketrunspythoncourse-250713173548-d56f84f8/75/Docketrun-s-Python-Course-for-beginners-pptx-29-2048.jpg)