Embed presentation
Downloaded 18 times

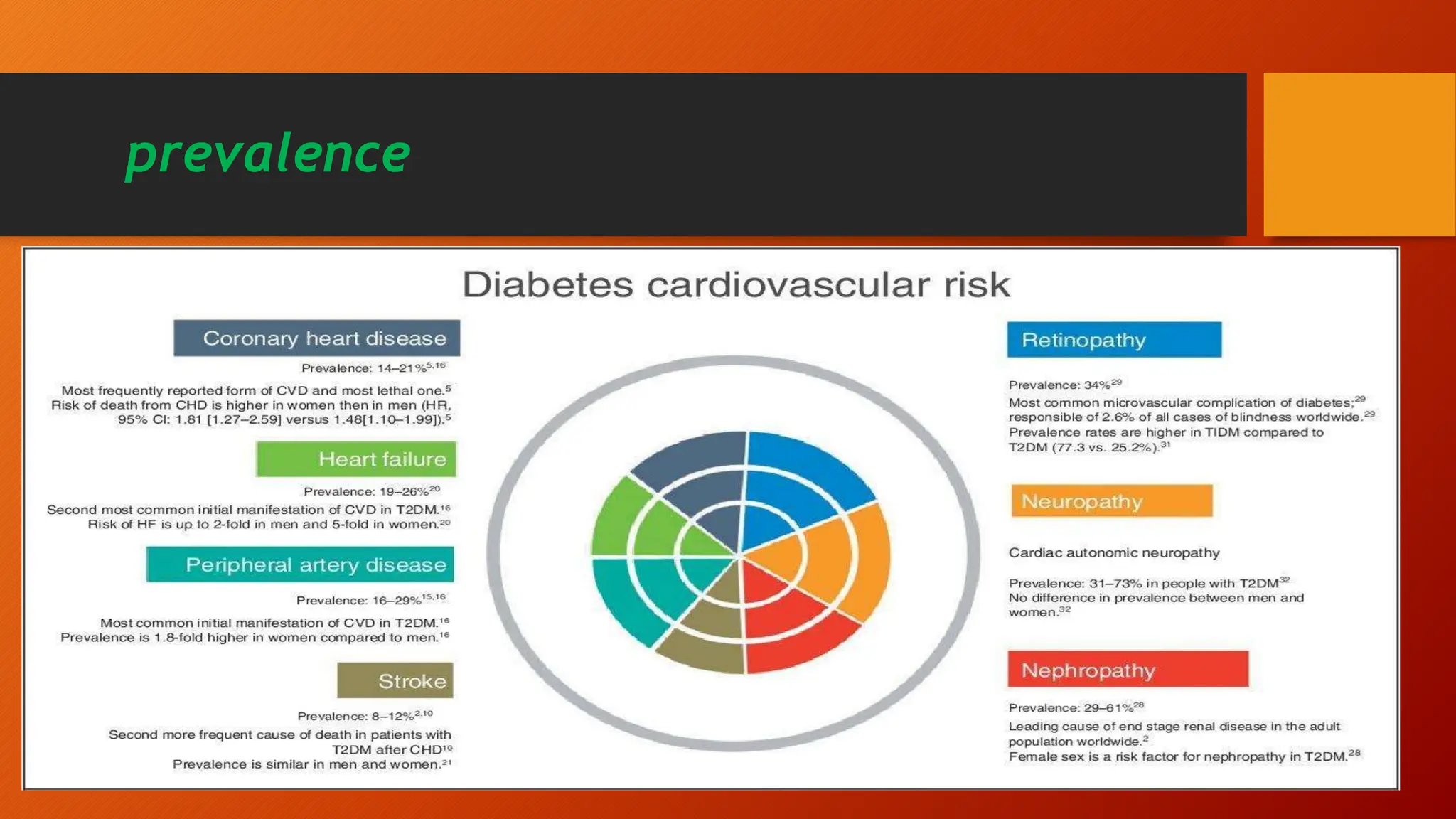

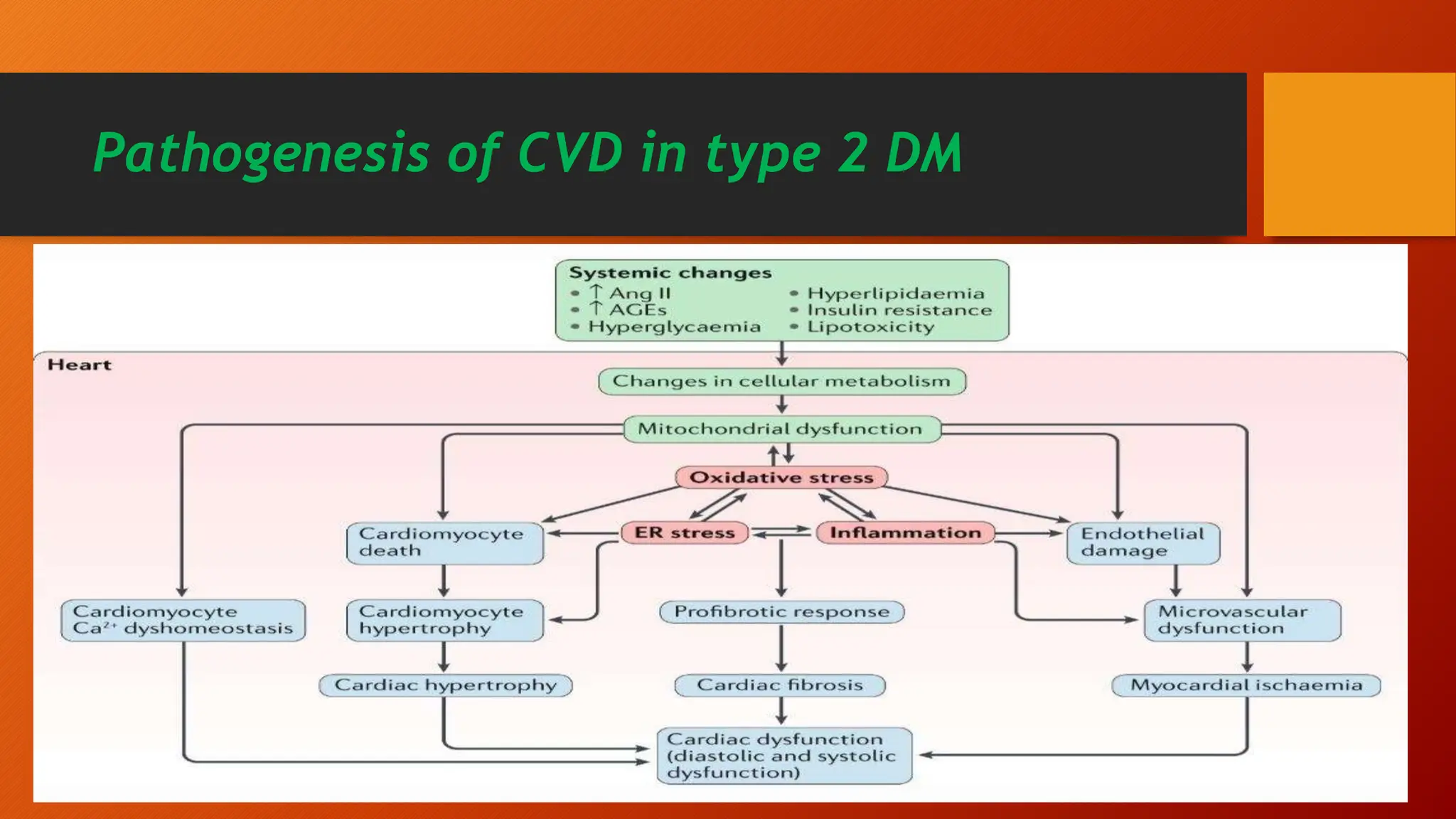
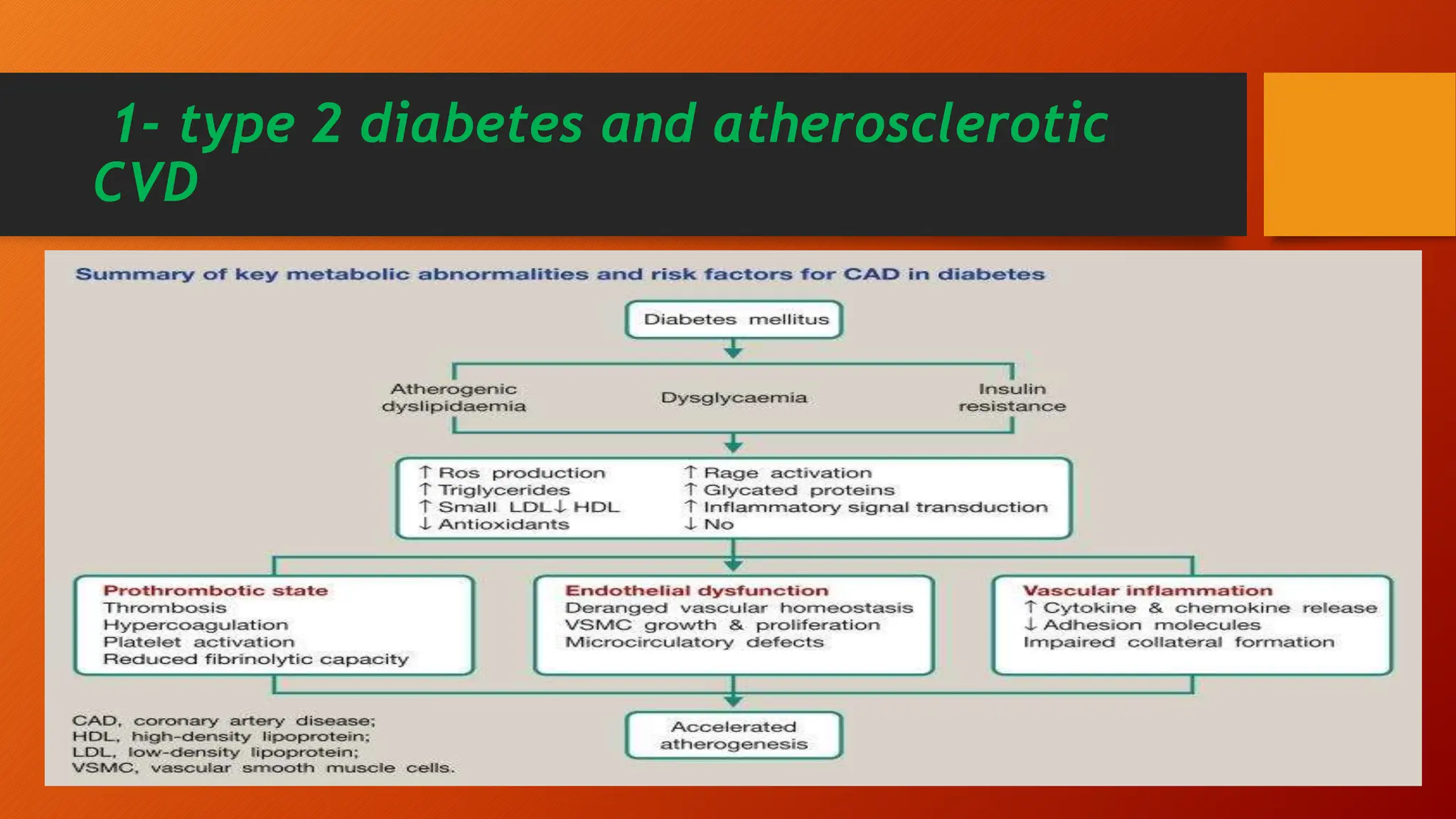
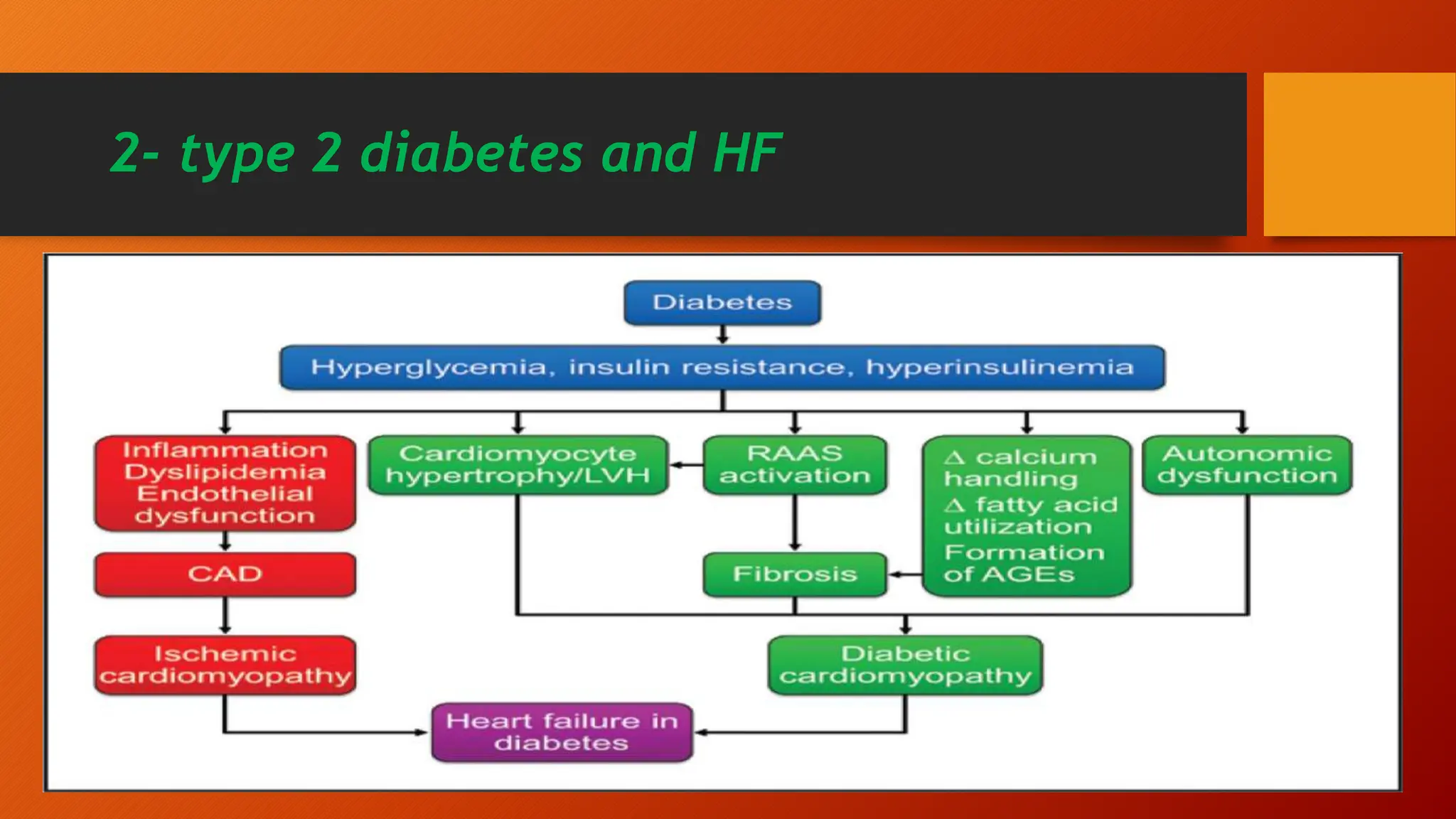
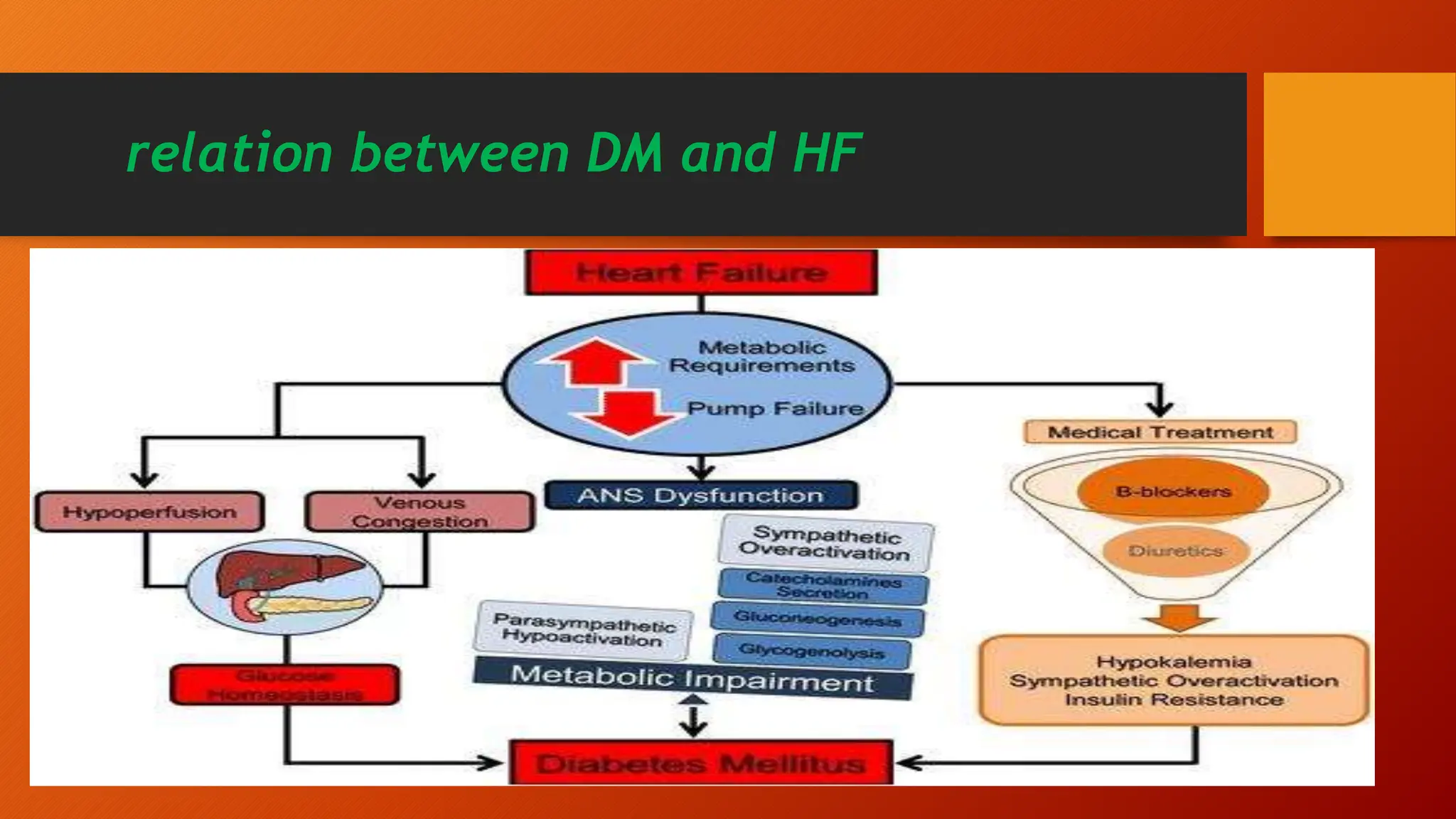
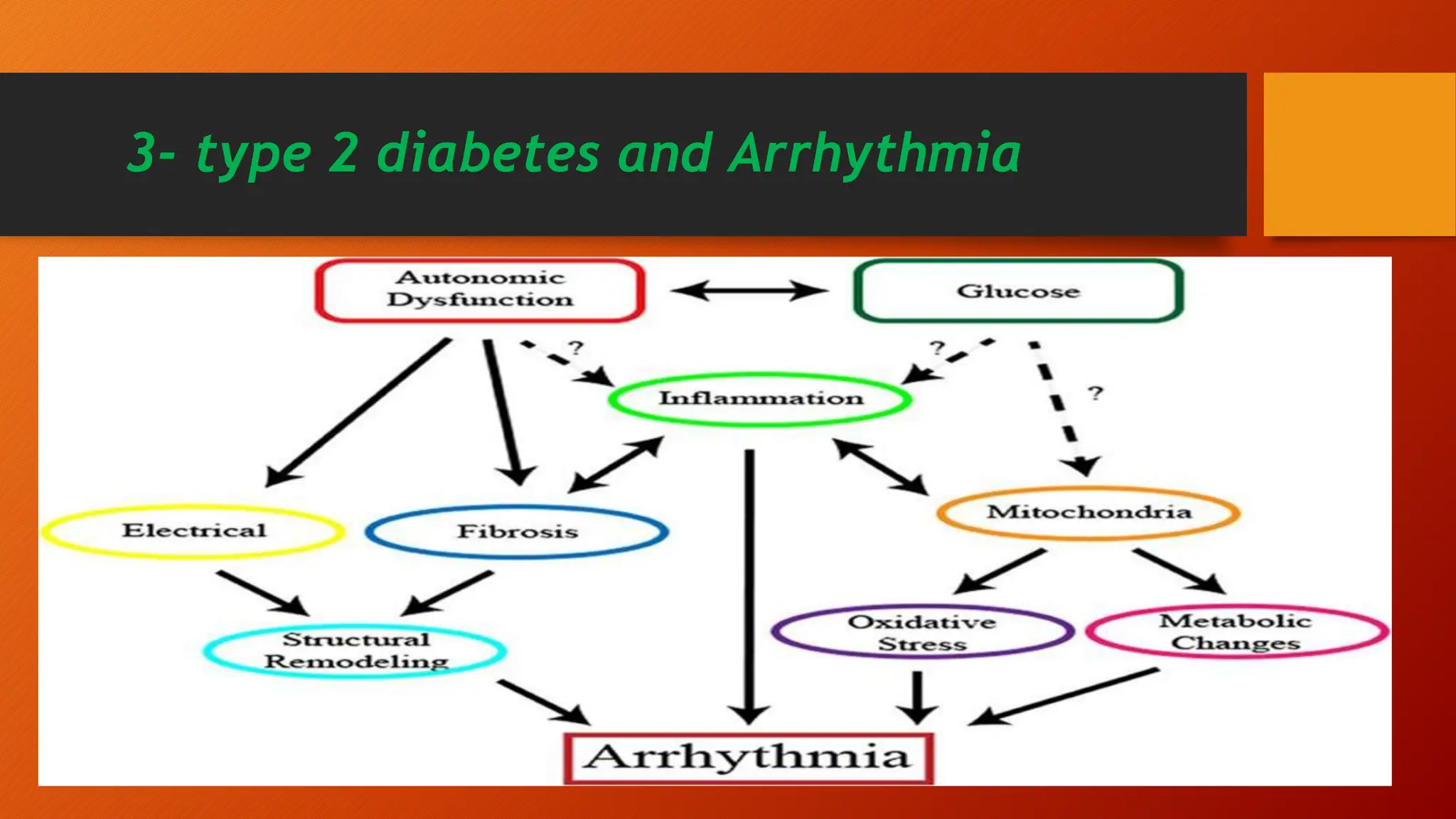
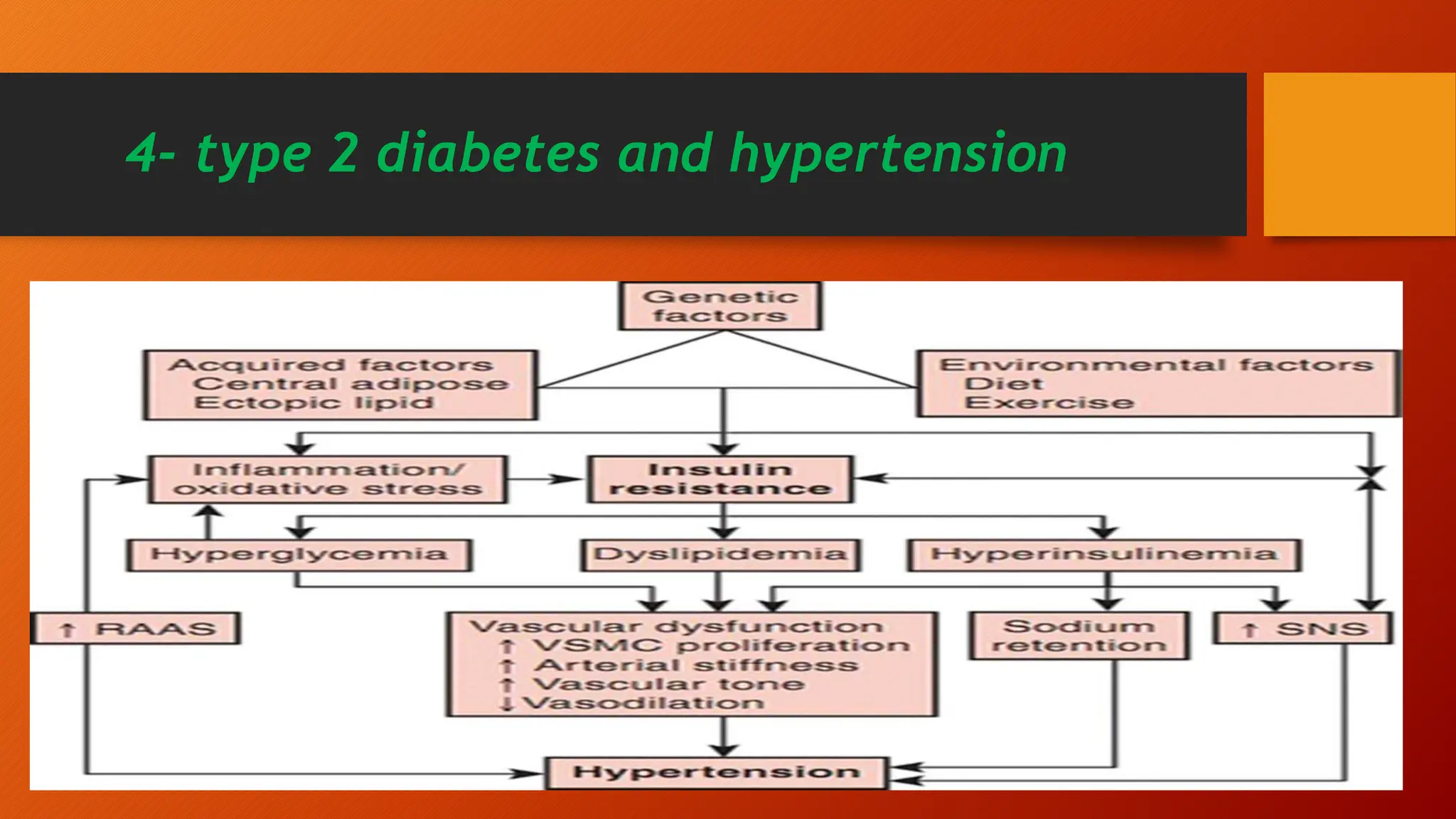


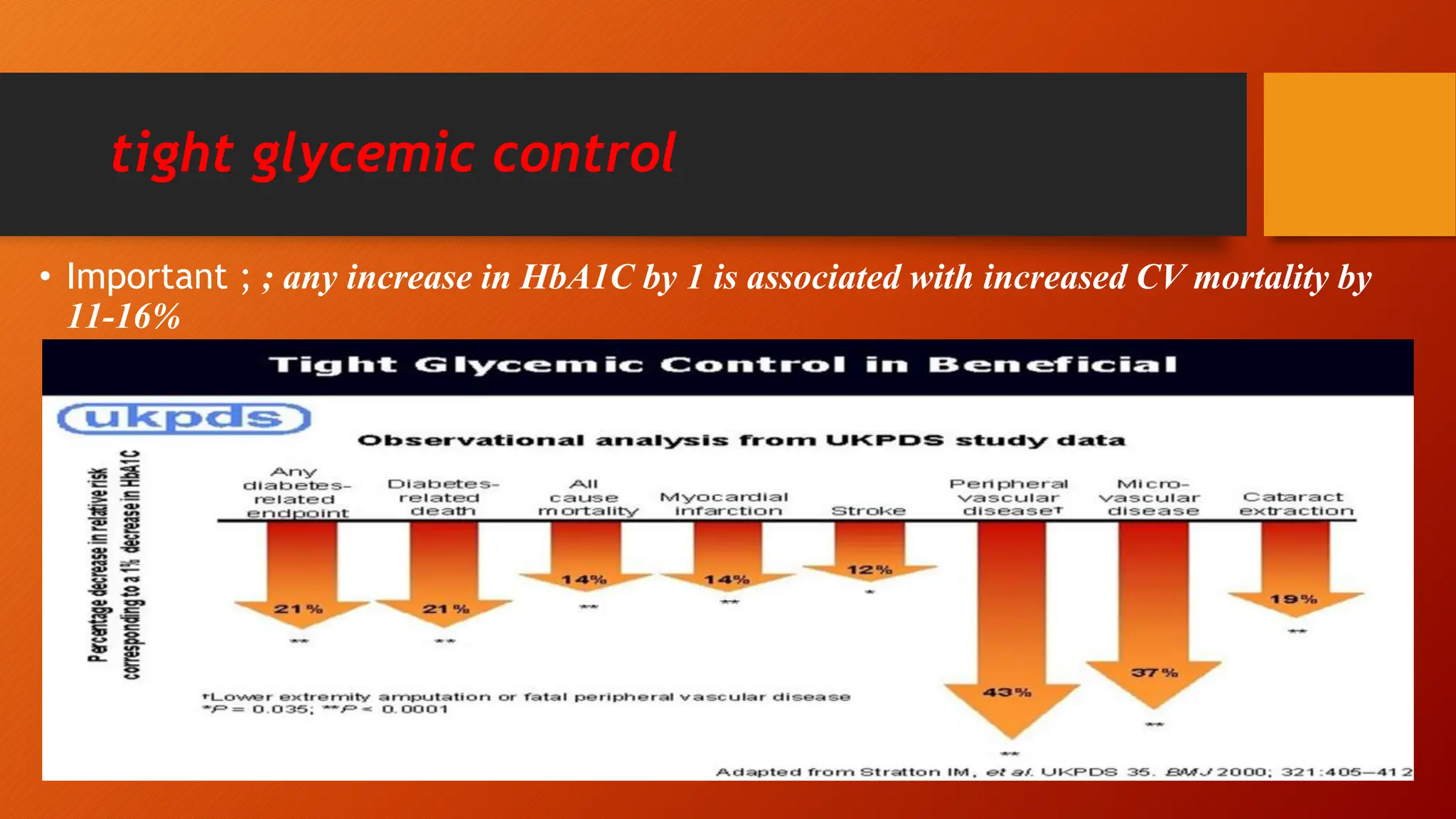


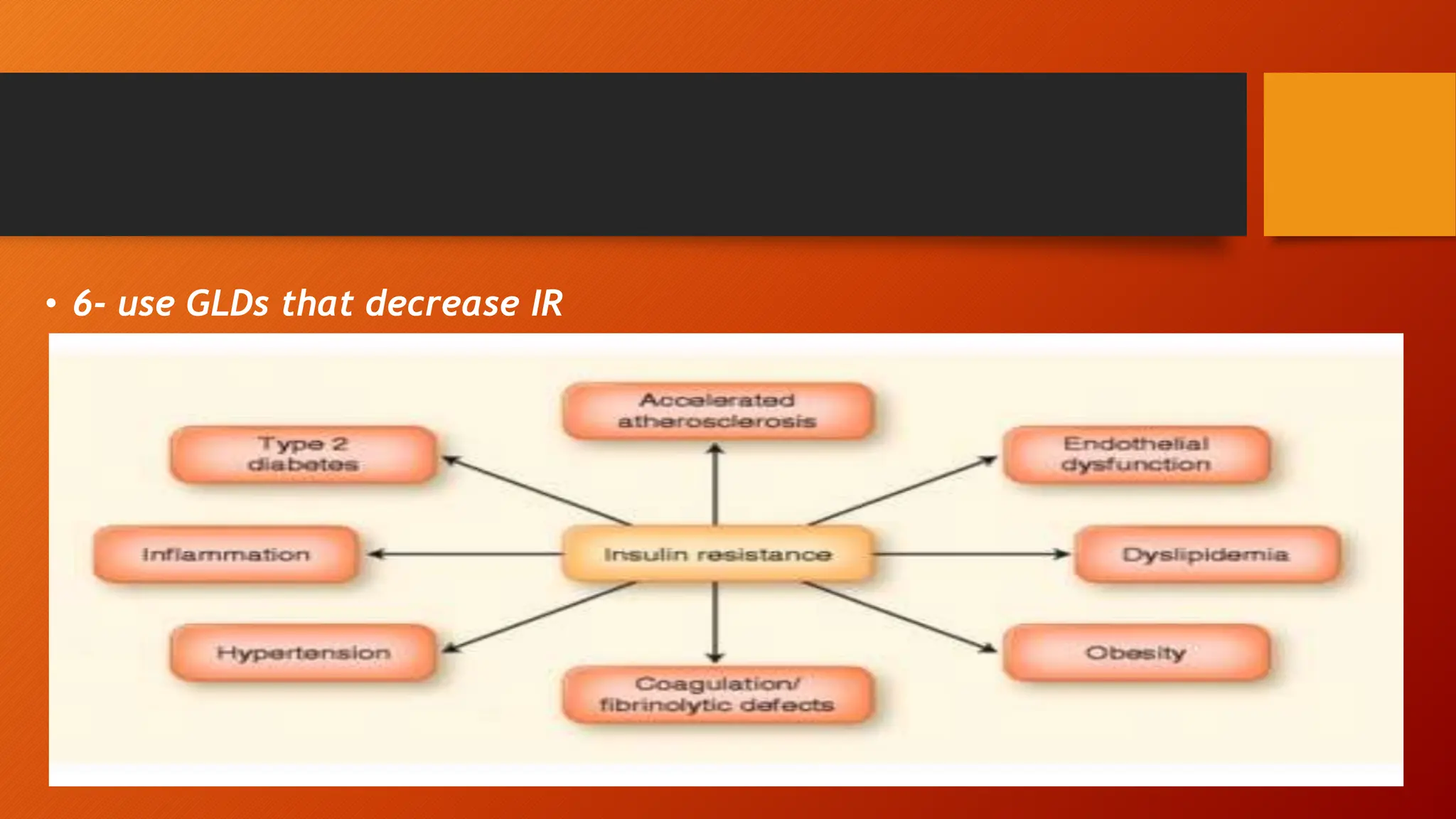

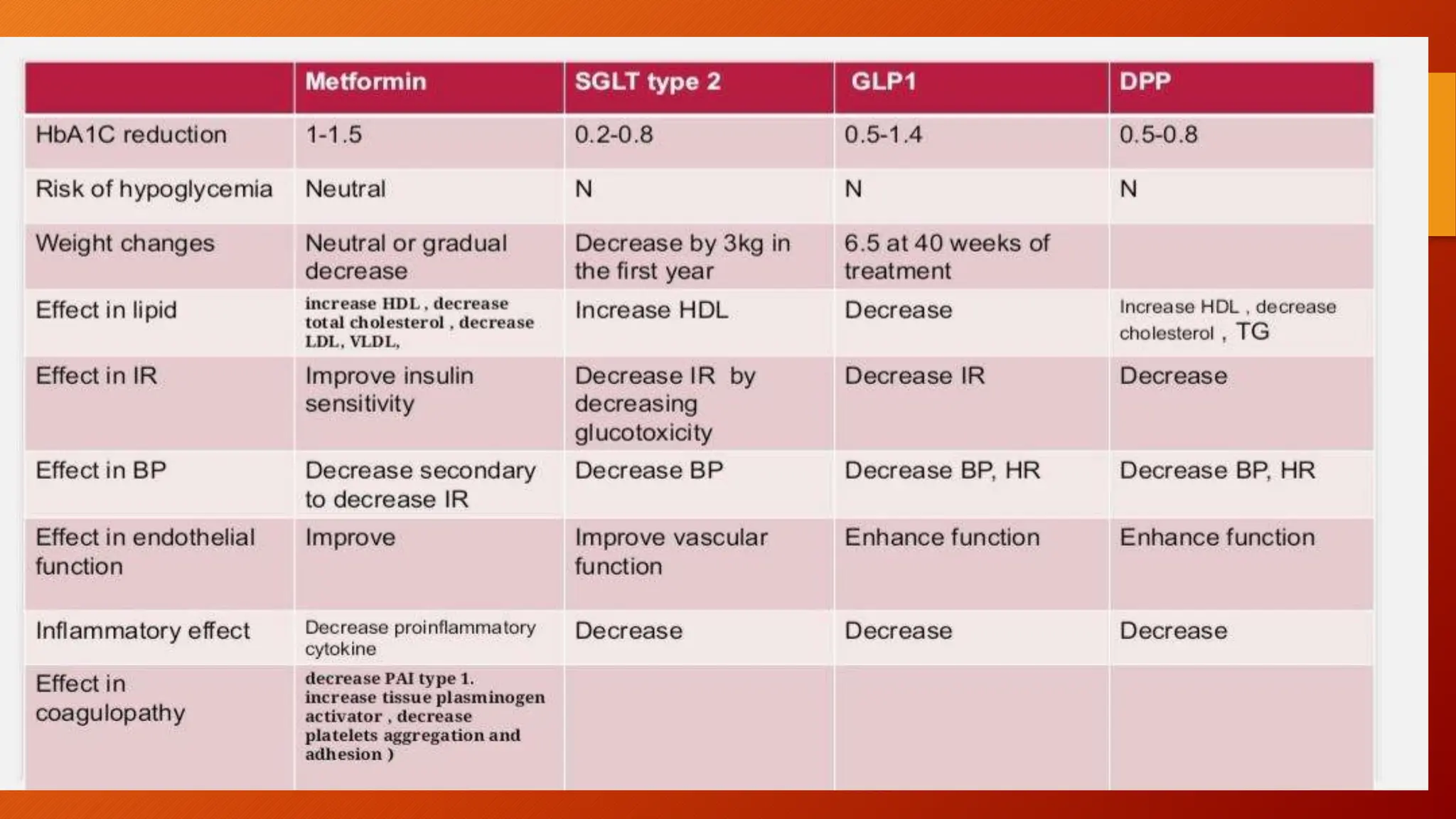
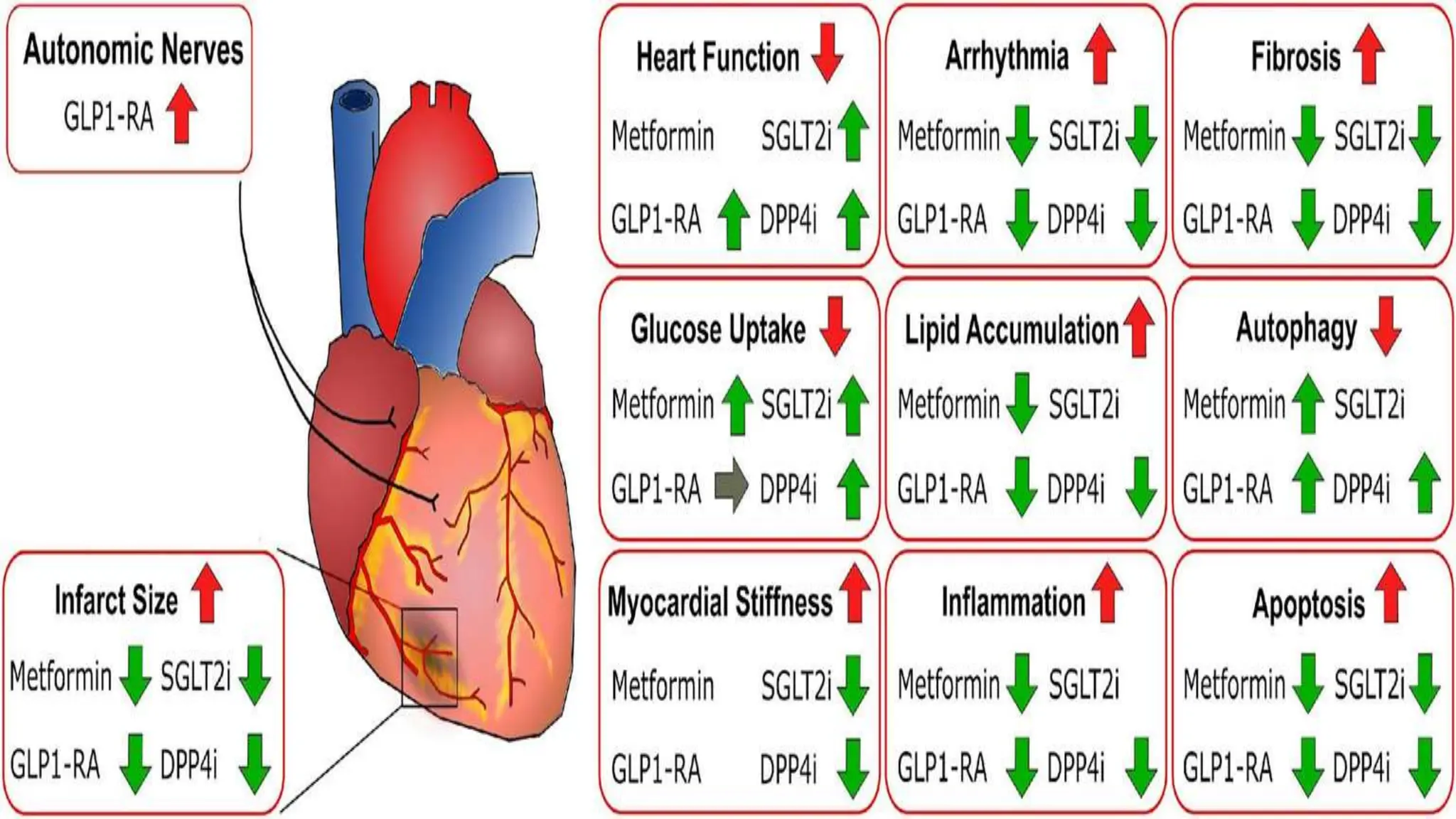
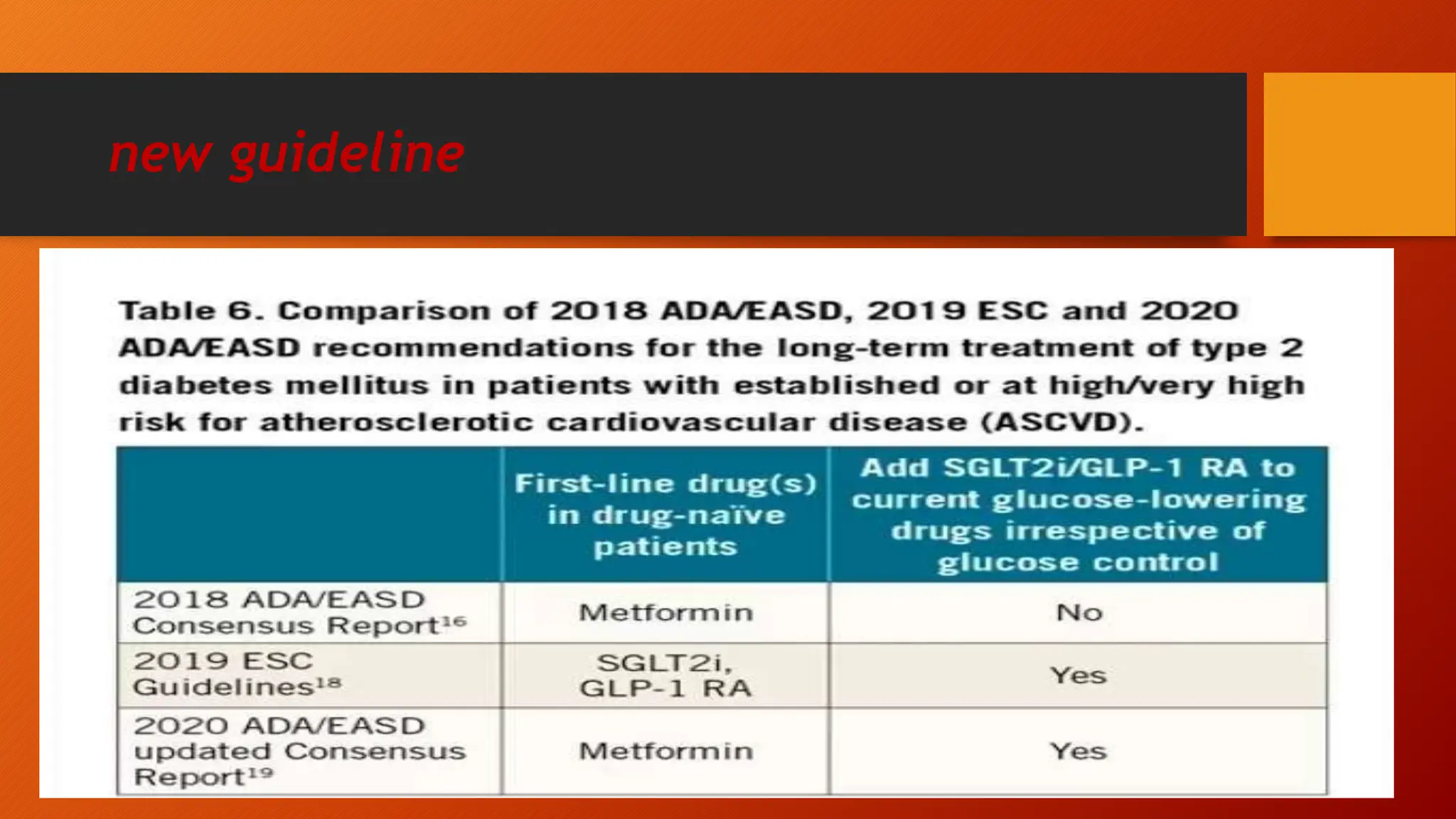
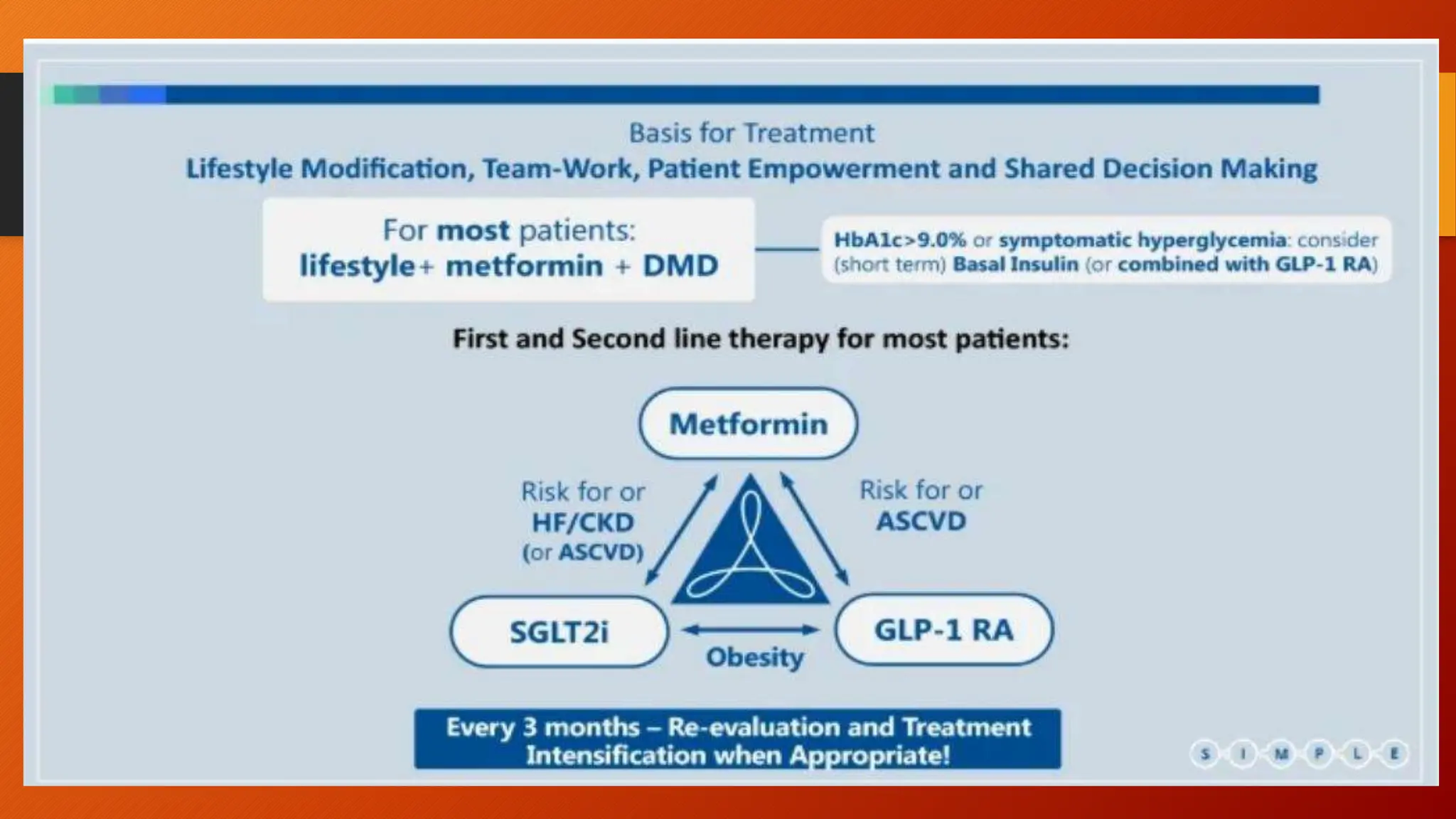
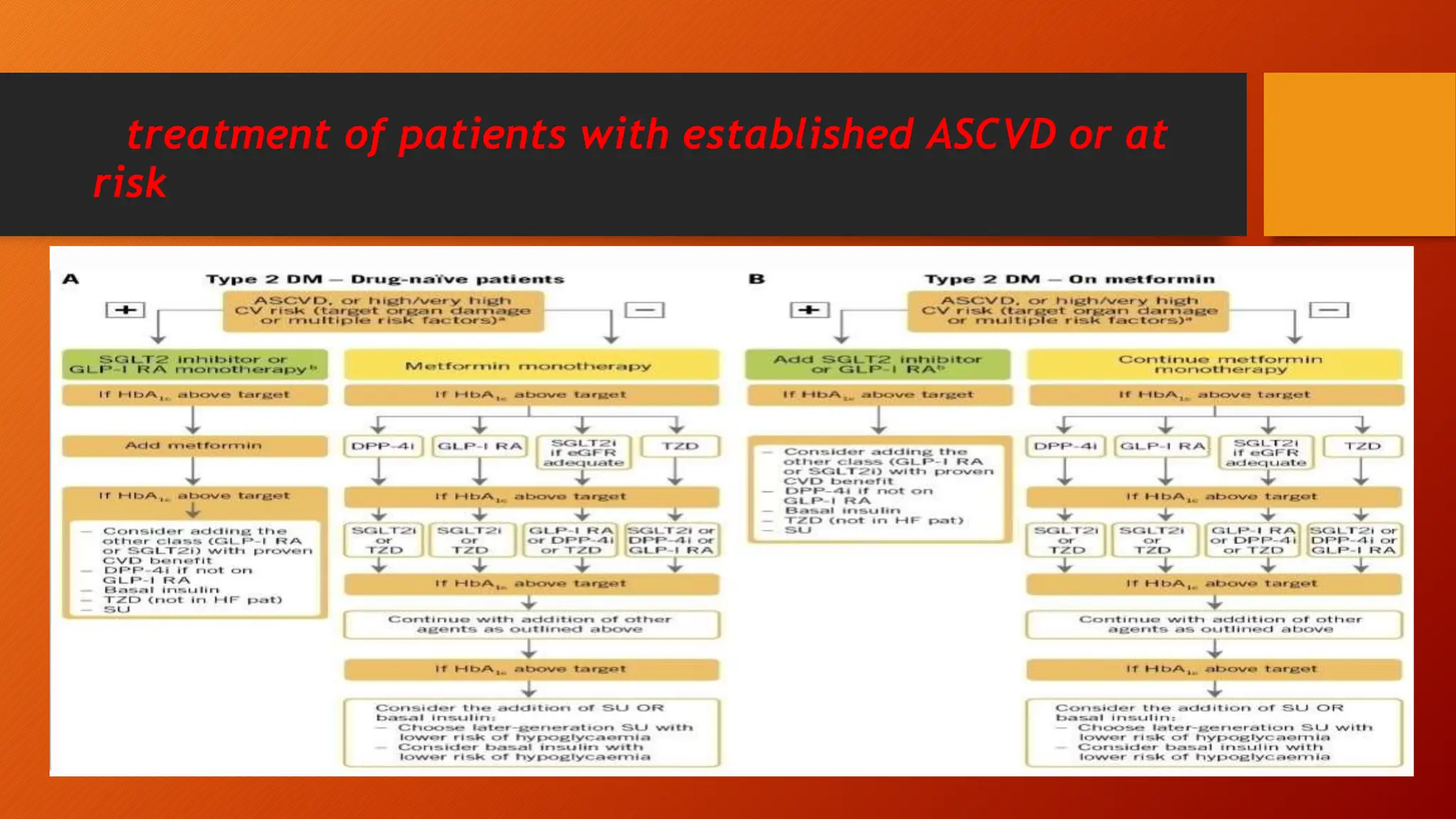
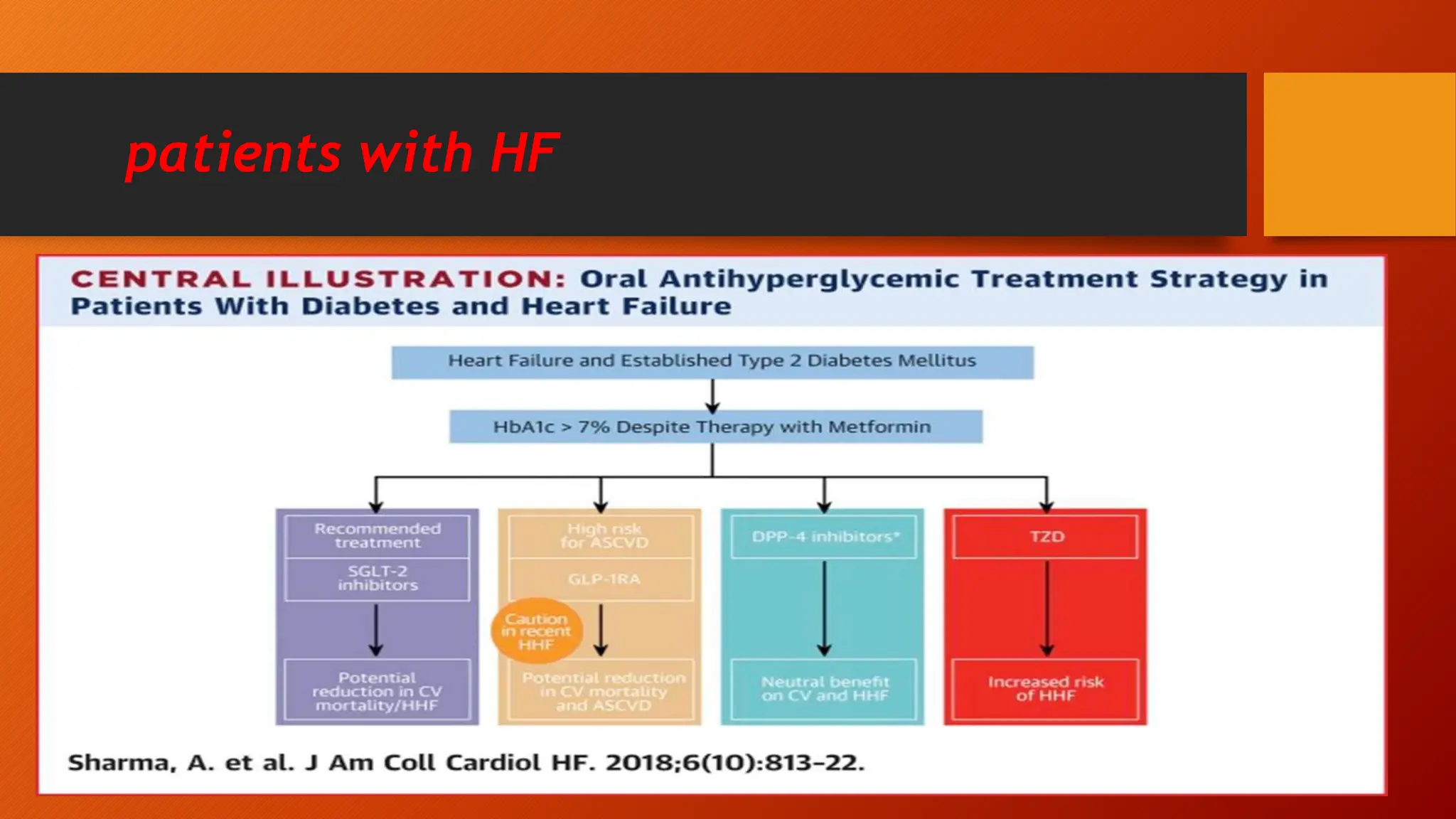
Type 2 diabetes is a significant independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD), influenced by factors such as glycemic variability, hypertension, and obesity. Effective treatment requires targeting tight glycemic control while managing all cardiovascular risk factors, avoiding hypoglycemia, and utilizing medications that provide cardiovascular benefits. Emphasis is placed on early use of disease-modifying drugs and addressing endothelial dysfunction to improve patient outcomes.






















