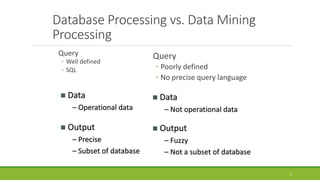
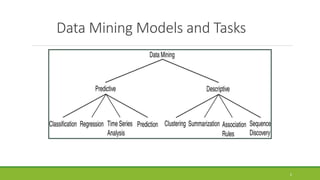
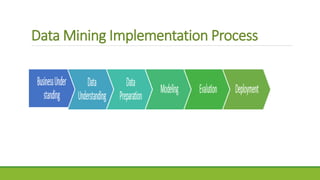
This document introduces data mining. It defines data mining as the process of extracting useful information from large databases. It discusses technologies used in data mining like statistics and machine learning. It also covers data mining models and tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, and forecasting. Finally, it provides an overview of the data mining process and examples of data mining tools.