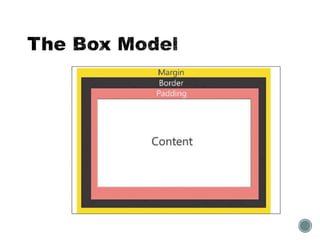
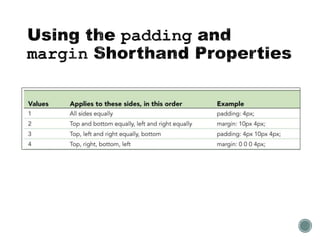
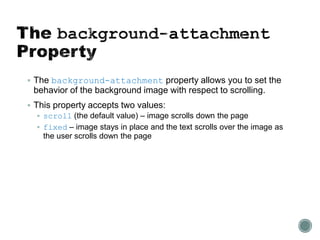
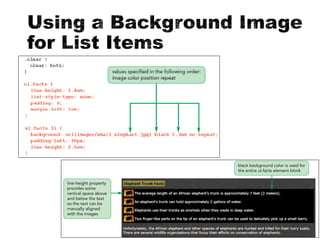
The document describes the CSS box model and its properties including padding, border, and margin which control the internal white space, border, and external white space of elements. It explains how to set values for these properties individually or using shorthand. Background properties like image, color, position and repeat are also covered. The float and clear properties for positioning elements are defined. Finally, cascading and style precedence in CSS are briefly explained.