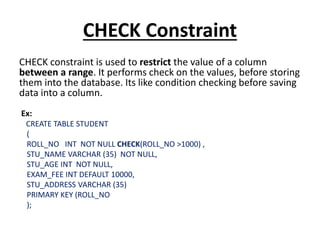
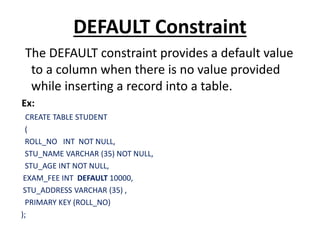
This document discusses database constraints. It explains that constraints are used to specify rules for data in tables to maintain integrity. There are two levels of constraints - column and table level. The main types of constraints are NOT NULL, UNIQUE, CHECK, DEFAULT, and key constraints like PRIMARY KEY and FOREIGN KEY. Constraints enforce limits on the data, make columns non-nullable, enforce unique values, check value ranges, provide default values, and relate tables through primary and foreign keys. Maintaining constraints helps ensure only valid data is stored in the database.