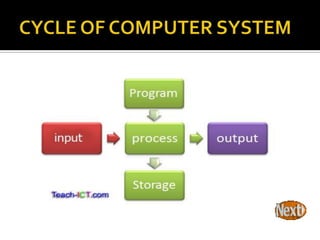
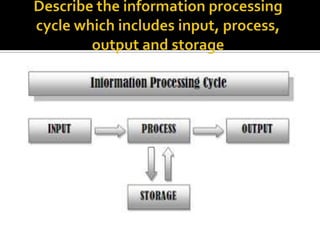
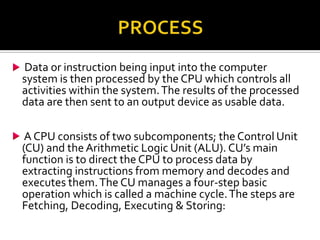
A computer system takes inputs, processes them using hardware and software, and produces outputs. It has input devices that provide data, a central processing unit (CPU) that processes the data, and output devices that display or store the processed data. Storage devices like hard drives are used to store programs and data for future use, as primary storage in RAM is only temporary. The system takes inputs, processes them using programs stored in storage, and creates outputs.