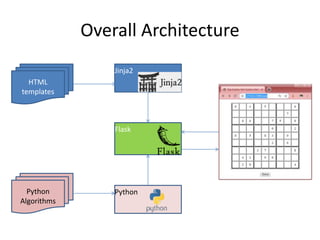
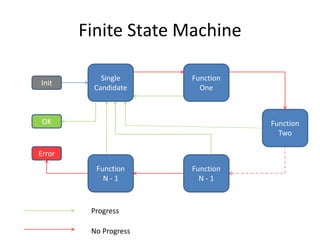
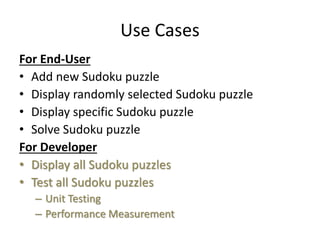
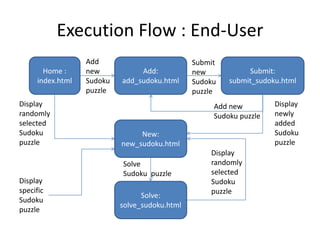
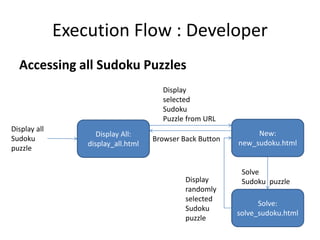
The document describes Digi-Sudoku, a Sudoku solving application. It discusses the overall architecture, which uses Python algorithms, HTML templates, and Flask. It also describes the finite state machine used for solving puzzles and lists some use cases like adding and solving puzzles. Key aspects like naming conventions and references are also covered. The document proposes future enhancements like a database to store puzzles and deploying on a microservices architecture.