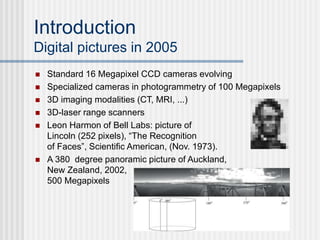
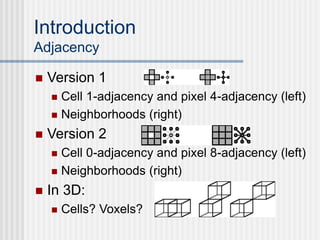
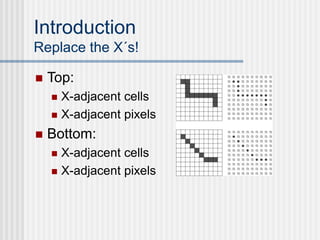
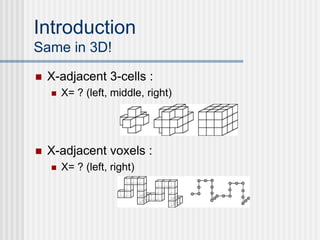
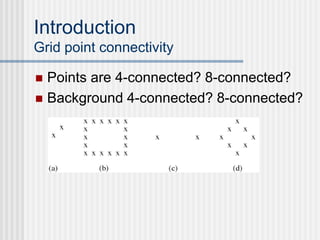
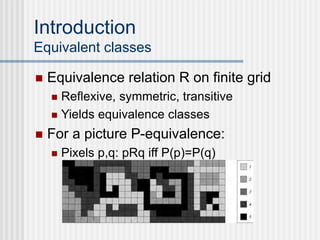
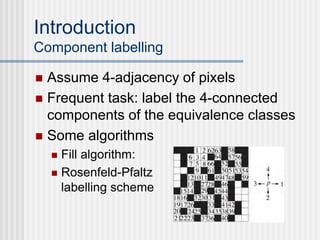
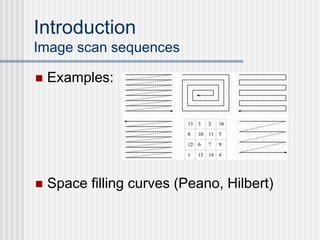
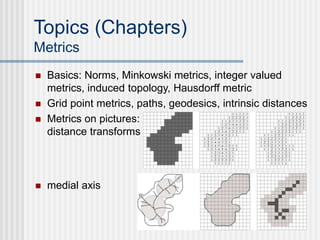
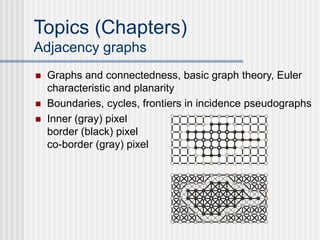
This document outlines the course "Digital Geometry and Image Processing" which focuses on geometric methods for analyzing digital images. The course is for graduate students in information engineering and will cover topics like metrics, adjacency graphs, topology, curves and surfaces in grids. It will use two primary textbooks and meet on Tuesdays and Thursdays. Selected additional topics will include moments, spatial relations, and properties of digital images.