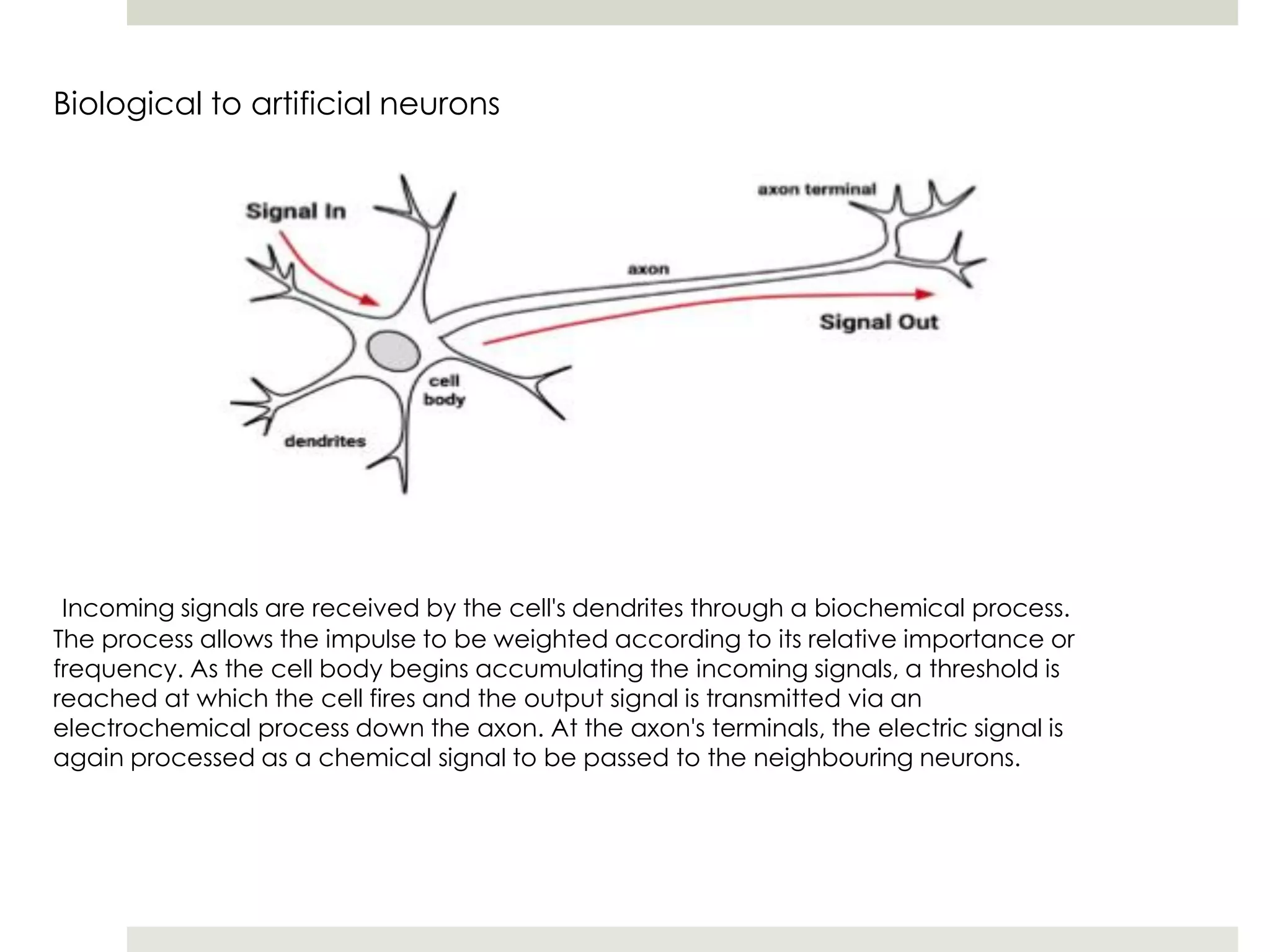
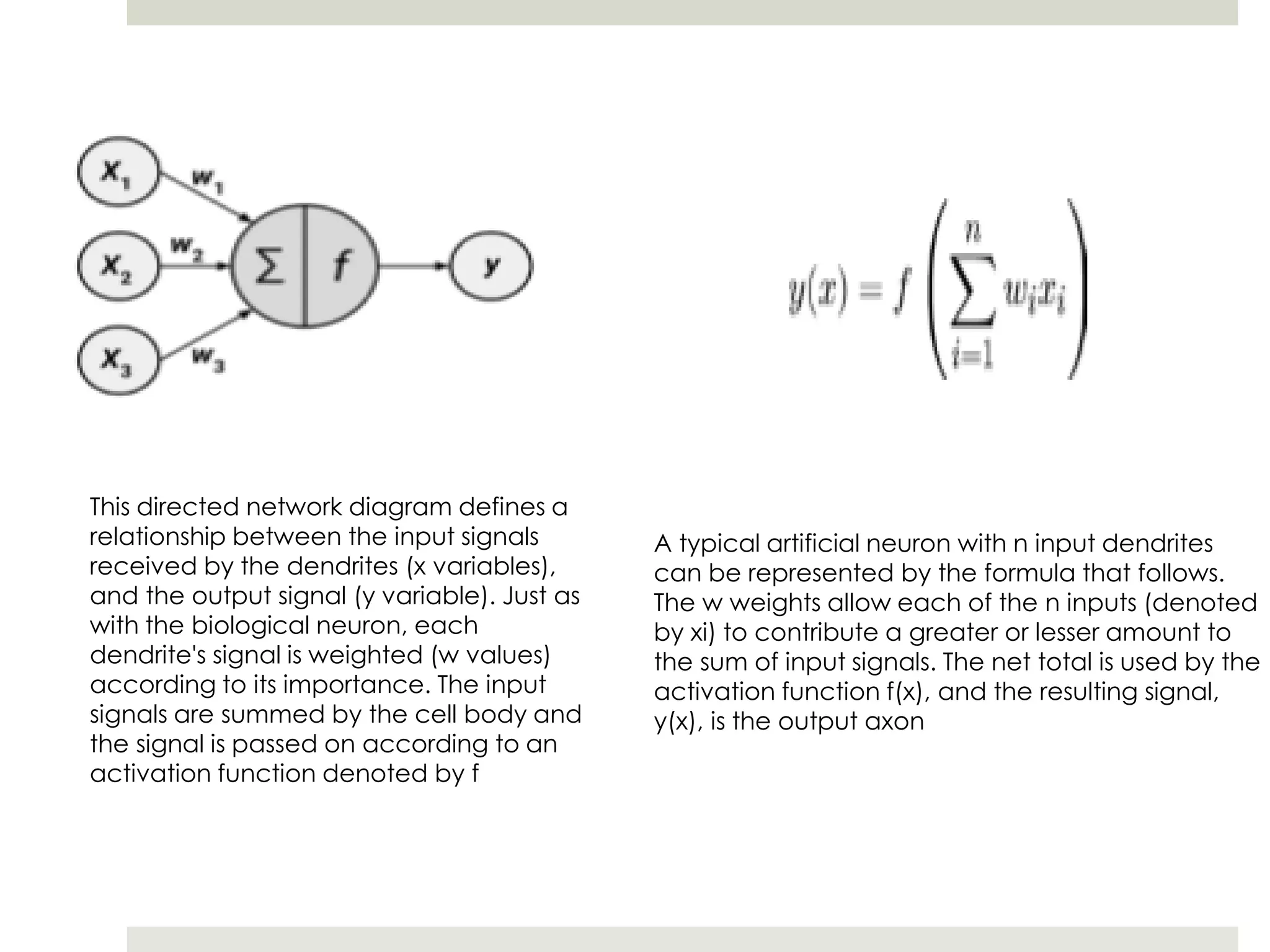
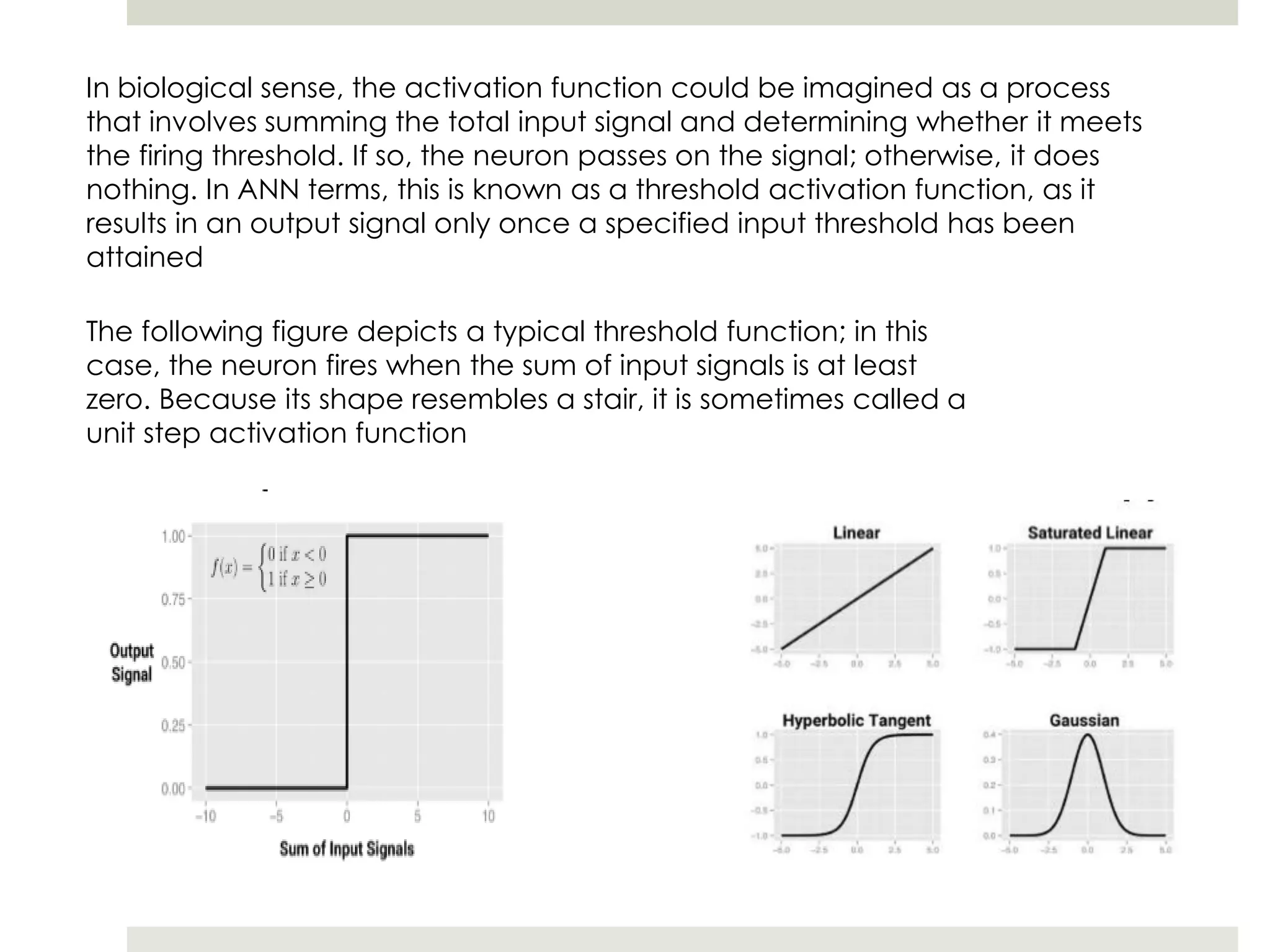
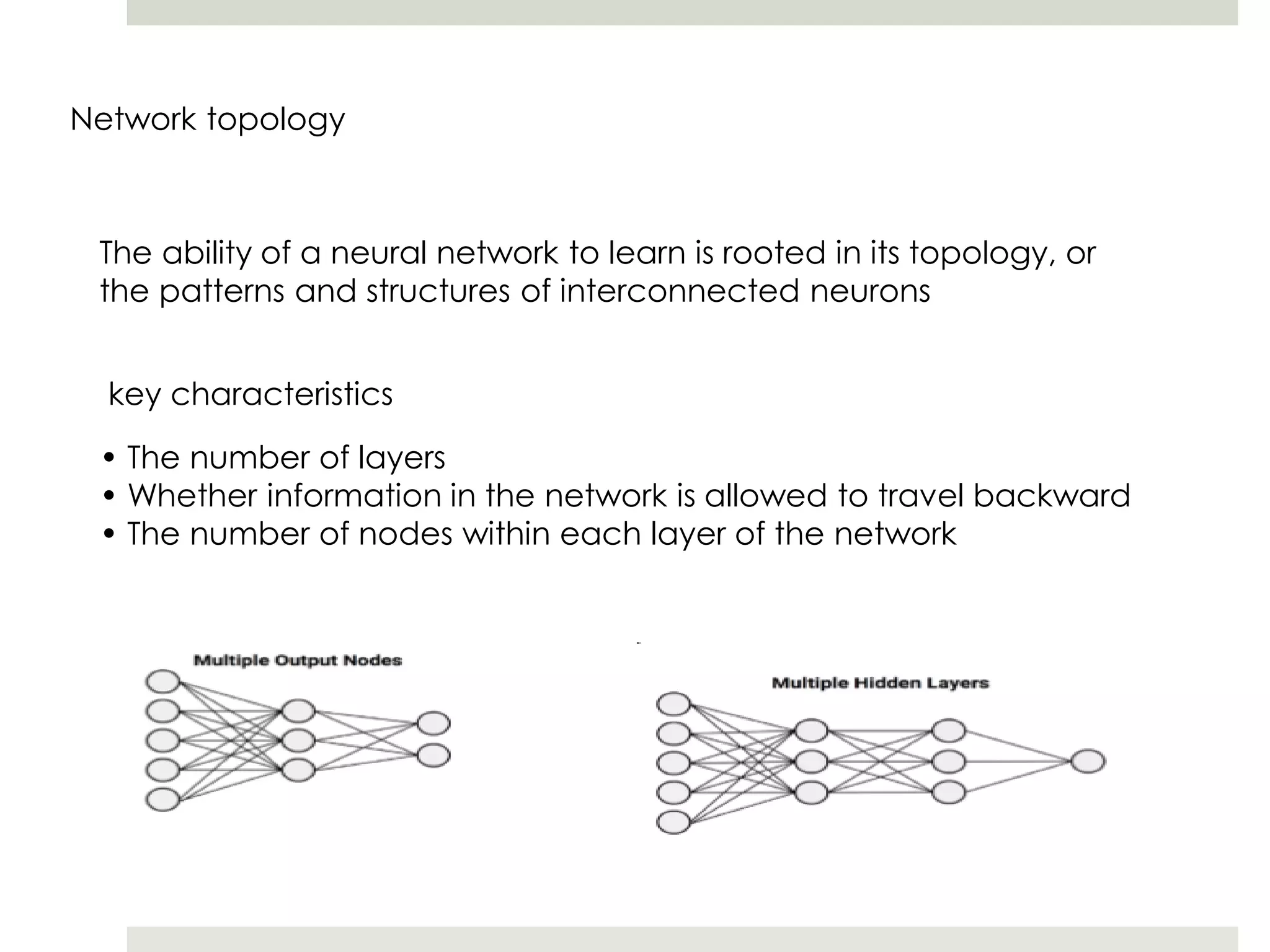
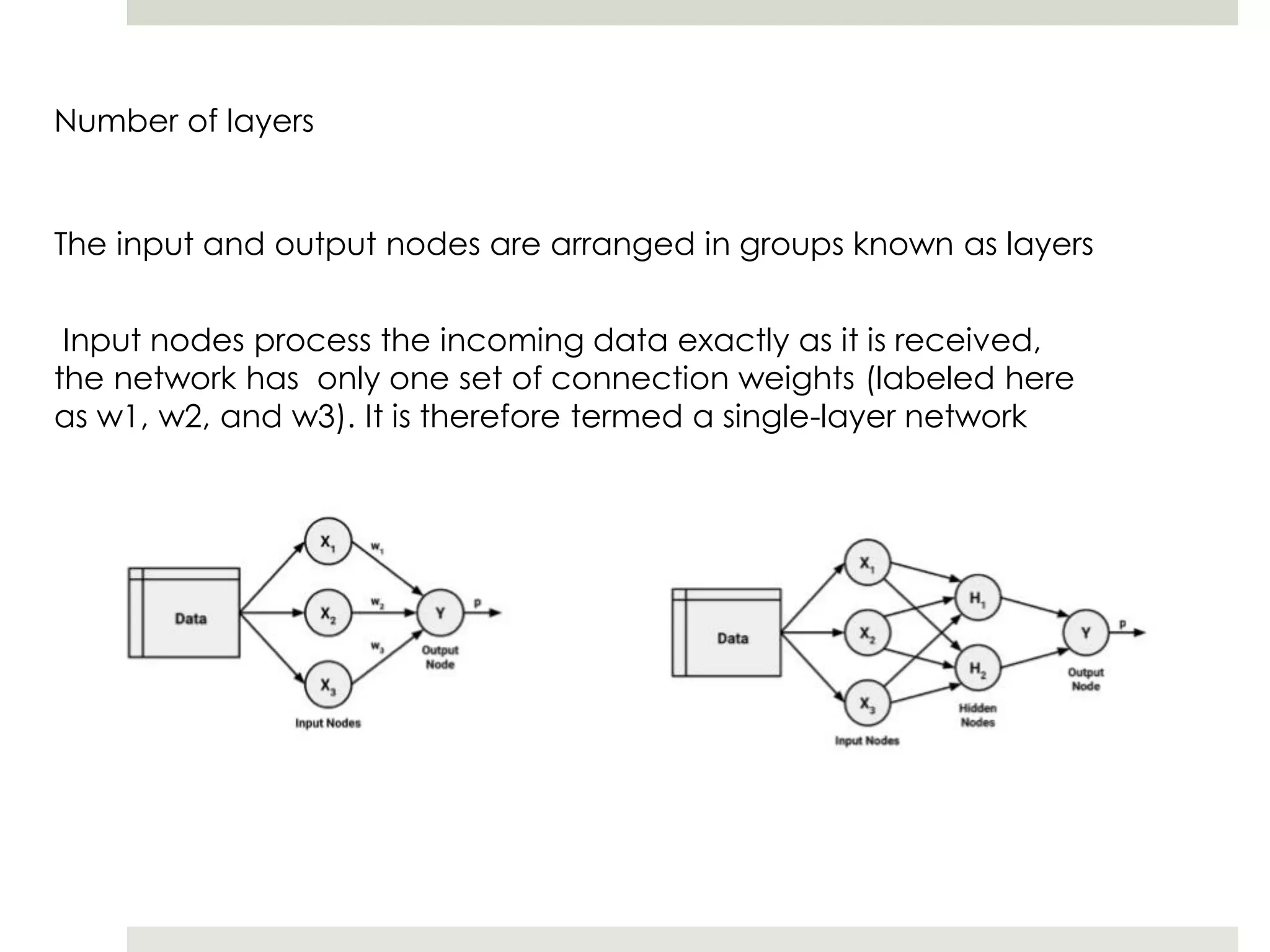
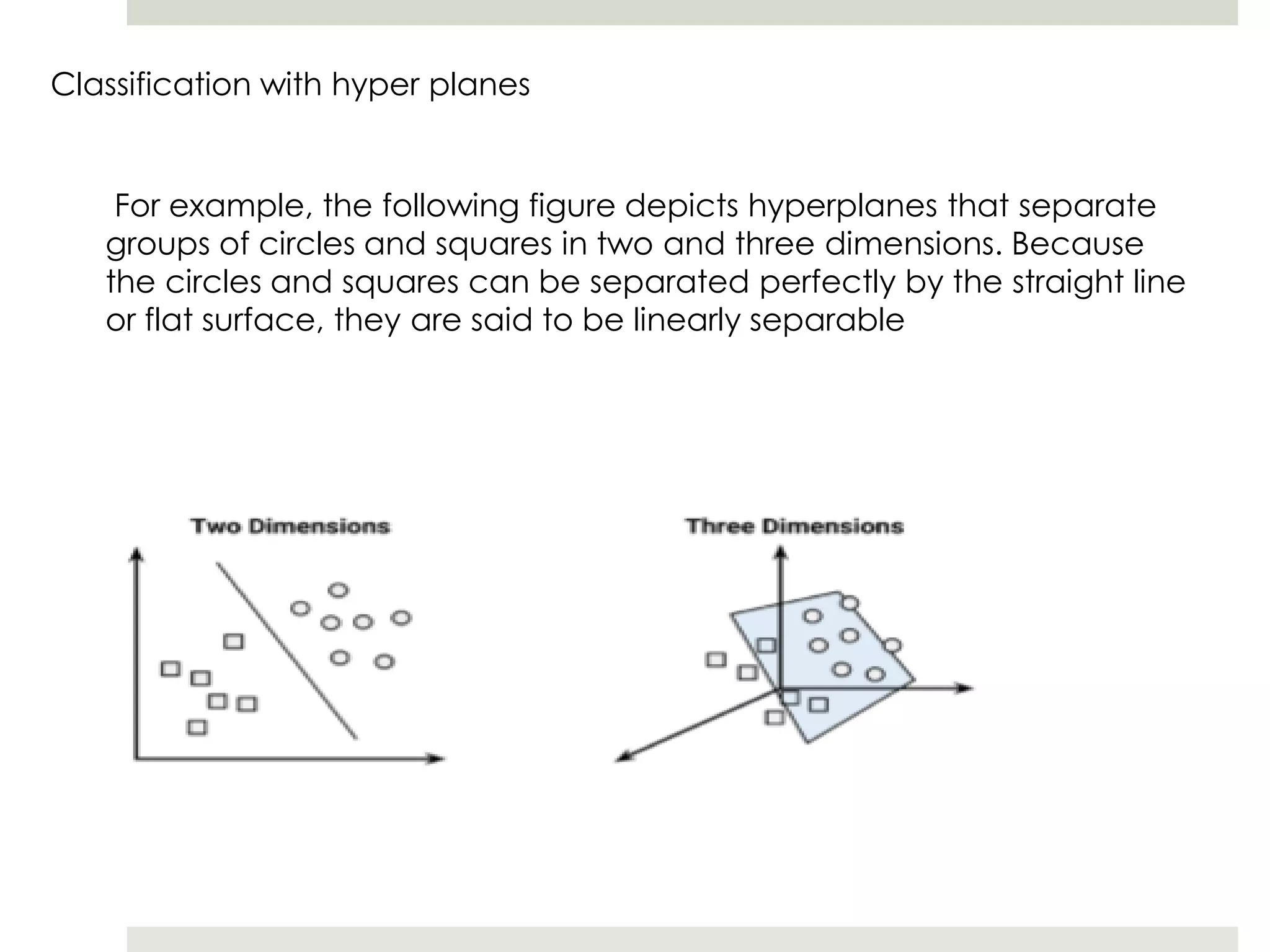
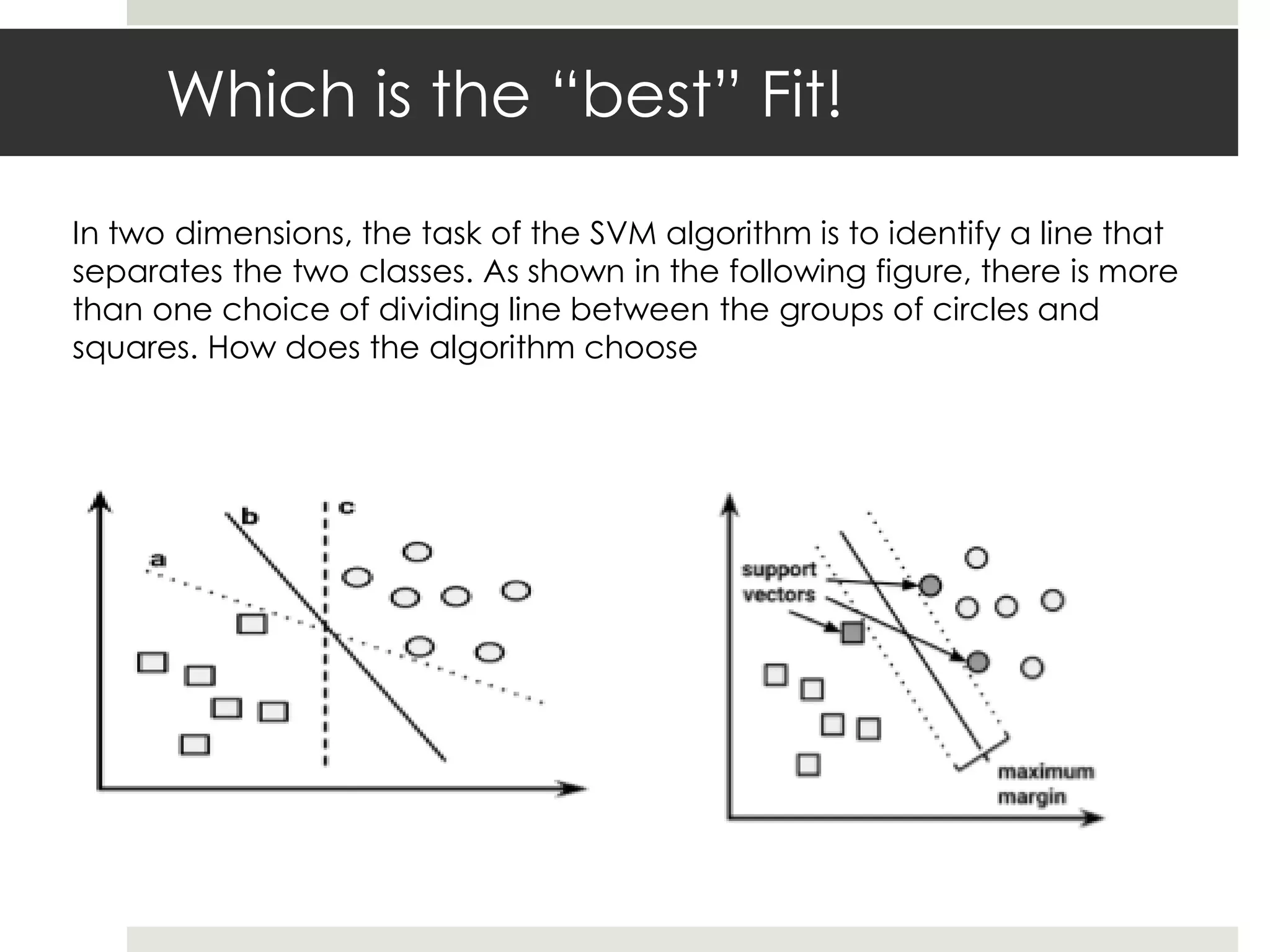
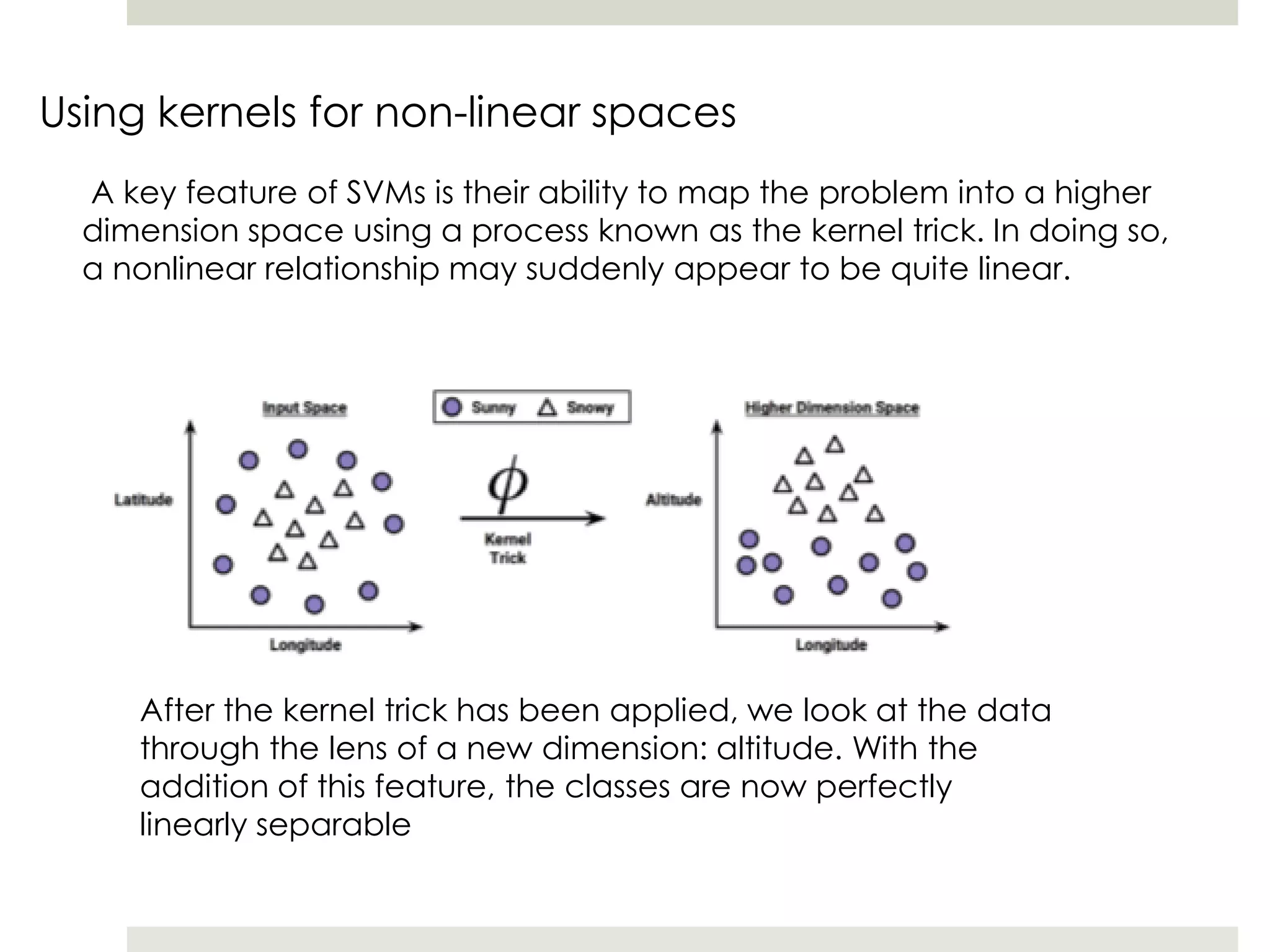
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) model relationships between input and output signals using a network of artificial neurons, analogous to biological neurons in the human brain. ANNs have fewer neurons compared to biological brains and operate based on weighted input signals, thresholds, and activation functions. Support Vector Machines (SVMs) create hyperplanes to separate data points and can utilize the kernel trick to manage non-linear relationships by mapping data into higher-dimensional spaces.