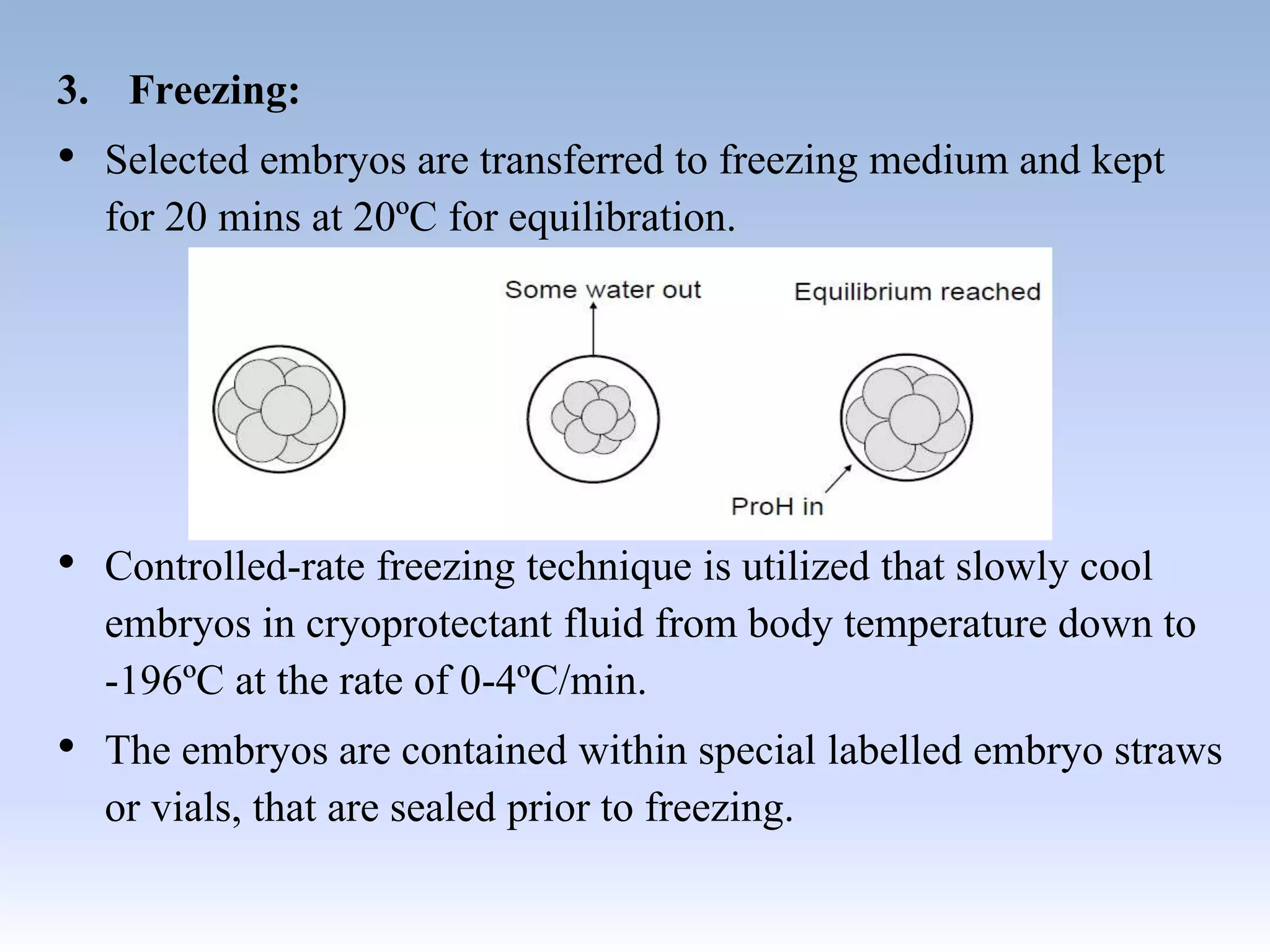
Cryopreservation allows for the long-term storage of biological tissues like sperm and embryos at sub-zero temperatures, typically in liquid nitrogen. For sperm, the process involves collecting semen samples and freezing them using methods like slow freezing or rapid freezing. Frozen sperm can later be thawed and used in assisted reproduction. Embryo cryopreservation collects embryos after fertilization and selection of high-quality embryos, then freezes and stores the embryos for future use through controlled-rate freezing and thawing processes. Both techniques effectively stop biological activity at low temperatures and allow for indefinite storage of reproductive cells and tissues.