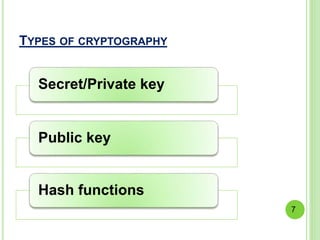
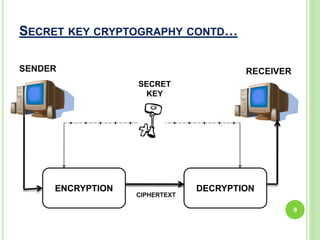
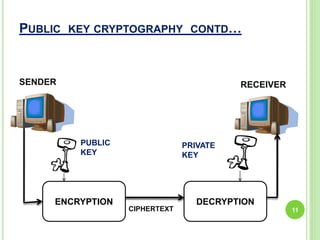
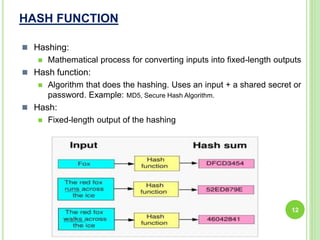
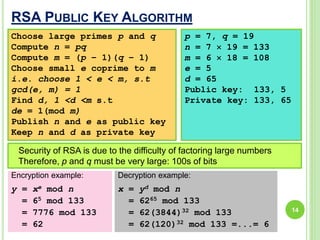
This document summarizes a seminar on cryptography presented by Ashish. It defines cryptography as the science of encrypting messages to make them secure. It outlines the basic terms used in cryptography like plaintext, ciphertext, encryption, and decryption. It describes the different categories of cryptography including secret key cryptography, public key cryptography, and hash functions. Popular algorithms for encryption like DES, AES, RSA, and algorithms for hashing like MD5 and SHA are also mentioned. Finally, it discusses applications of cryptography in areas like defense, e-commerce, and data security and provides references used for the seminar.