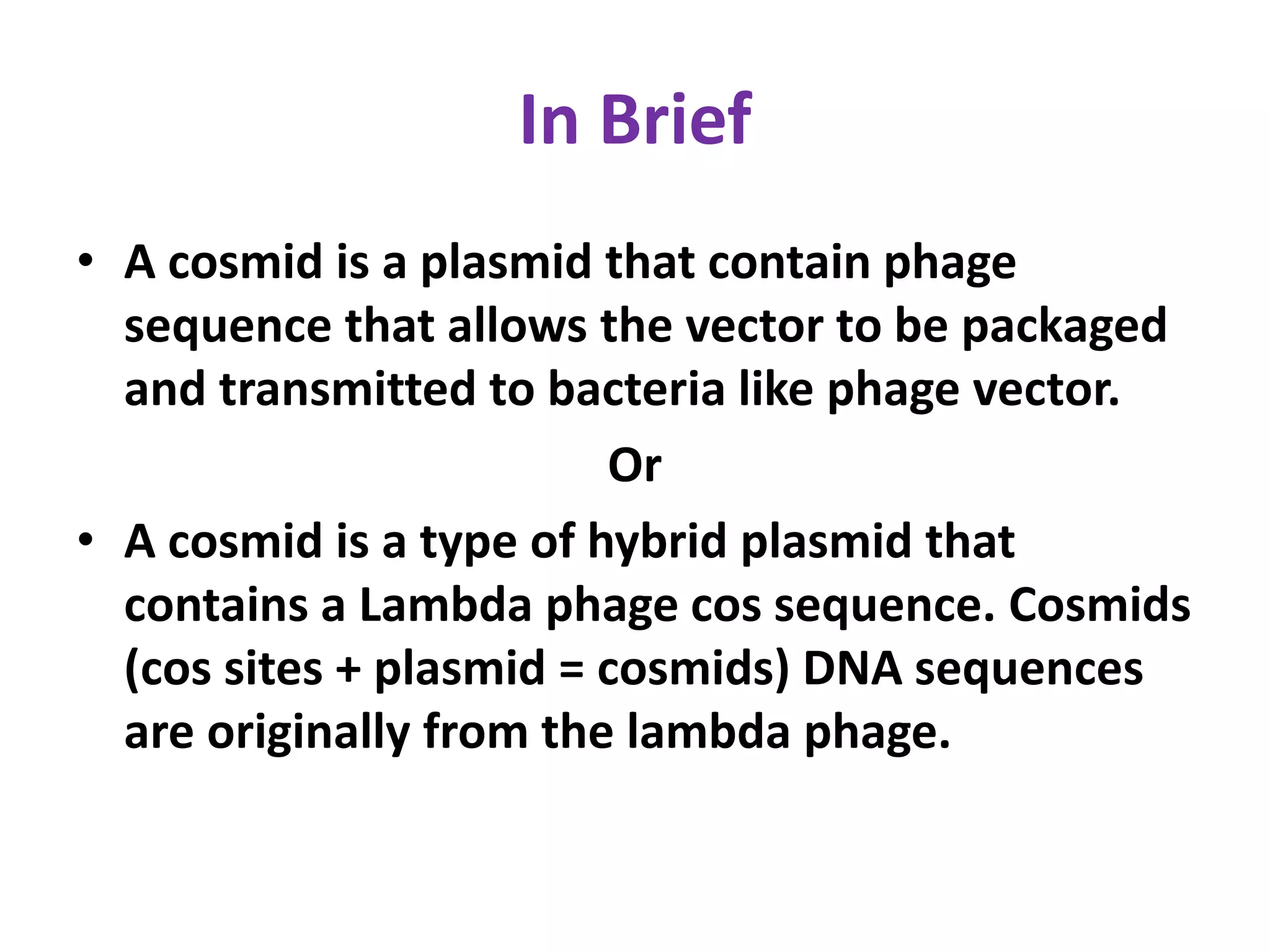
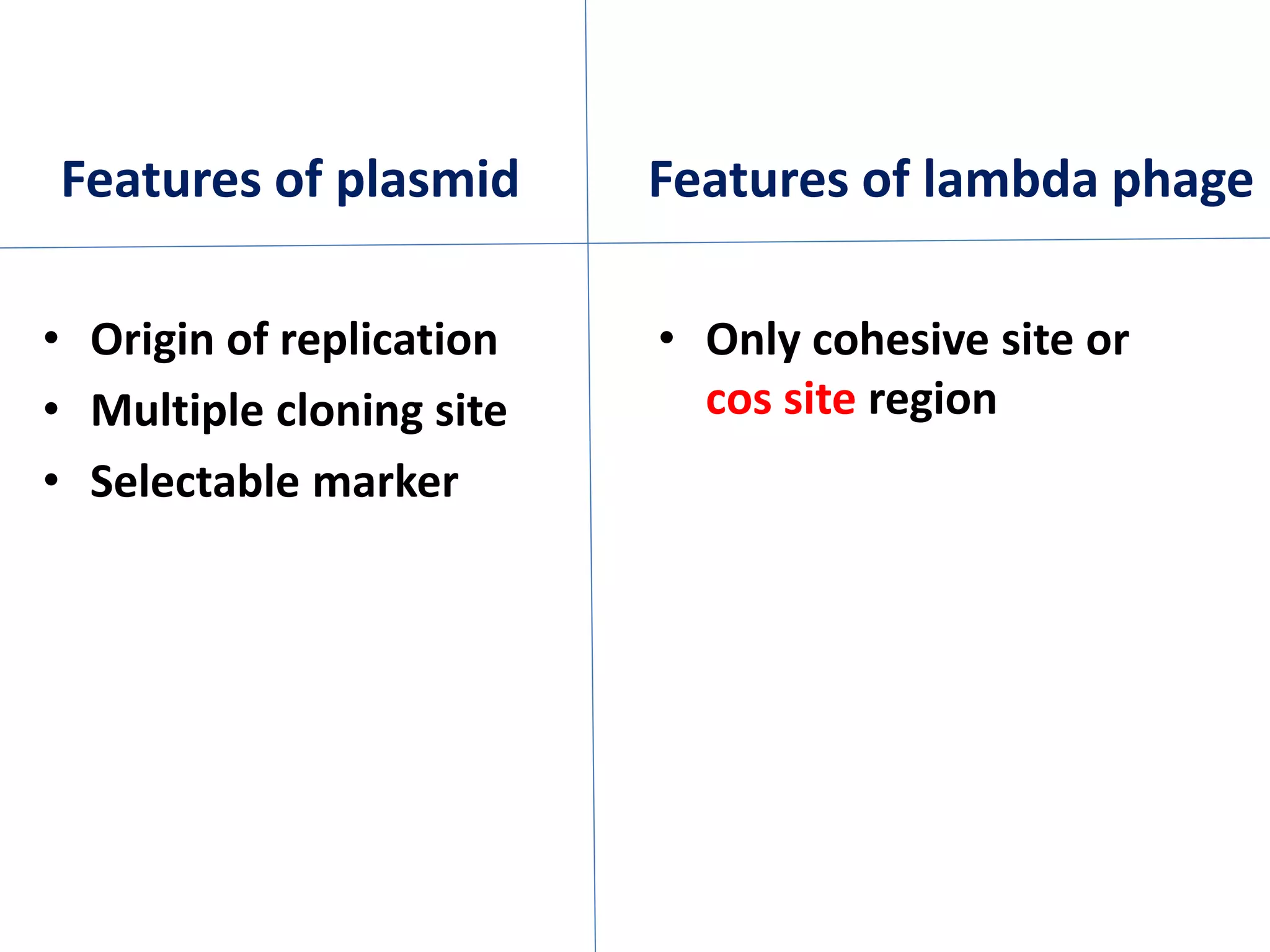
Cosmids are hybrid cloning vectors that combine features of plasmids and bacteriophages. They contain approximately 200 base pairs of DNA from the lambda phage, including the cos site sequence, which allows the vector to be packaged into phage particles and transduced into bacteria like a phage. Cosmids can accommodate large foreign DNA inserts of 35-45 kilobase pairs and are commonly used to construct genomic libraries.