This document outlines different methods for handling deadlocks in operating systems, including deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery. It discusses the four necessary conditions for deadlock and defines a resource-allocation graph model. For deadlock prevention, it describes ways to ensure that the mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait conditions cannot simultaneously hold through protocols like requesting all resources at start, releasing resources before requesting new ones, preempting held resources, and imposing a total ordering of resource types. Deadlock avoidance uses additional process information to decide if a request should wait. Detection identifies deadlocks in the system state, while recovery terminates processes or preempts resources.





![7
Deadlocks (Galvin)
DEADLOCK DETECTION
If a systemdoesnot employeither a deadlock-preventionor a deadlockavoidance algorithm, thena deadlocksituationmayoccur. Inthis environment,
the systemmayprovide:
An algorithmthat examines the state of the systemto determine whether a deadlockhas occurred
An algorithmto recover from the deadlock
In the followingdiscussion, we elaborate onthese two requirements as theypertainto systems withonlya single instance of eachresource type, as well
as to systems with several instancesof eachresource type. At this point, however,we note that a detection-and-recoveryscheme requiresoverheadthat
includes not onlythe run-time costs of maintaining the necessaryinformationandexecutingthe detection algorithm but alsothe potentiallosses
inherent in recoveringfrom a deadlock.
Single Instance of Each Resource Type
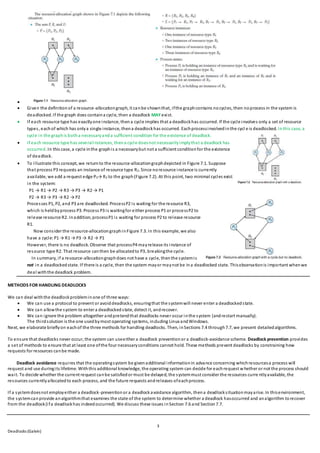
If all resources have onlya single instance, then we candefine a deadlock detectionalgorithmthat usesa variant of the resource-allocation graph, called
a wait-for graph. We obtainthisgraphfrom the resource-allocation graph by removing the resource nodes andcollapsing the appropriate edges. More
precisely, anedge from Pi to Pj in a wait-for graph implies that process Pi is waitingfor processPj to release a resource that Pi needs. An edge Pi → Pj
exists ina wait-for graphifandonlyif the correspondingresource allocationgraphcontains two edges Pi → Rq and Rq → Pj for some resource Rq . In
Figure 7.9, we present a resource-allocationgraphandthe correspondingwait-for graph.
As before, a deadlock exists inthe system if andonlyif the wait-for graphcontains a cycle. To detect deadlocks, the systemneeds to maintain the
wait for graphandperiodicallyinvoke analgorithm that searches for a cycle inthe graph. An algorithmto detect a cycle in a graphrequires an order of
n2 operations, where n is the number of vertices inthe graph.
Several Instances of a Resource Type
The wait-for graph scheme is not applicable to a resource-allocation system withmultiple instances ofeachresource type. We turn now to a deadlock
detection algorithm that is applicable to sucha system. The algorithm employs several time-varyingdata structures that are similar to those used inthe
banker’s algorithm:
• Available. A vector of length m indicates the number of available resources ofeachtype.
• Allocation. An n × m matrix defines the number of resources of each type currentlyallocated to each process.
• Request. An n × m matrix indicates the current request of each process. If Request[i][j] equals k, thenprocess Pi is requesting k more instances of
resource type Rj .
The ≤ relation betweentwo vectors is defined as in Section7.5.3. To simplifynotation, we again treat the rows in the matricesAllocationand Request as
vectors;we refer to them as Allocationi and Requesti . The detectionalgorithm describedhere simplyinvestigateseverypossible allocationsequence for
the processes that remainto be completed. Compare this algorithm withthe banker’s algorithm of Section7.5.3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deadlocksprefinal-161014115456/85/Deadlocks-prefinal-7-320.jpg)

