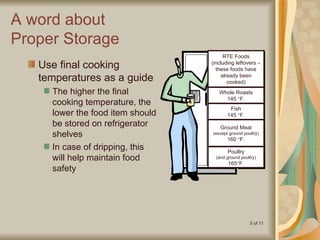
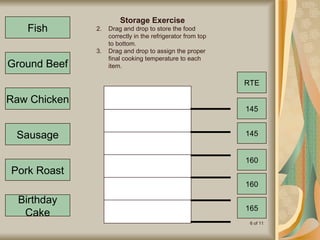
The document defines cross-contamination as the transfer of bacteria between objects or people, often leading to foodborne illnesses. It provides examples of improper food handling practices and emphasizes the importance of hygiene, proper storage, and sanitation in preventing cross-contamination. Recommendations include washing hands and utensils between handling raw and ready-to-eat foods to ensure food safety.