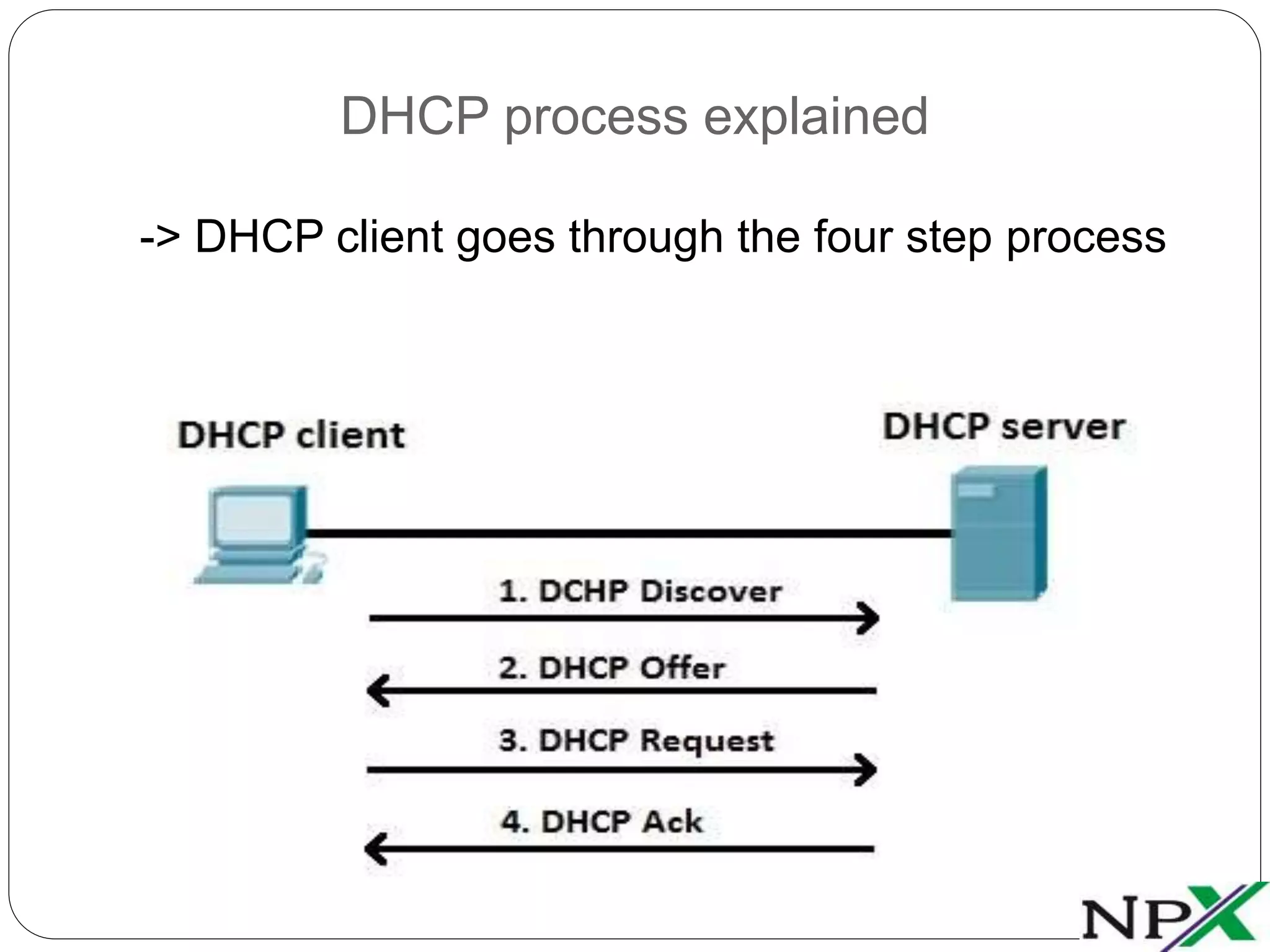
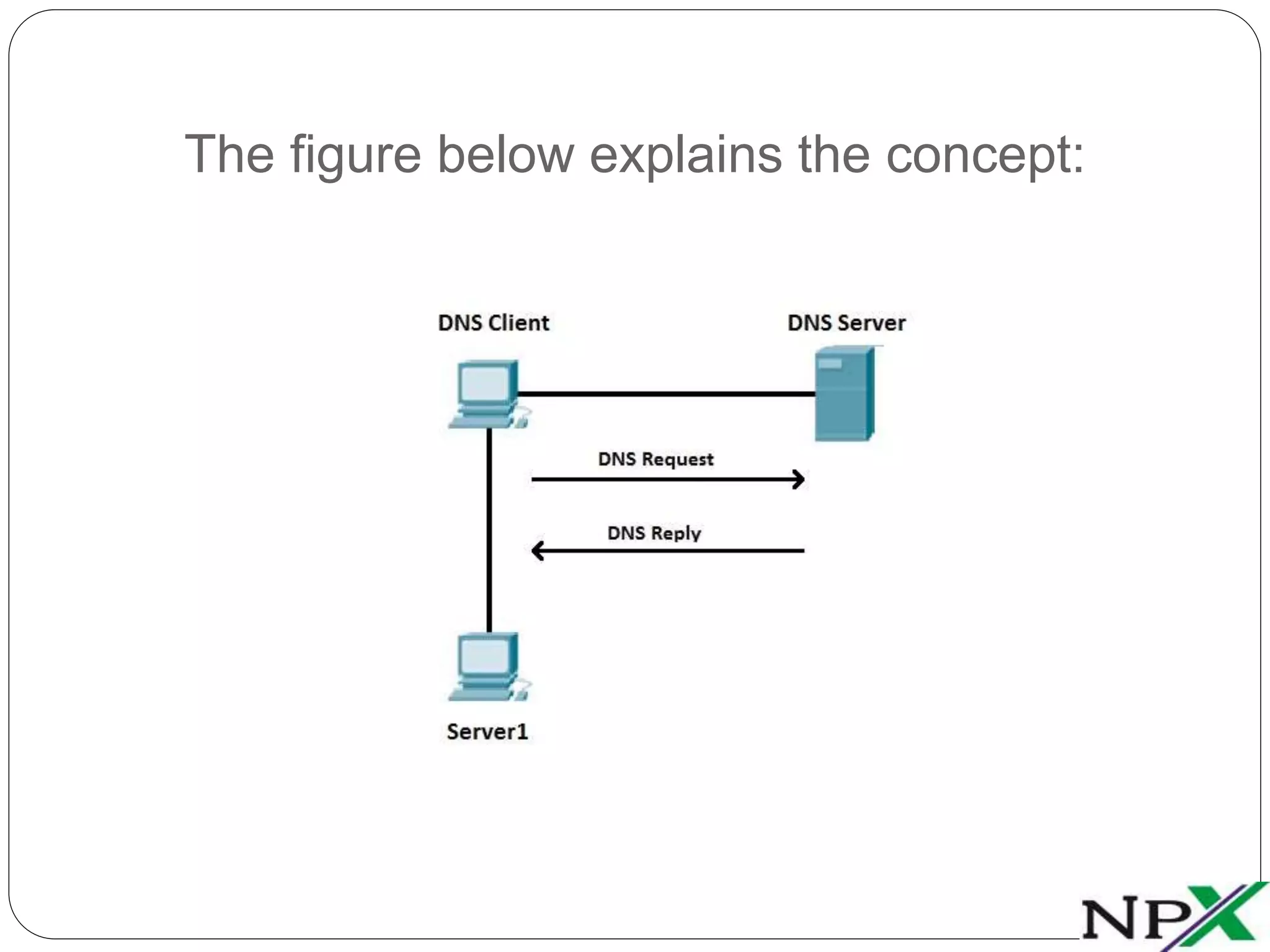
DHCP is a client-server protocol that assigns network parameters like IP addresses to devices from a server's address pool. A DHCP client broadcasts a request and the DHCP server responds with an offered address via acknowledgement packets. DNS translates human-friendly hostnames to IP addresses by querying a DNS server's address records, allowing users to access resources by name instead of numeric address. Together, DHCP and DNS simplify network configuration and access.