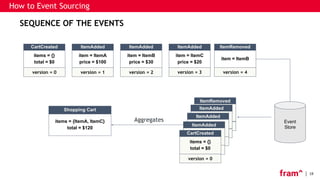
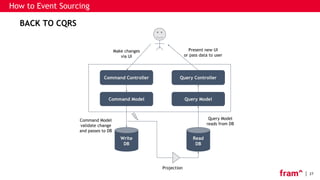
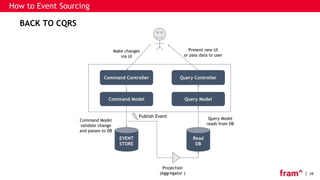
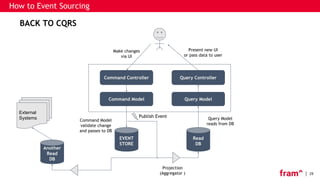
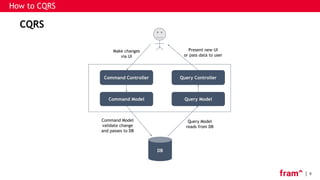
The document discusses Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) and Event Sourcing, outlining their definitions, benefits, implementation methods, and when to use them. It emphasizes how CQRS enables independent scaling of reads and writes while Event Sourcing captures state changes as a sequence of events, facilitating historical data access and performance improvements. The document also includes frameworks for implementing these patterns and highlights scenarios where CQRS is beneficial or not recommended.










![15
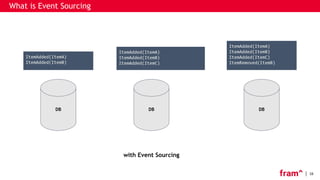
What is Event Sourcing
DB
Order {
items=[itemA, itemB]
}
DB
Order {
items=[itemA, itemB, itemC]
}
DB
Order {
items=[itemA, itemC]
}
without Event Sourcing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cqrseventsourcinges-190710070512/85/fram-TechTalk-1-CQRS-and-Event-Sourcing-ES-15-320.jpg)