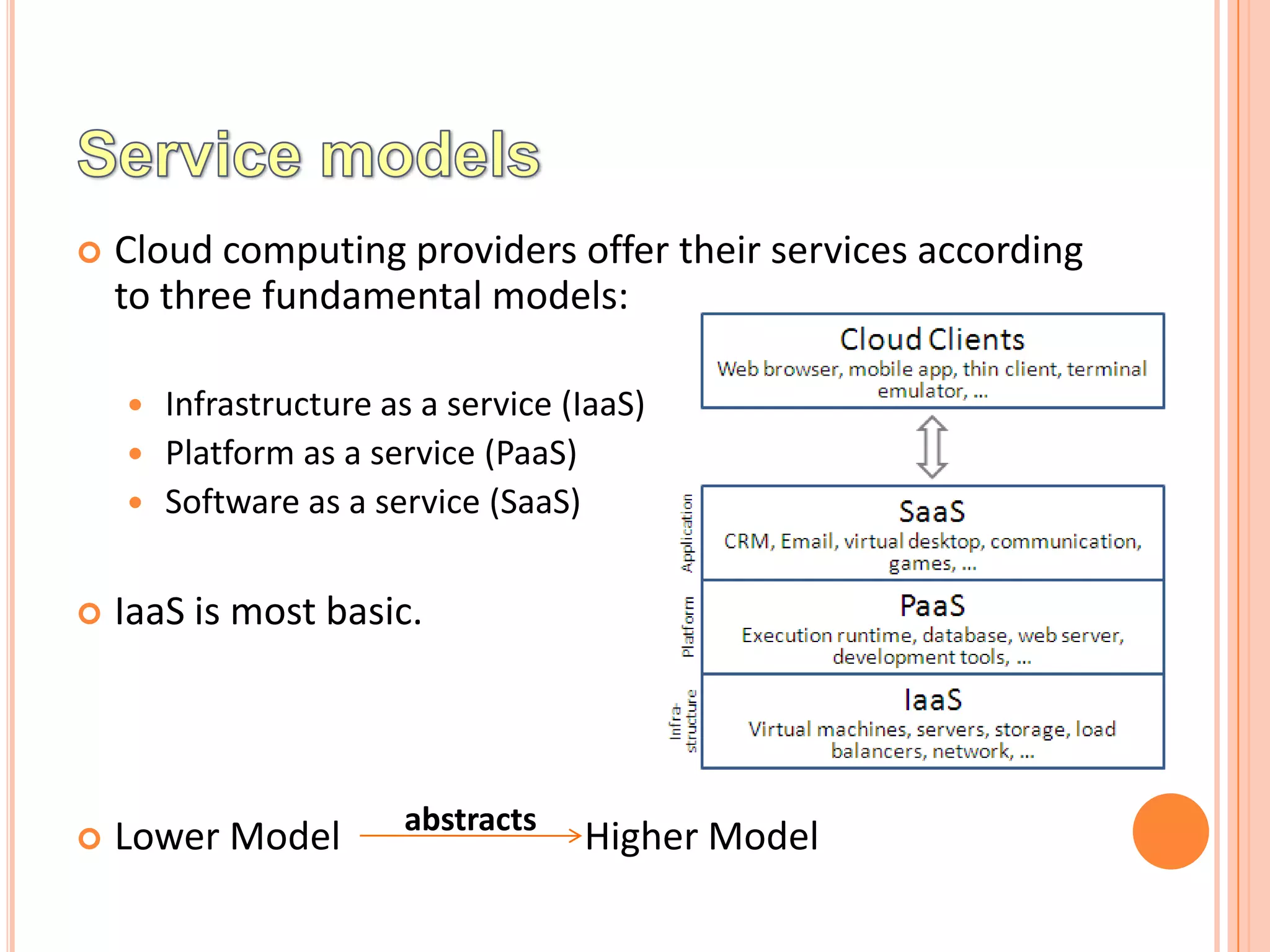
The document discusses cloud computing models including infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS). IaaS provides basic computing resources, storage, and networking capabilities. PaaS provides development tools and environments for building applications. SaaS provides users access to applications via the internet without installation or maintenance of software.