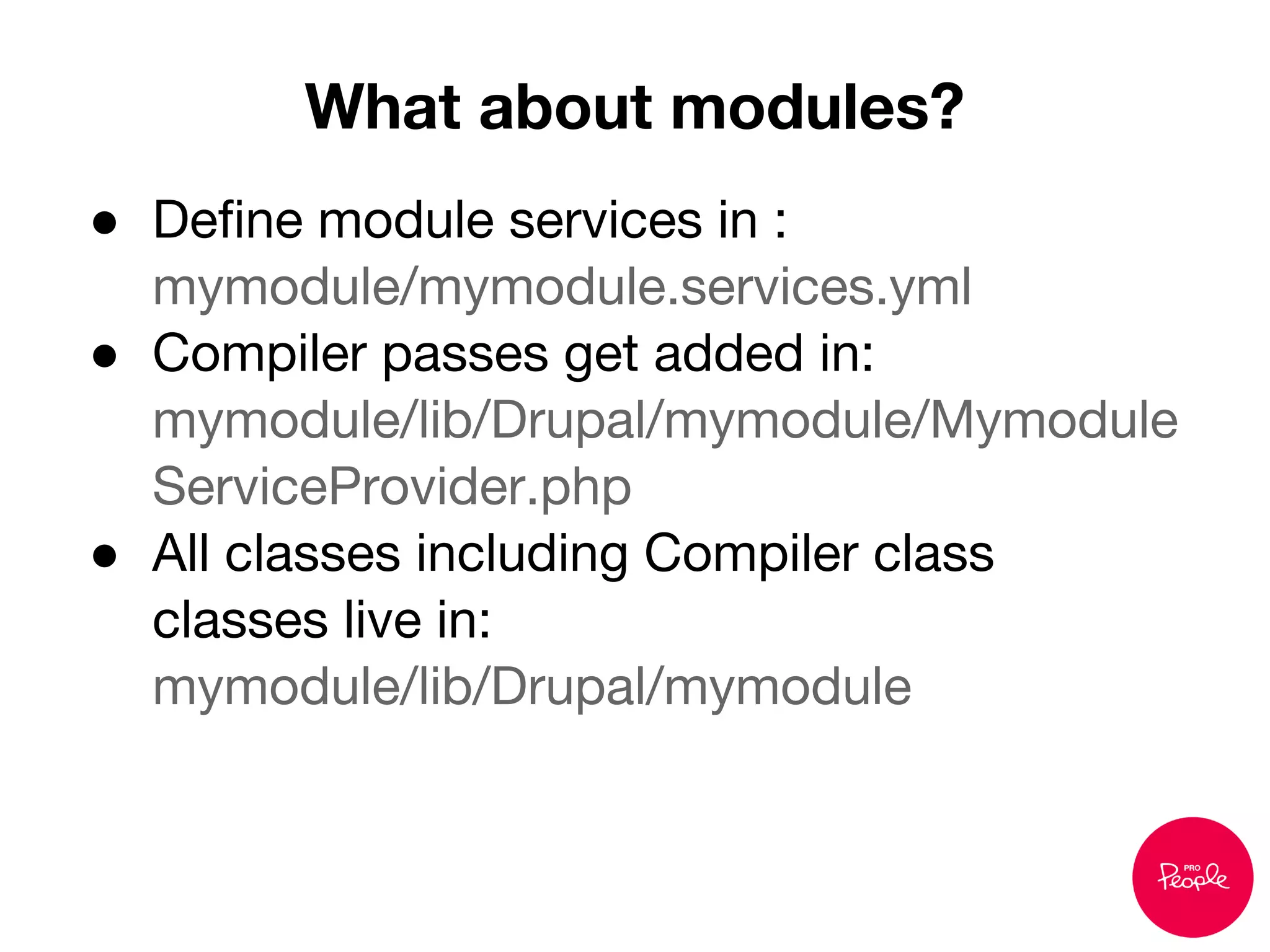
This document discusses dependency injection in Drupal 8. It begins by explaining the problems with Drupal 7 code, such as strong dependencies on globals and an inability to reuse or test code easily. It then introduces dependency injection as a design pattern that can help address these issues by reducing hard-coded dependencies. The document outlines how dependency injection works in Symfony and will work in Drupal 8 through the use of a service container that allows injecting dependencies into classes.
















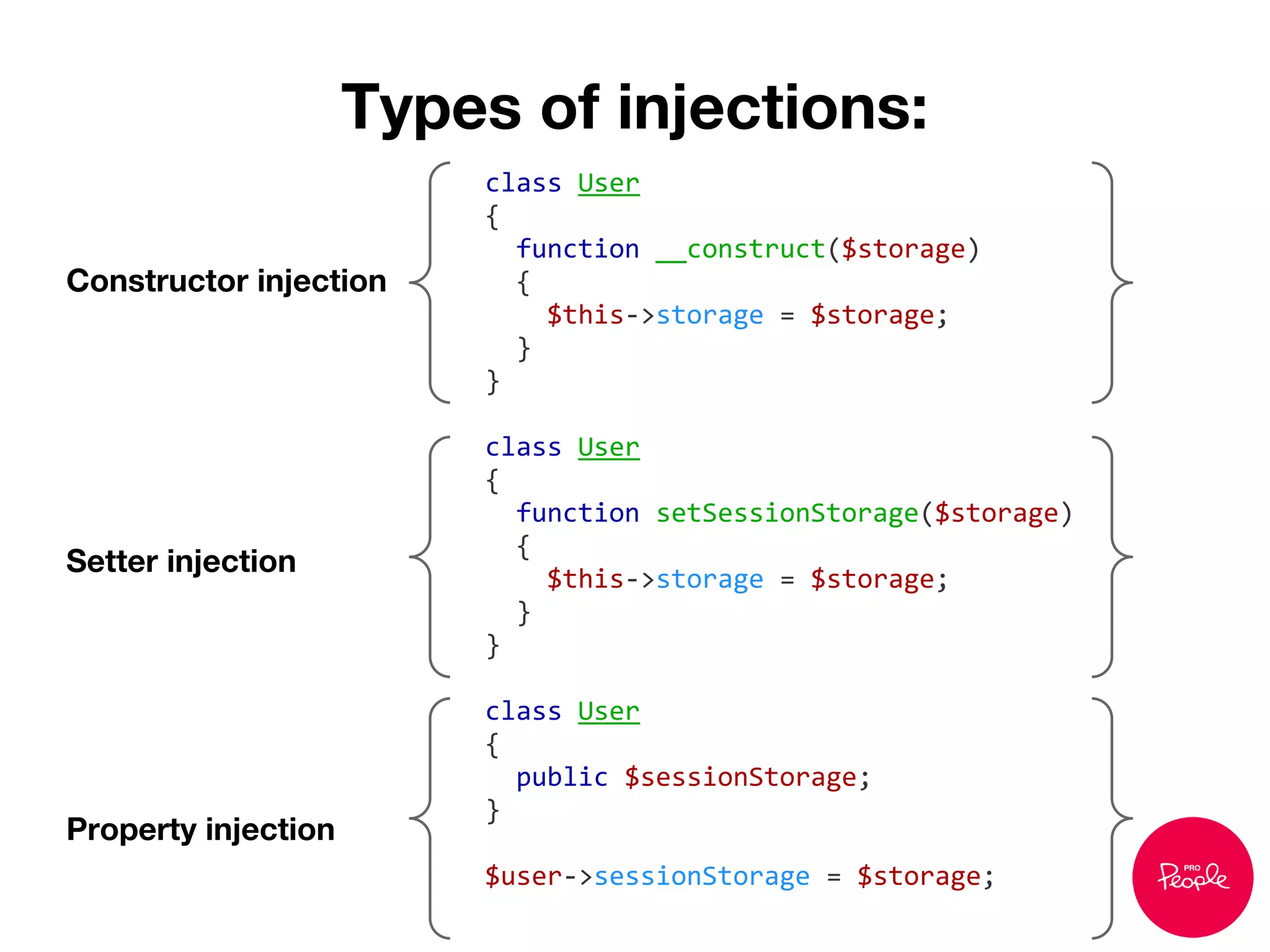
![User class uses sessions to store language
class SessionStorage
{
function __construct($cookieName = 'PHP_SESS_ID')
{
session_name($cookieName);
session_start();
}
function set($key, $value)
{
$_SESSION[$key] = $value;
}
function get($key)
{
return $_SESSION[$key];
}
// ...
}
class User
{
protected $storage;
function __construct()
{
$this->storage = new SessionStorage();
}
function setLanguage($language)
{
$this->storage->set('language', $language);
}
function getLanguage()
{
return $this->storage->get('language');
}
// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjection-130914082156-phpapp01/75/Dependency-injection-in-Drupal-8-17-2048.jpg)





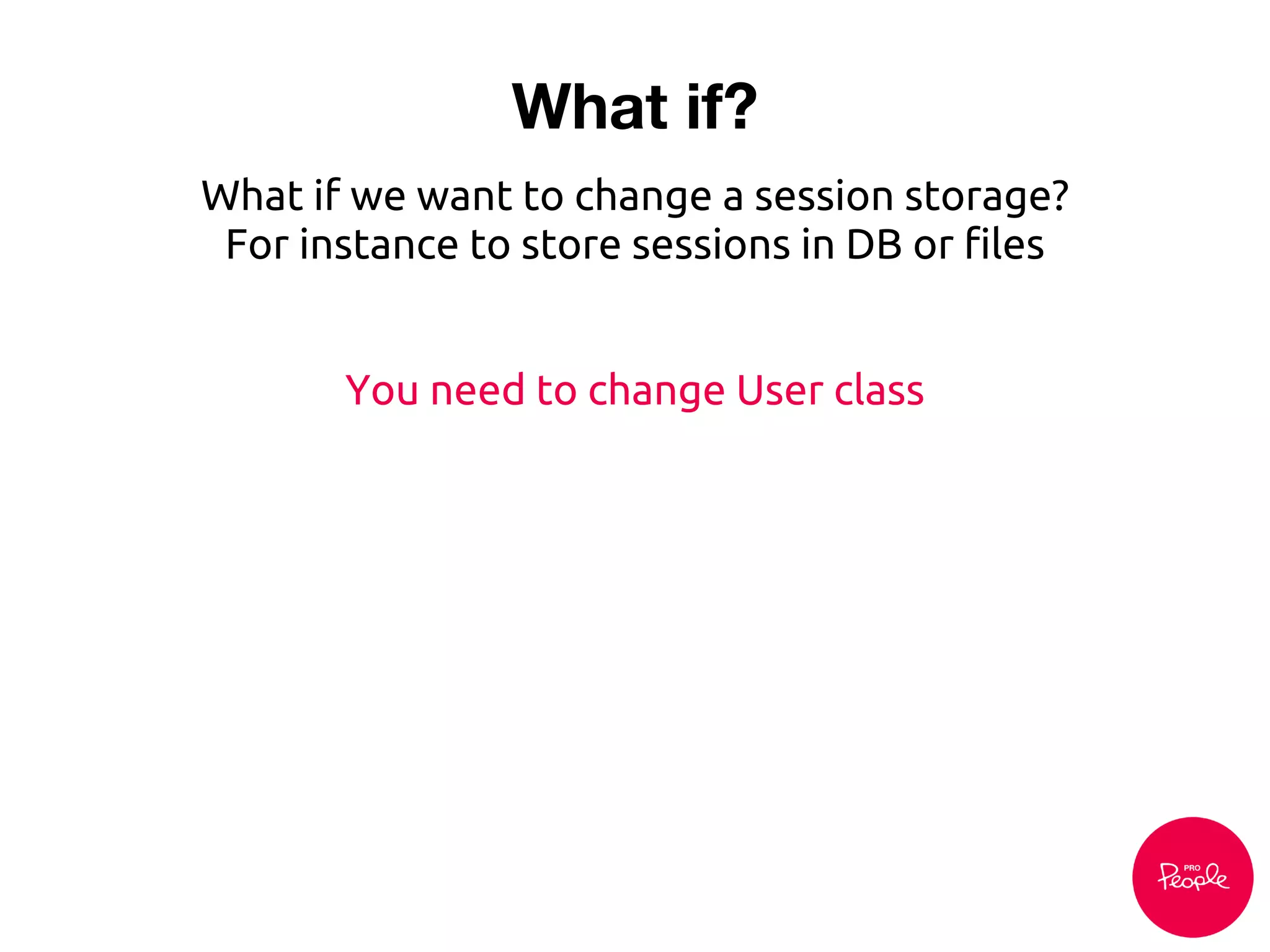
![What if?
class User
{
function __construct($storageOptions)
{
$this->storage = new SessionStorage($storageOptions
['session_name']);
}
// ...
}
$user = new User(array('session_name' => 'SESSION_ID'));
Send an array of options as User argument
What if we want to change a session cookie name?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjection-130914082156-phpapp01/75/Dependency-injection-in-Drupal-8-23-2048.jpg)












![Using YAML
parameters:
mailer.class: Mailer
mailer.transport: sendmail
services:
mailer:
class: "%mailer.class%"
arguments: ["%my_mailer.transport%"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjection-130914082156-phpapp01/75/Dependency-injection-in-Drupal-8-38-2048.jpg)
![Using YAML
parameters:
mailer.class: Mailer
mailer.transport: sendmail
services:
mailer:
class: "%mailer.class%"
arguments: ["%my_mailer.transport%"]
Loading a service from yml file.
require_once '/PATH/TO/sfServiceContainerAutoloader.php';
sfServiceContainerAutoloader::register();
$sc = new sfServiceContainerBuilder();
$loader = new sfServiceContainerLoaderFileYaml($sc);
$loader->load('/somewhere/services.yml');](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjection-130914082156-phpapp01/75/Dependency-injection-in-Drupal-8-39-2048.jpg)




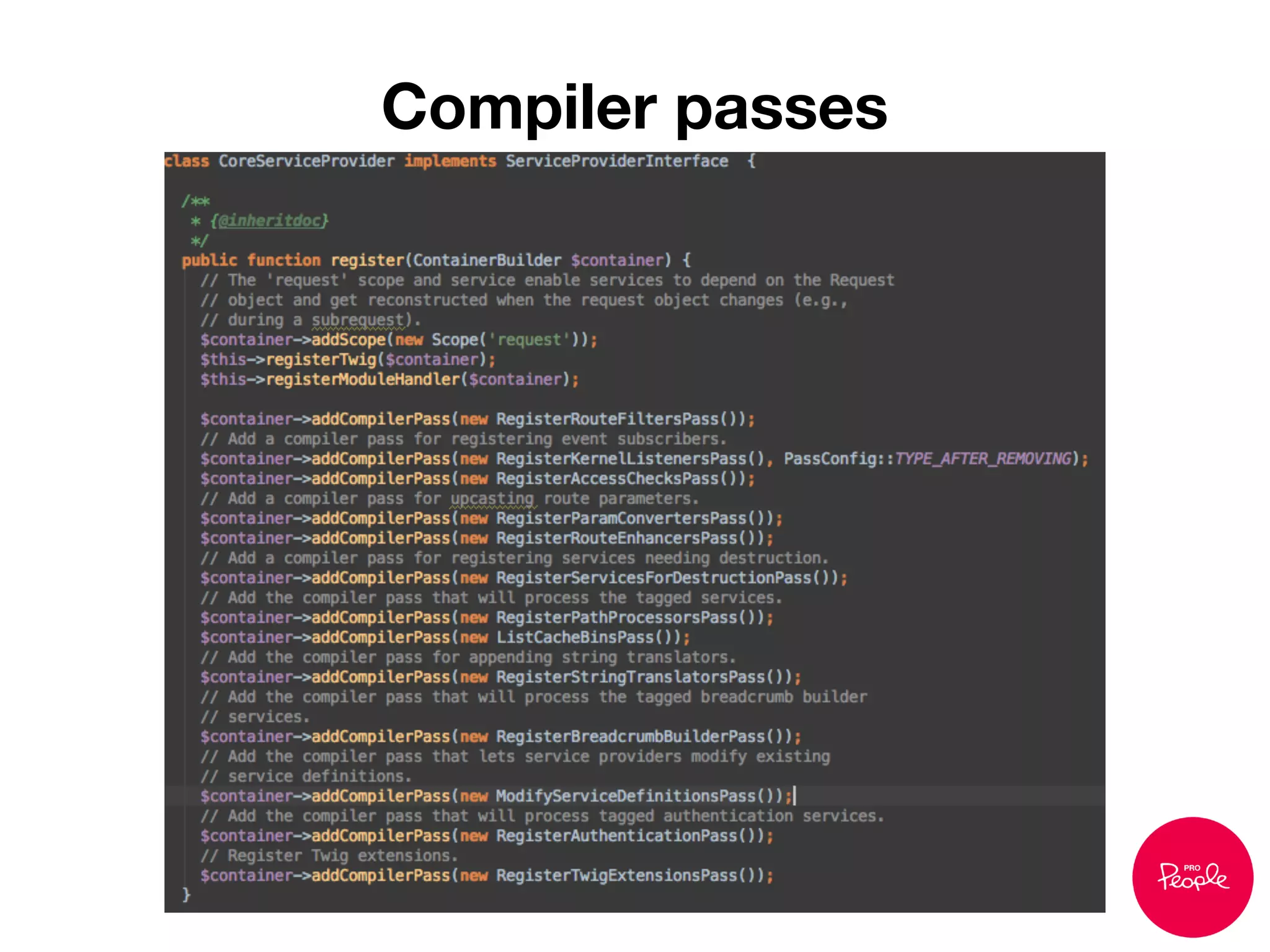



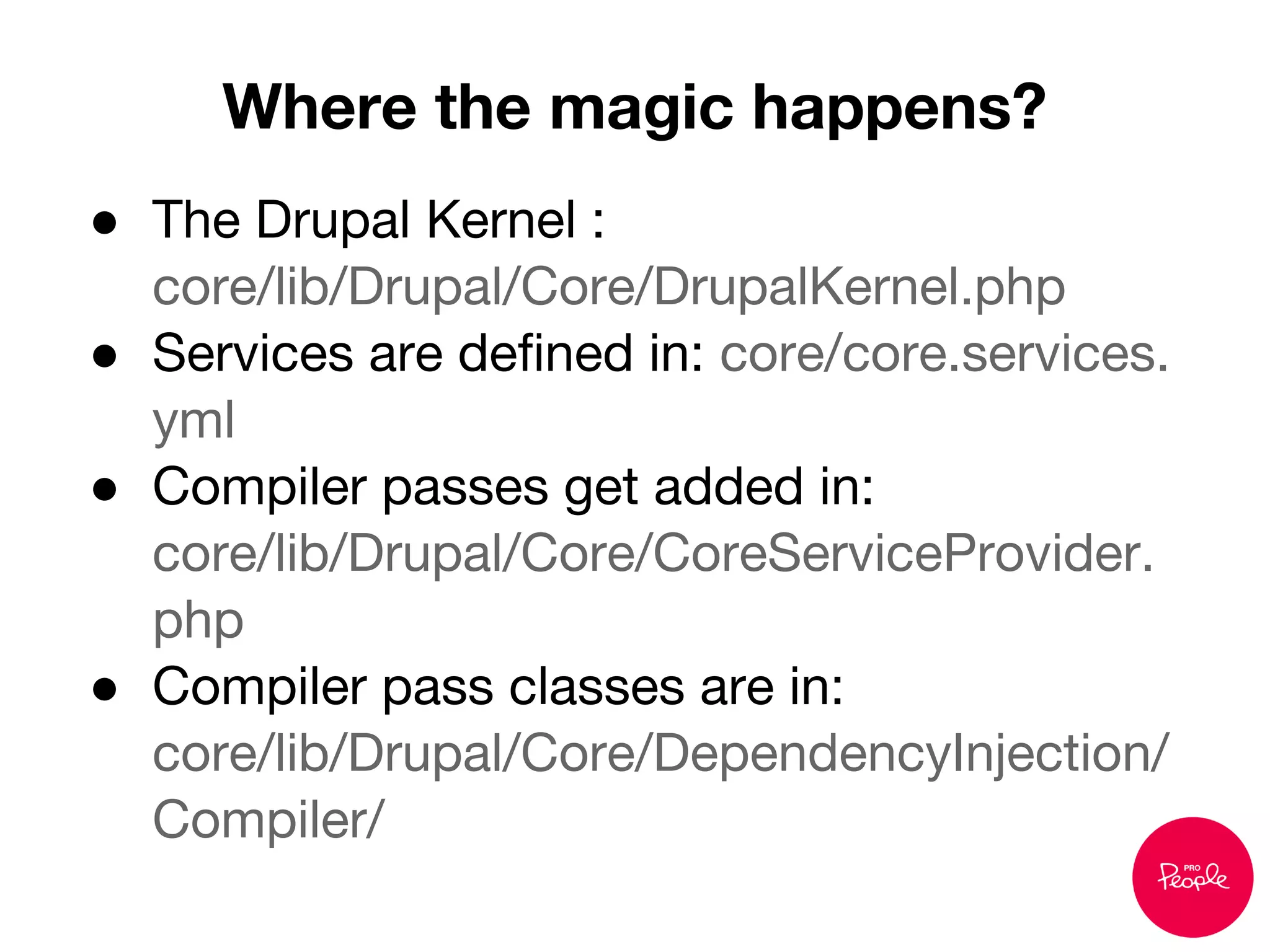
![1. Write OO code and get wired into the container.
2. In case of legacy procedural code you can use:
Drupal::service(‘some_service’);
Example:
Drupal 7:
$path = $_GET['q']
Drupal 8:
$request = Drupal::service('request');
$path = $request->attributes->get('_system_path');
Ways to use core’s services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjection-130914082156-phpapp01/75/Dependency-injection-in-Drupal-8-52-2048.jpg)