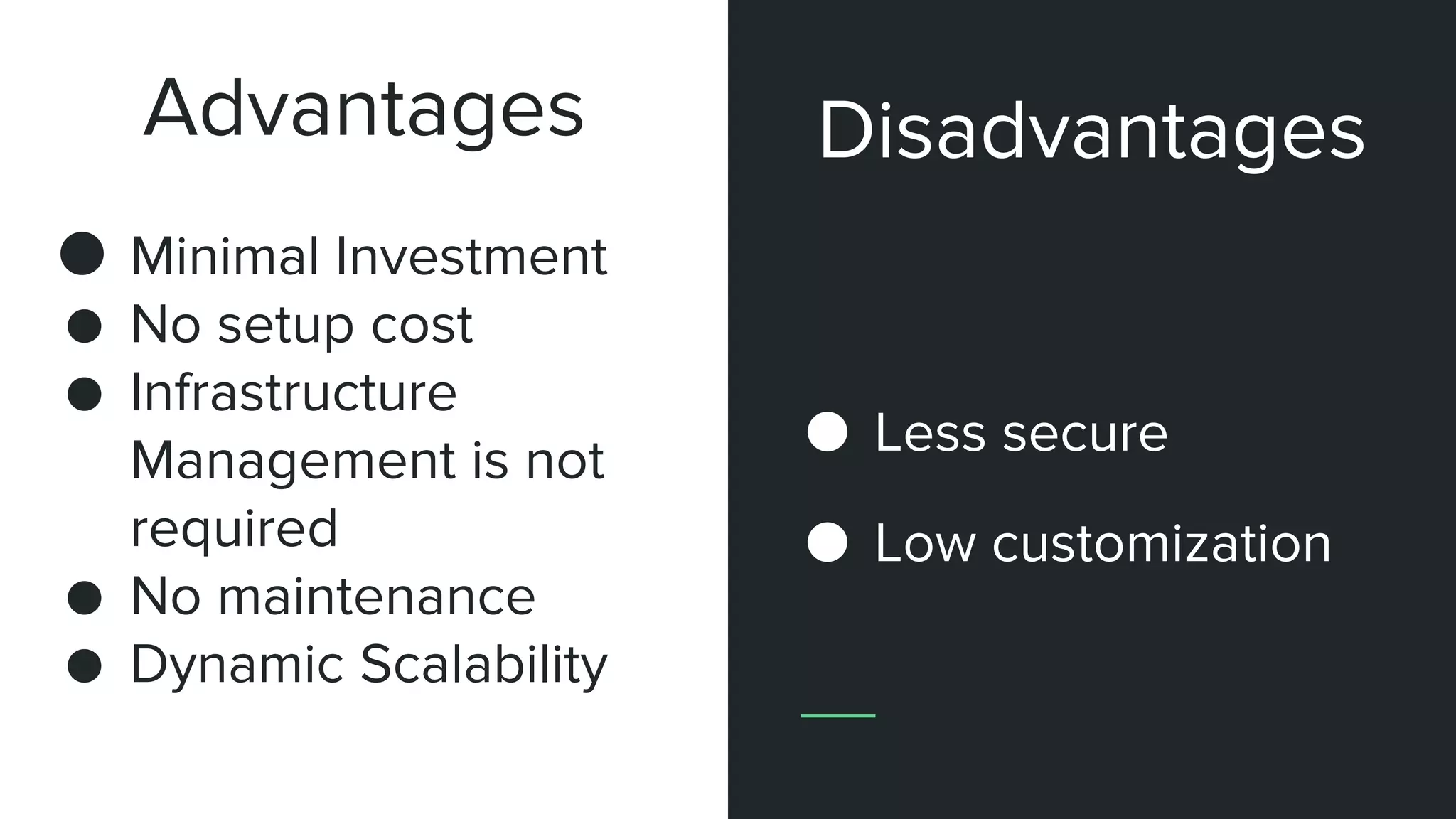
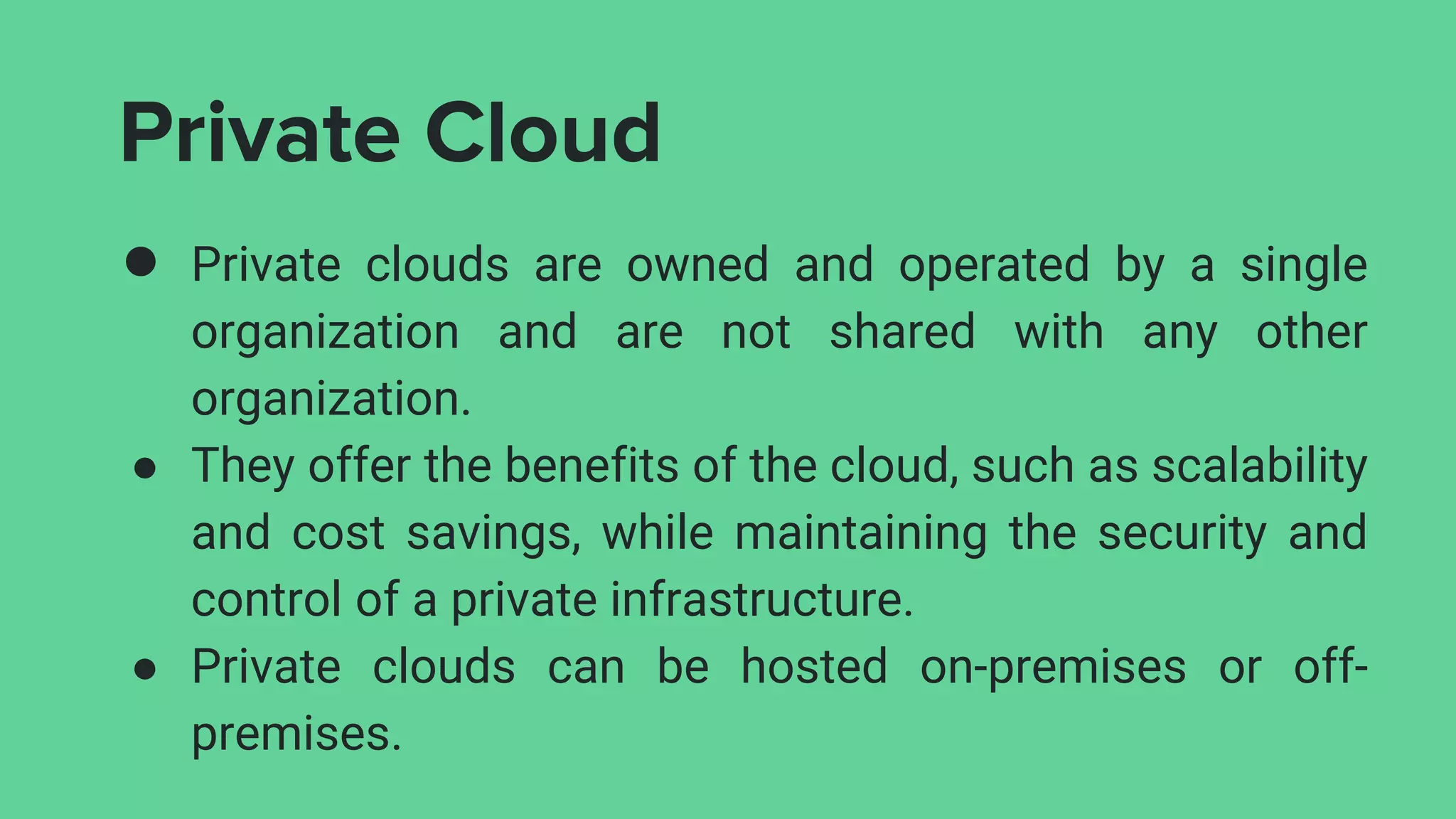
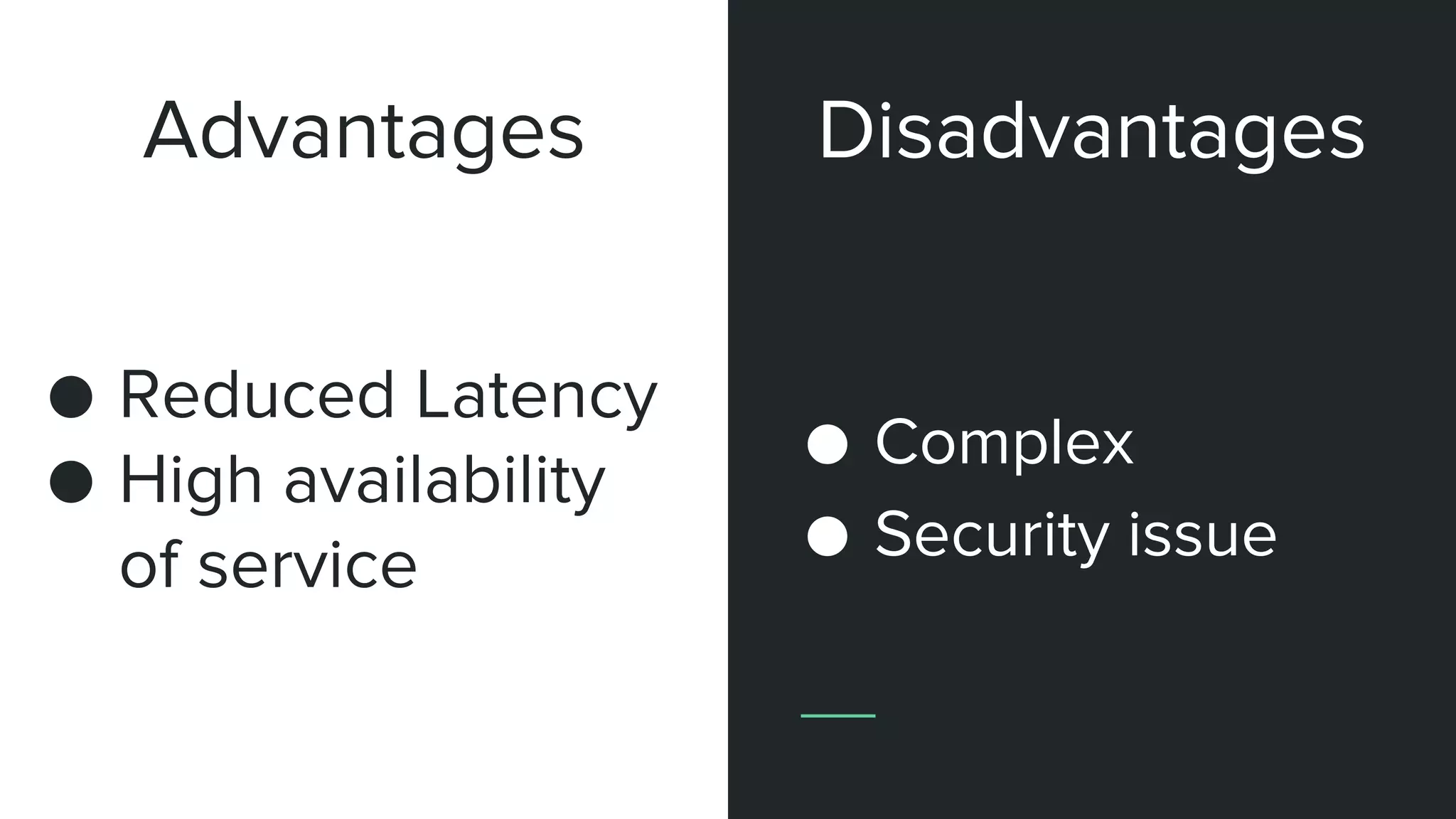
The document discusses various deployment models of cloud computing, including public, private, hybrid, community, and multi-cloud. It outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each model, such as cost-effectiveness and scalability for community clouds, and emphasizes flexibility and vendor choice in multi-cloud strategies. The overview helps organizations determine the best cloud solutions based on their specific needs and resources.