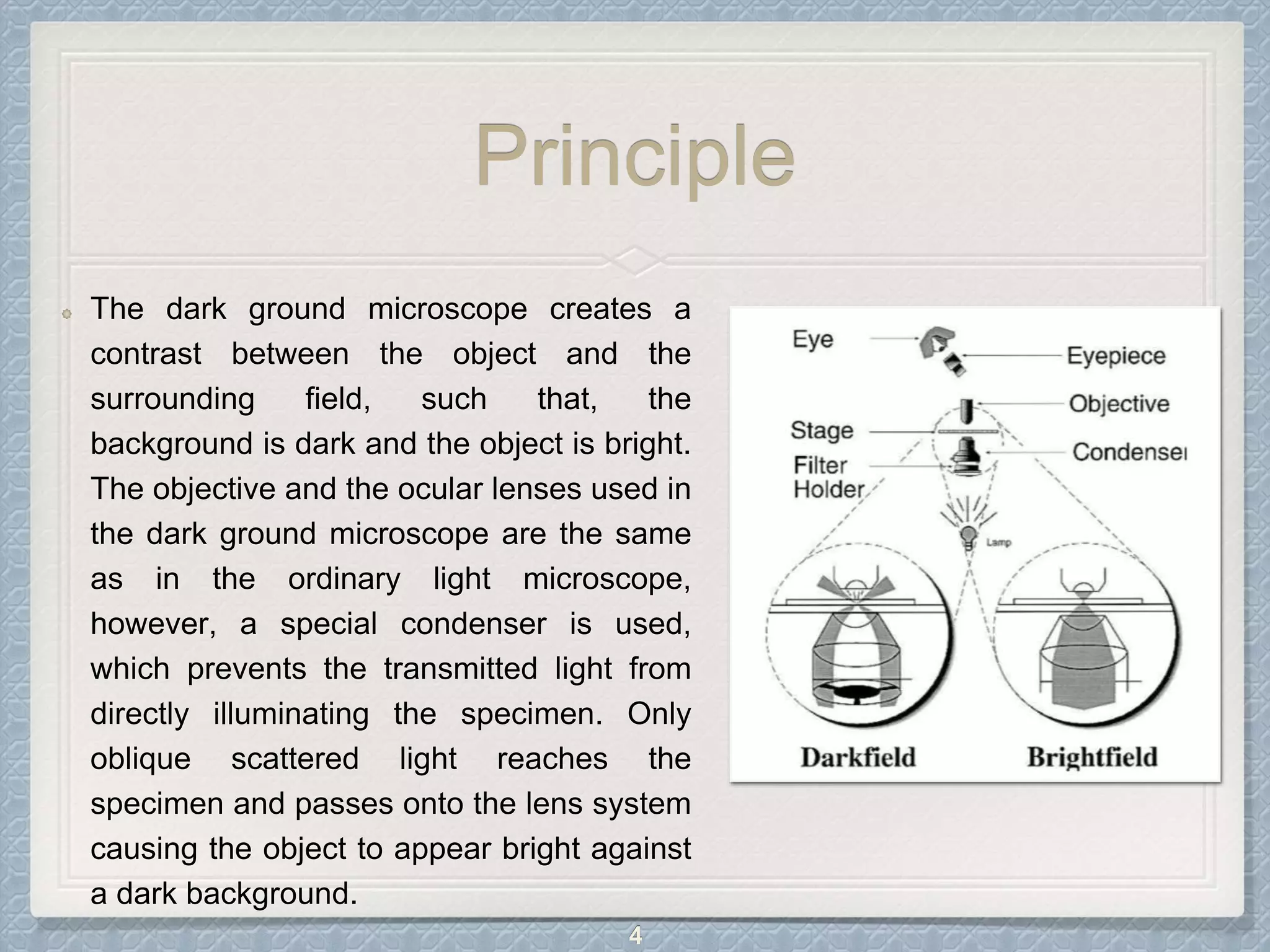
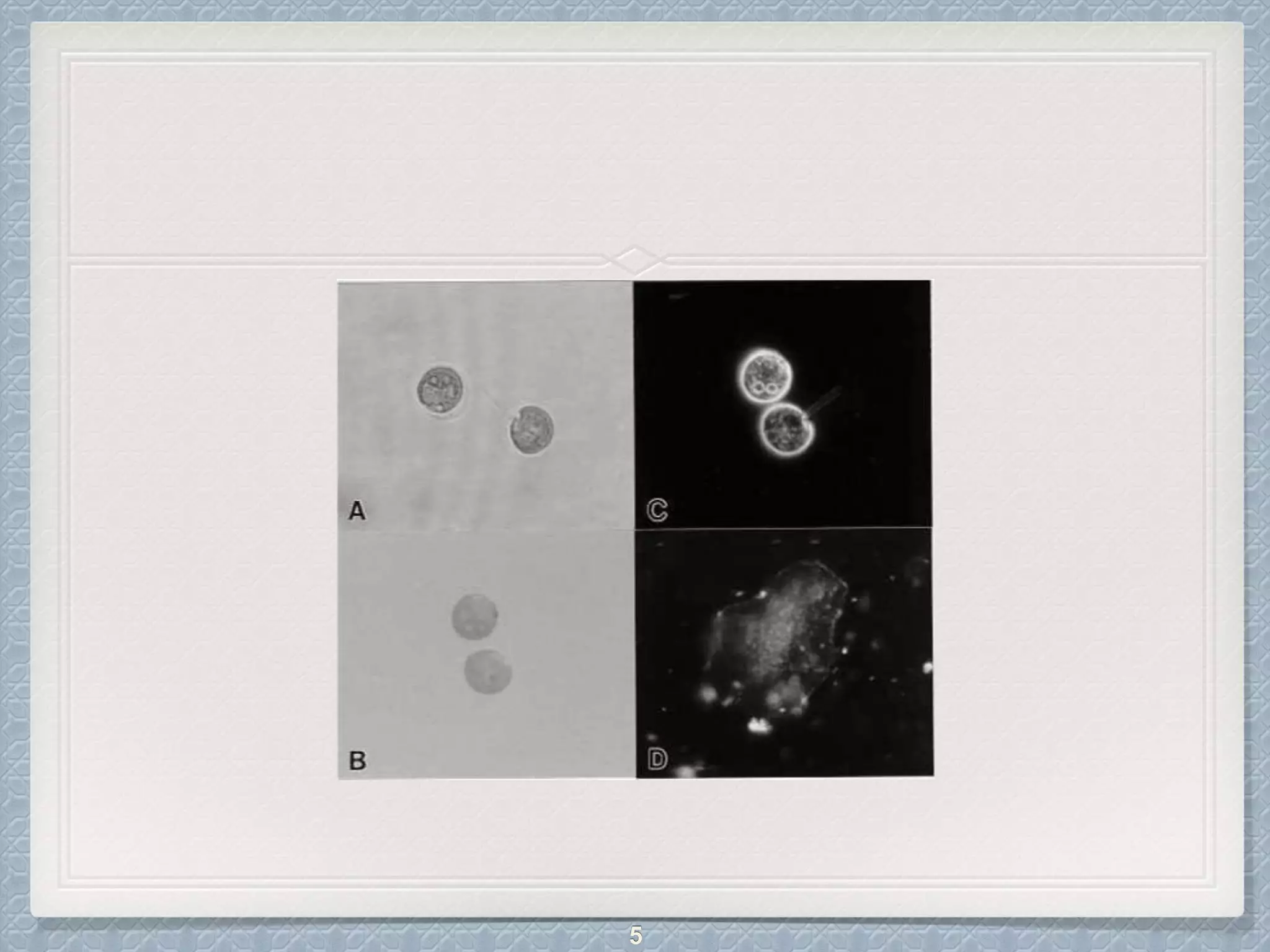
Dark field microscopy is a technique that uses a dark field condenser containing an opaque disk to block light entering the objective lens directly. Only light reflected off the specimen enters the lens, causing specimens to appear bright against a dark background. This technique is useful for viewing unstained, transparent specimens like bacteria, algae, and fibers. It has advantages like viewing details on surfaces but disadvantages like image degradation from non-uniform specimens or particles on the optics. Dark field microscopy finds applications in diagnosing syphilis and viewing various microorganisms, minerals, and cells.