Embed presentation
Downloaded 69 times



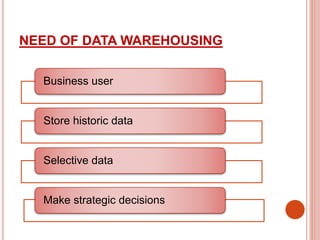
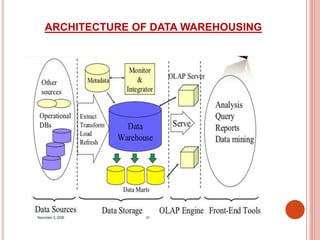

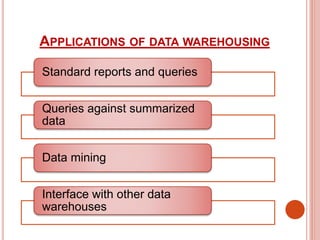



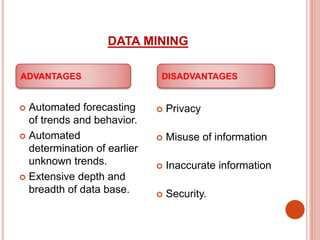


The presentation discusses data warehousing as a subject-oriented, integrated, and time-varying data collection that aids decision-making, highlighting its advantages like competitive advantage and enhanced customer service, as well as drawbacks such as complexity and security issues. It also covers data mining, which focuses on extracting knowledge from large datasets, including its architecture, advantages, disadvantages, and applications across various sectors like marketing and healthcare. Both concepts emphasize the importance of effective data management for strategic business decisions.












