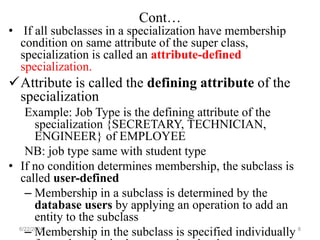
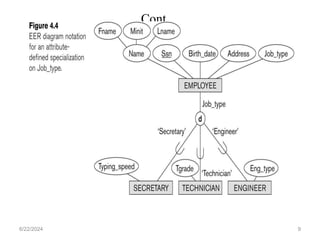
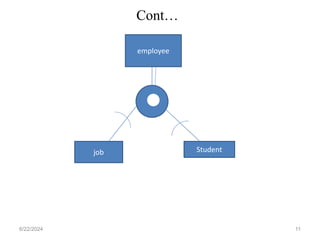
The document covers the fundamentals of enhanced entity-relationship and object modeling, focusing on concepts such as subclass, superclass, specialization, generalization, and inheritance. It explains how subclasses are subsets of entities in a superclass and outlines the processes of specialization and generalization. Additionally, it addresses constraints such as disjointness and completeness in specialization/generalization relationships.