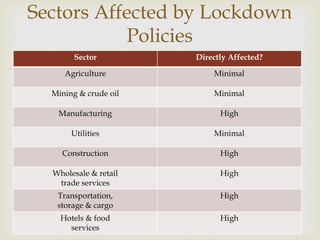
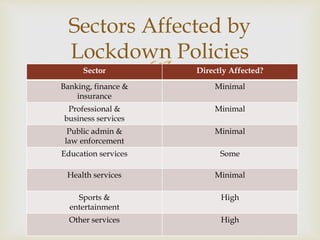
The document summarizes the economic impact of COVID-19 on the Indian economy. It notes that while India has successfully contained the virus so far, the pandemic has disrupted normal economic activity. Key sectors like manufacturing, construction, wholesale/retail trade, and transportation have been highly affected. The government has introduced various economic relief measures, and states have provided cash transfers and food rations to support citizens. Overall, COVID-19 presents an opportunity for India to play a leadership role globally, but economic recovery will be challenging given pre-existing slower growth.