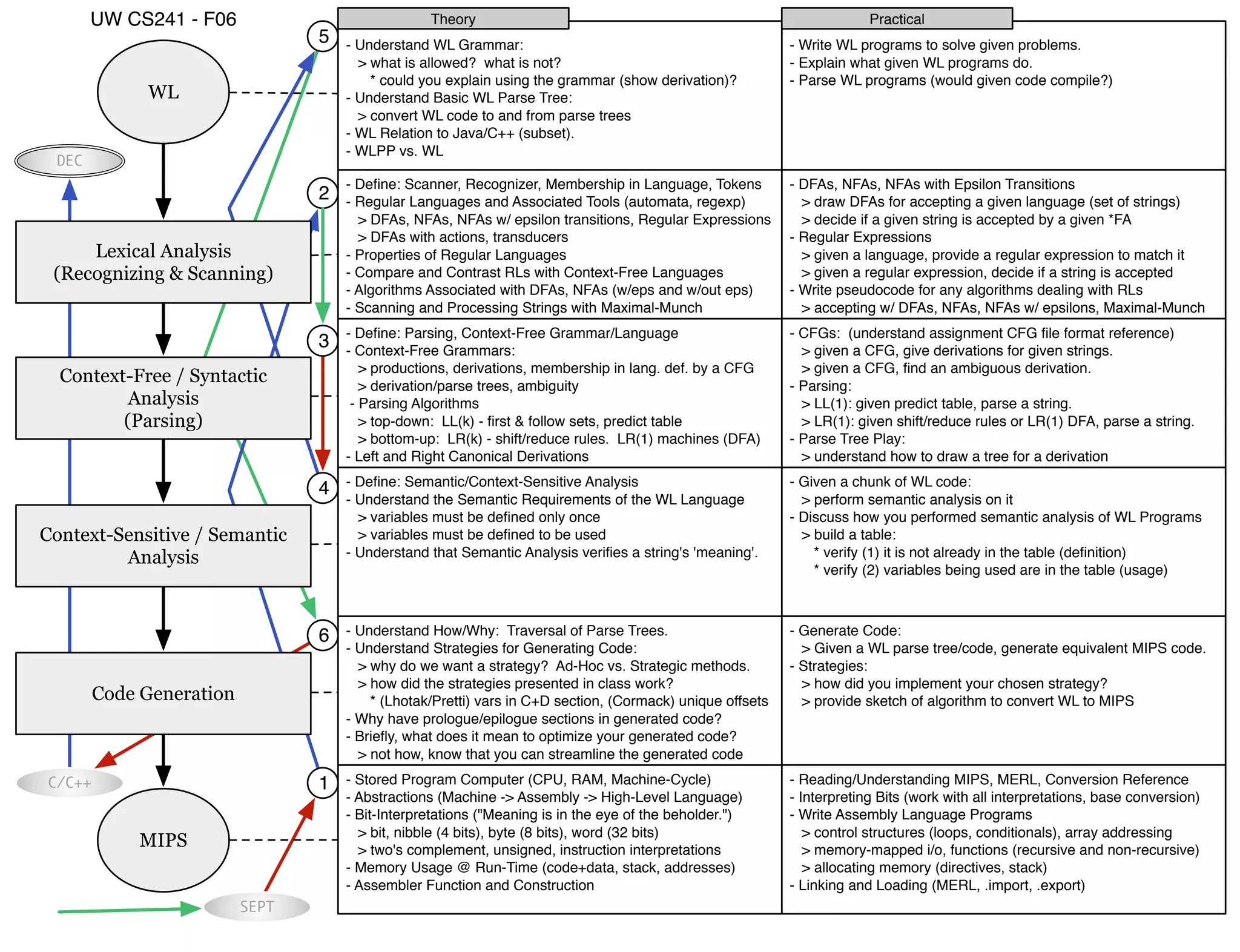
This document provides an overview of topics related to compiler design and implementation including: lexical analysis, parsing, semantic analysis, code generation, assembly language programming, finite automata, parsing algorithms, and the WL programming language. It lists specific tasks like performing semantic analysis on WL programs, generating MIPS assembly code from WL parse trees, drawing finite automata, and parsing strings using various grammars. It also defines key concepts and compares programming languages.
![If you used it for the assignments you might need to know about it:
* COMPILE JAVA: javac filename.java (produces .class files)
* RUN JAVA: java ClassName <inputfile (runs main() method, System.in sees inputfile's contents)
* CAN REDIRECT INPUT AND OUTPUT USING: cmdname <inputfile and cmdname >outputfile
* BASIC UNIX CMDS:
ls (list files), cd dirname (change directory), mkdir dirname (make a directory)
man programname (get help on a program called programname), xxd filename (hexdump filename)
dos2unix (converts Windows rn endline sequences to Unix n newline sequences)
* EDITING IN CSCF ENVIRONMENT:
pico, vi/vim, emacs (text editors allow you to edit files)
* COMPILING C++ IN CSCF ENVIRONMENT: g++ -o exename filename0.cc filename1.cc ...
* EXECUTING COMPILED C++ CODE: ./exename (or, if no -o option given to g++) ./a.out
If you needed to do it on A10, you might need to do it on the exam:
- Compare C++ to Java. Compare C++ and WLPP.
- What are pointers? How do you de-reference a pointer (*p)? How can you get the address of a variable (&v)?
- How do you write a basic C++ program? int main() { ... }
- What are includes? What must you include to use printf(...)? How do you use printf(...)? How can you use the 'NULL' symbol?
- How do you create a struct? How does struct compare to class?
- What is operator overloading? How can you overload the '+' operator (for example)?
- pointer addition vs. [] syntactic sugar.
- 'new' keyword. 'delete' keyword. What do they do, why must we use them both in C++ but not in Java (delete doesn't exist in Java)?
- What are '.h' files and what are '.cc' files? What are function prototypes?
C/C++
UNIX
Other Materials You Might Need](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3544b90c-a381-45ef-8c24-9e9a3cfc294c-160714064340/75/cs241-f06-final-overview-2-2048.jpg)