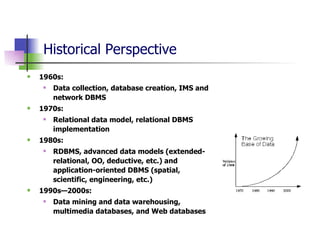
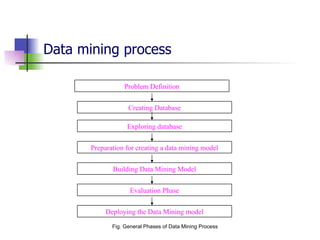
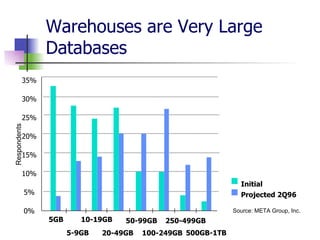
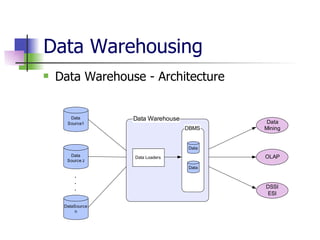
Data mining and data warehousing have evolved since the 1960s due to increases in data collection and storage. Data mining automates the extraction of patterns and knowledge from large databases. It uses predictive and descriptive models like classification, clustering, and association rule mining. The data mining process involves problem definition, data preparation, model building, evaluation, and deployment. Data warehouses integrate data from multiple sources for analysis and decision making. They are large, subject-oriented databases designed for querying and analysis rather than transactions. Data warehousing addresses the need to consolidate organizational data spread across various locations and systems.