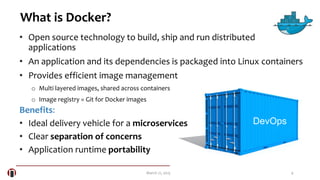
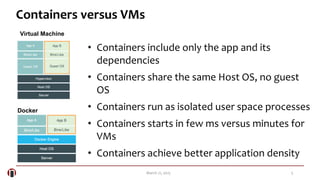
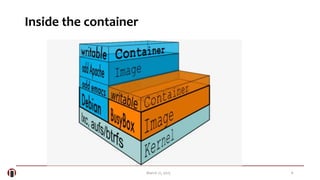
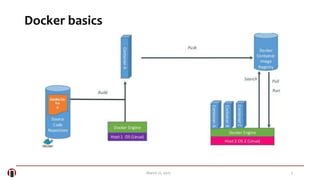
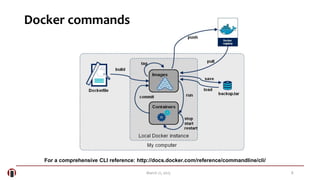
The document summarizes a meetup about Docker and microservices. It includes an agenda for presentations on Docker 1.5 features, networking, and Q&A. Two speakers are introduced who will discuss Docker introductions, features, basics, commands, and networking. An overview of Docker is provided explaining it as a tool to build, ship and run distributed applications using containers and image management.




![11March 21, 2015
Container statistics
docker stats CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
• Returns a live stream of stats for running containers
• Can be run on multiple containers
• API endpoint provides more stats
$ sudo docker stats redis1 redis2
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE/LIMIT MEM % NET I/O
redis1 0.07% 796 KiB/64 MiB 1.21% 788 B/648 B
redis2 0.07% 2.746 MiB/64 MiB 4.29% 1.266 KiB/648 B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microservices-meetup-docker15-150321161312-conversion-gate01/85/Docker-1-5-features-South-Bay-Microservices-meetup-March-2015-11-320.jpg)


![14March 21, 2015
Docker exec
docker exec [OPTIONS] CONTAINER COMMAND [ARG...]
• Runs a new command in a running container
• Only works if the container is running (i.e. not paused/stopped)
• Does not restart if the container is restarted
$ sudo docker run –d –-name mongo mongo
$ sudo docker exec –it mongo /bin/bash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microservices-meetup-docker15-150321161312-conversion-gate01/85/Docker-1-5-features-South-Bay-Microservices-meetup-March-2015-14-320.jpg)
