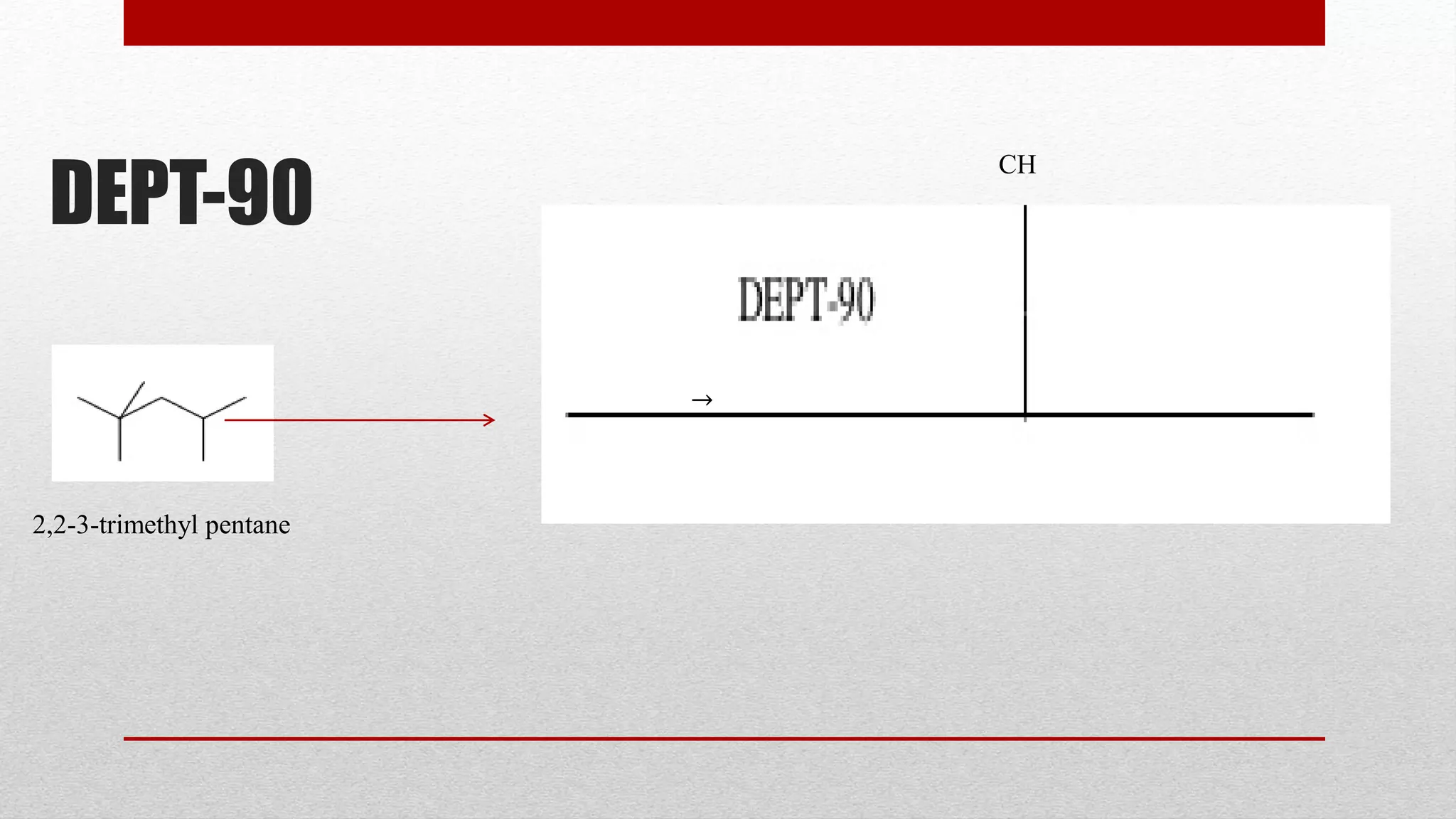
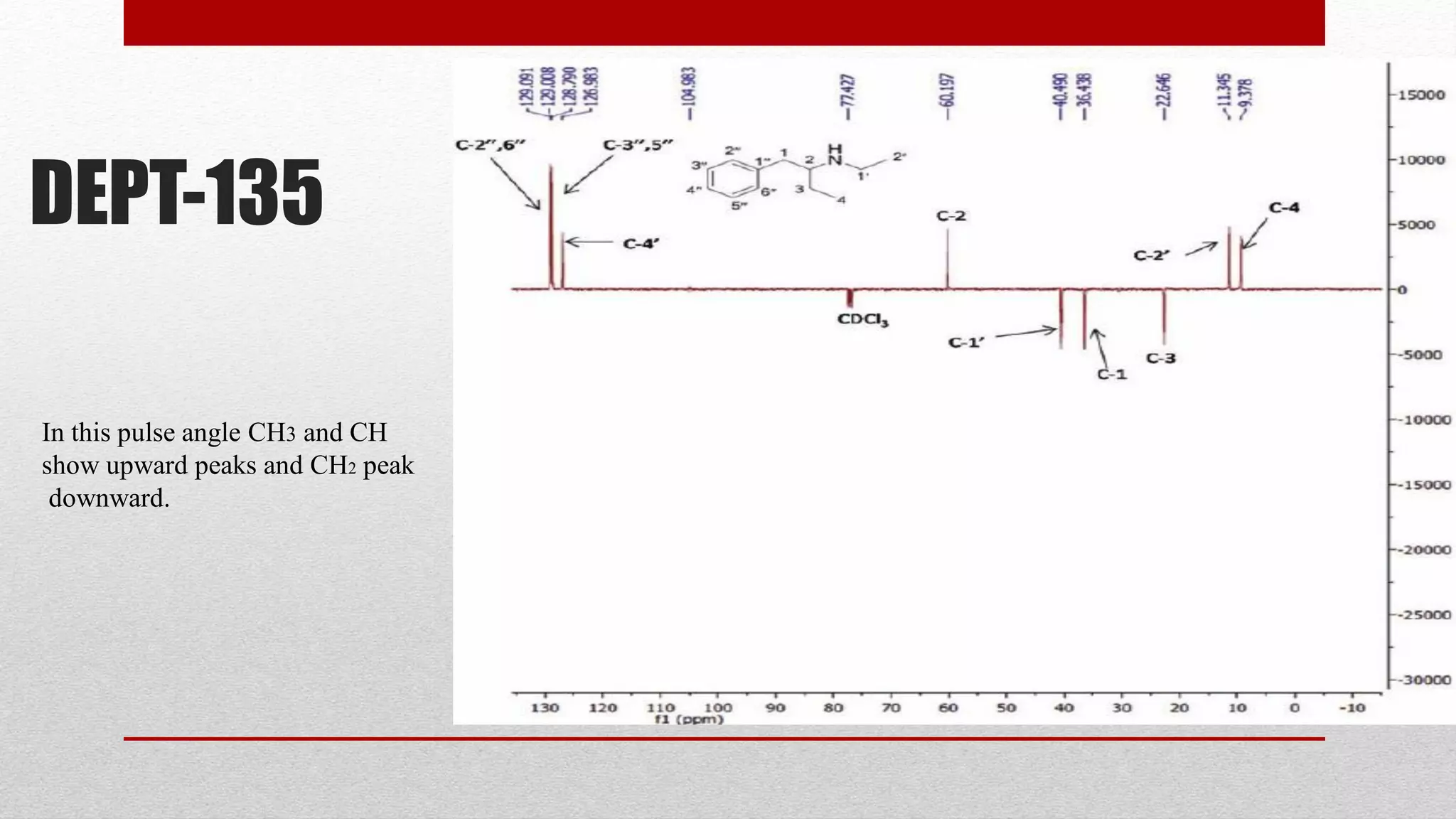
The document discusses the DEPT NMR experiment, which is used to determine the multiplicities of carbon-13 atoms. It introduces the DEPT experiment as using polarization transfer to provide more information than traditional off-resonance decoupled experiments. DEPT experiments are performed at different pulse angles (45°, 90°, 135°) to distinguish between CH, CH2, and CH3 groups. Examples of DEPT spectra are provided for isoamyl acetate and diethyl phthalate to demonstrate the peaks observed for different carbon types. The document provides an overview of the DEPT experiment and how it improves upon previous carbon NMR techniques.