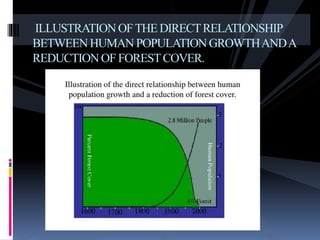
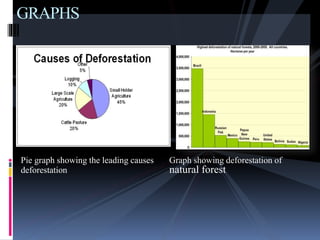
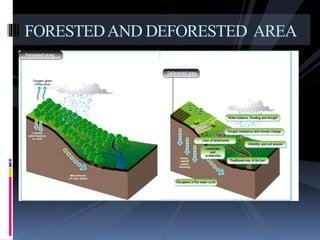
Deforestation is the conversion of forested areas to non-forested land. It occurs for various reasons like timber, agriculture, infrastructure development, and fuel needs. Deforestation has negative environmental consequences such as increased carbon emissions, loss of biodiversity, soil erosion, and disrupted water cycles. Some solutions to deforestation include sustainable logging, reforestation, afforestation, and increasing awareness about environmental protection. Pakistan has one of the highest deforestation rates in the world primarily due to fuel wood consumption and population growth.