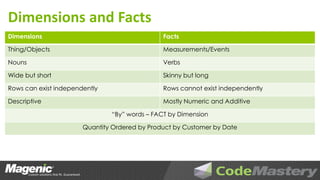
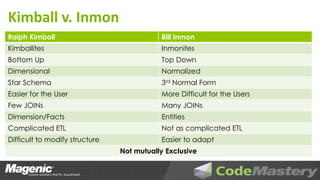
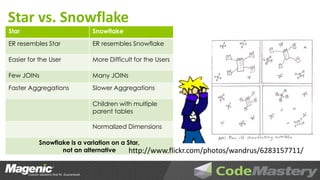
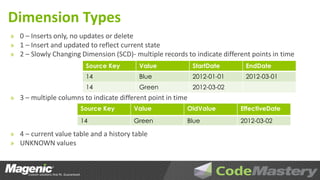
The document outlines the principles of data warehouse design and dimensional modeling by Aaron Lowe, emphasizing the necessity of a cohesive information model that integrates data from various operational systems. It discusses the distinctions between different data modeling methodologies, including Kimball and Inmon, and highlights key concepts such as dimensions, facts, and the significance of how data relationships are structured. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of data completeness and the importance of metadata management in ensuring accurate and timely reporting for business insights.